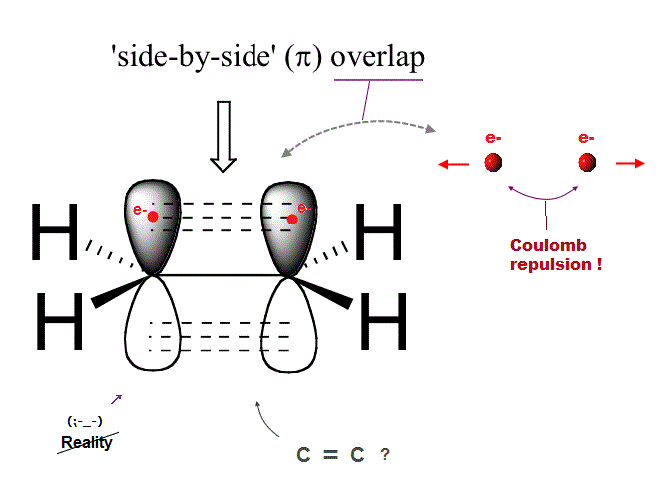
(Fig.1) Ethene carbon double bond ( H2-C=C-H2 ) is NOT "pi" bond !

Quantum mechanics claims that carbon double bond ( C=C ) is caused by pi bond between two parallel electrons.
But in fact, this "pi bond" model in quantum mechanics cannot form actual stable bond, because two negative electrons repel and avoid each other !
So orbitals of these two repulsive electrons tend to avoid lining up side by side parallel to each other ! This model doesn't describe reality.
(Fig.2) Unrealistic double (= pi ) C=C bond in quantum mechanics ↓
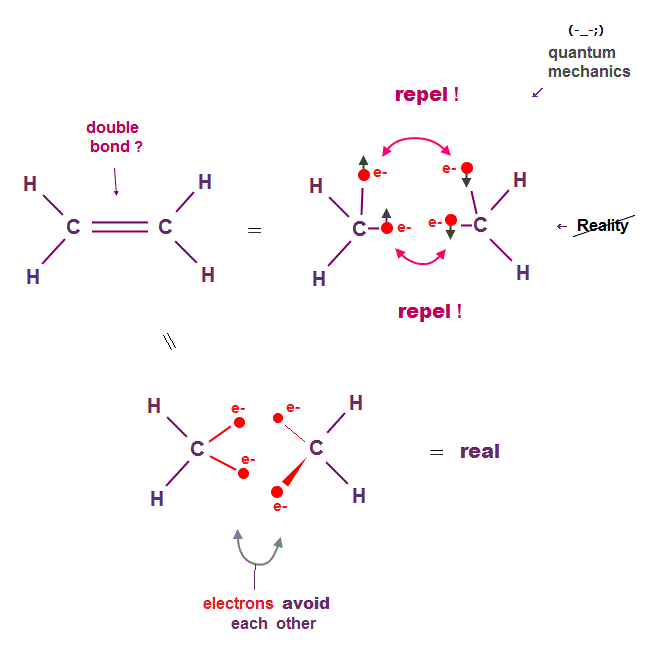
Quantum mechanics claims that double bonds such as C=C consist of parallel π bond with a pair of two opposite spins.
This model clearly ignores Coulomb repulsion among electrons, so wrong. Schrodinger equation cannot handle multi-electron atoms.
Quantum mechanics just chooses fake trial functions also in double bonds, so useless forever.
True molecular bond model has to obey two important conditions, Coulomb force and de Broglie waves in valence electrons.
(Fig.3) Point-like electron ( radius r → 0 ), rotation v → ∞

Angular momentum is given by mv × r ( v = velocity, r = radius ).
Electron spin also has angular momentum 1/2ħ, they claim
The problem is an electron is very tiny, point-like.
The point-like particle means its radius r is almost zero.
So to get the angular momentum 1/2ħ, the electron spinning must far exceed light speed ( this p.5, this )
So the electron spin lacks reality.
Even Pauli ridiculed the idea of "spinning electron".
But in "s" orbital of Schrodinger's hydrogen, this electron spin is the only generator of magnetic moment.
So they had no choice but to accept this strange spin ( Not as real spinning and speed ).
(Fig.4) ↓ Spin magnetism has nothing to do with molecules !

Electron spin was originally defined as "tiny magnet", though its "spinning" speed far exceeds light speed c.
Its spin-spin magnetic interaction is too weak to explain actual phenomena such as Pauli exclusion principle and ferromagnetism.
So too weak spin has nothing to do with molecular bond ! In fact, spin is used only as "mark" to distinguish different spectra, ignoring its actual magnetic property.
(Fig.5) All opposite wave phases just cross each other in Neon
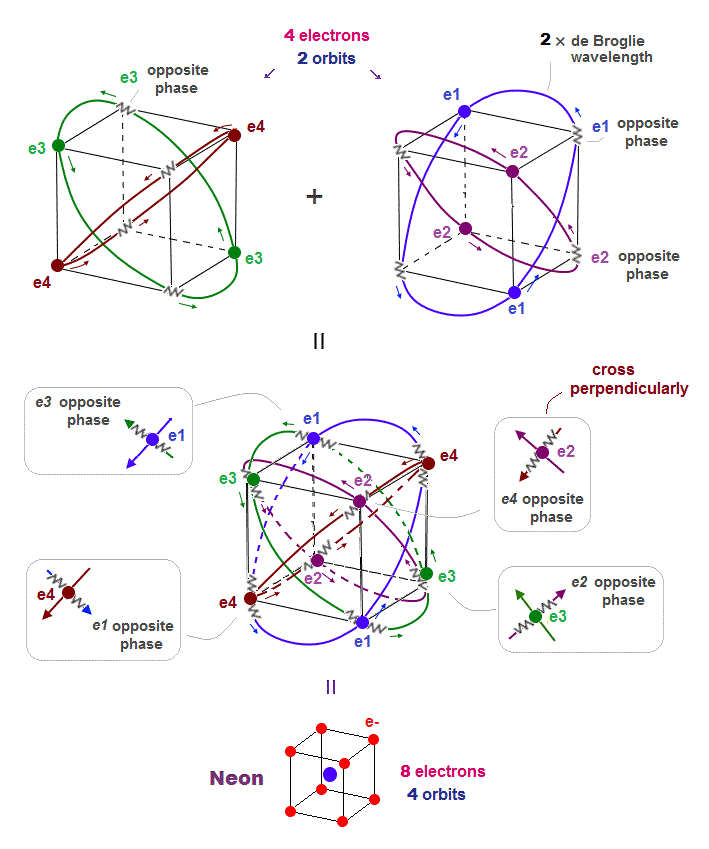
This page shows that de Broglie wavelength detemines the number of valence electrons. Neon, carbon, oxygen have 2 × de Broglie wavelength orbits.
Neon contains eight valence electrons. Neon belongs to the 2nd line in periodic table, meaning its orbit is 2 × de Broglie wavelength.
When just two 2 × de Broglie wavelenght orbits cross each other (= Fig.5 upper ), some electrons are free from their opposite wave phases.
With four orbits, all electrons and their opposite wave phases cross each other, forming stable noble gas Neon with no more room.
(Fig.6) Carbon (= C ) is 4 electrons and "holes" in 4 orbits.
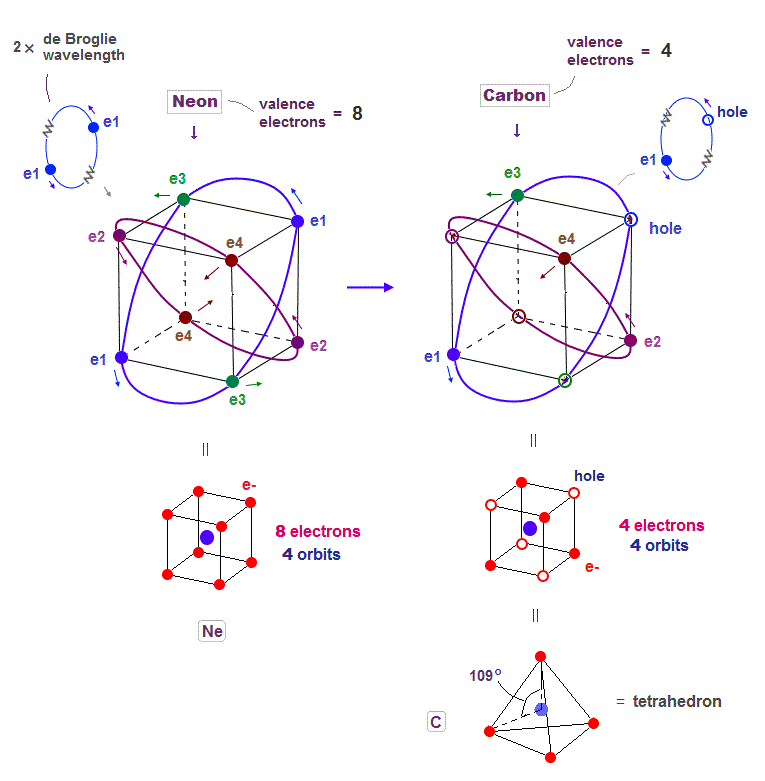
When each 2 × de Broglie wavelength orbit includes one electron and one hole, it generates four "holes". This is carbon (= C ) atom.
Carbon consisting of four valence electrons form tetrahedral structure with bond angle 109.5o.
(Fig.7) In C-C bond, an electron synchronize with another hole.
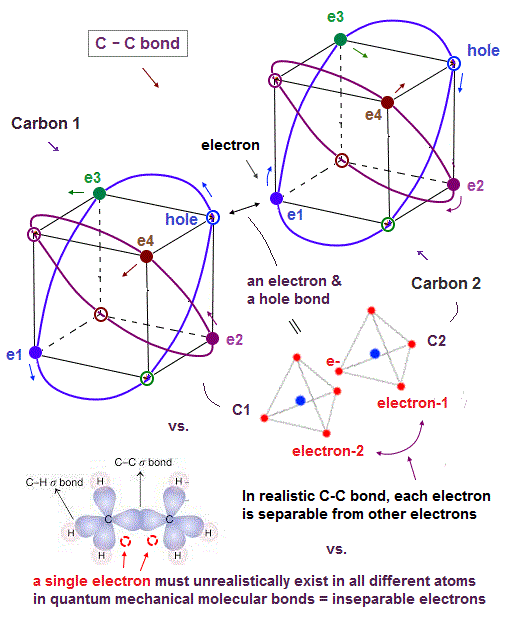
Without unrealistic spins, how is each molecular bond formed ? Considering Coloumb repulsion among electrons, an electron tends to approach "vacant hole".
So a pair of a valence electron and a hole ( inside other orbits ) is a true figure of molecular bond.
Also in carbon-carbon ( C-C ) bond, electons are thought to aim at stable hexahedral structure like Neon by electron-hole pairs.
Furthermore, for each electron to keep stable, an electron has to enter the place of the "same wave phase". A vacant hole meets this condition, too.
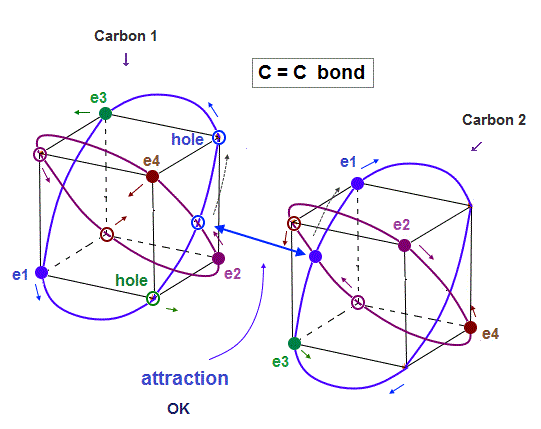
(Fig.8) In C=C bond, two electron-hole pairs are formed.
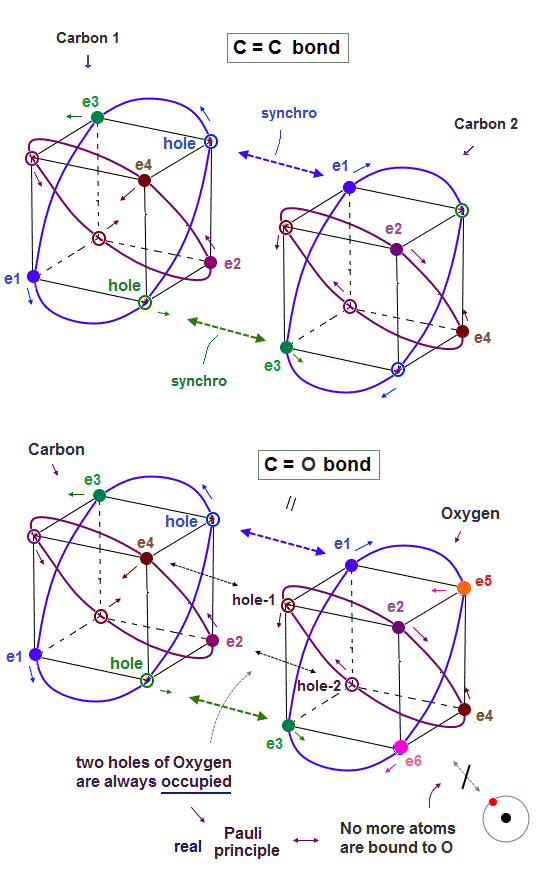
In C=C double bond, two electron-hole pairs are formed between two carbons.
In Fig.8, "e1" and "e3" electrons of carbon 2 approach correspondent holes of carbon 1, and make Neon-like hexahedral structure.
Comparing Fig.7 and Fig.8, you will easily find C=C bond is shorter than C-C bond.
(Fig.9) "e1" ( and "e2" ) electrons pass "midpoint" between two nuclei.
As two carbon nuclei are closer to each other, their repulsive Coulomb force becomes stronger.
To cancel this nuclear repulsion, each electron must enter between C = C nuclei.
Considering actual orbit of each electron, you find "e1" and "e2" electrons pass the midpoint between two nuclei periodically, which can cancel stronger internuclear repulsion.
(Fig.10) True oxygen orbits of 2 × de Broglie wavelength with two holes
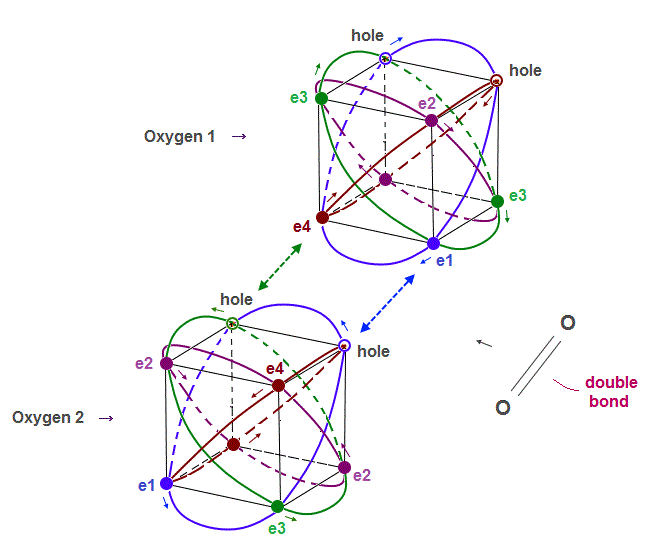
The destructive interference between opposite phases in de Broglie wave determines the number of valence electrons in all atoms.
Oxygen consists of 4 orbits of 2 × de Broglie wavelength with two holes.
A pair of a hole and a valence electron forms a molecular bond. Double bonds includes two pairs of holes and electrons. This model is realistic.
Different from carbon where the half is holes and another half is electrons, oxygen has more electrons than holes, which increases repulsion among electrons.
This is the reason why C=C bond energy is bigger (= stable ) than that of O=O.

2016/11/4 updated. Feel free to link to this site.