Home page Contents
Twin paradox disproves Einstein
Sagnac effect disproves Einstein


 paradox
paradox
 , Rindler, GPS contradict relativity.
, Rindler, GPS contradict relativity.
(Fig.M) Einstein relativity rejecting the light medium causes many irreparable paradoxes due to its unphysical Lorentz transformation.
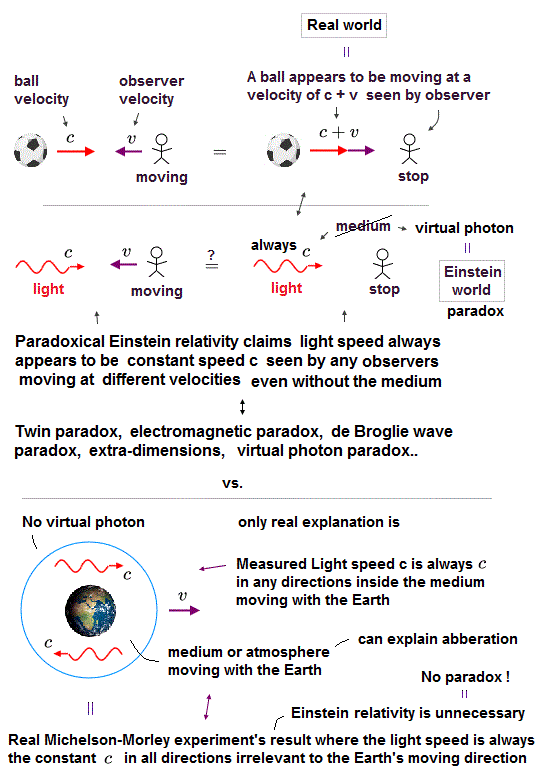
Einstein relativity paradoxically says there is No absolute frame nor light medium (= aether ) filling space, which means whether things are moving or not is uncertain and changed as seen by differently-moving observers.
↑ This unrealistic Einstein relativity lacking the real light medium cannot explain interference, diffraction and refraction of light wave, electron's de Broglie wave in two-slit interference, and Maxwell electromagnetic theory involving the medium.
In Einstein relativity lacking the absolute frame, all things' motions are relative and changeable as seen by different observers.
This-2nd-last-paragraph says -- Motion is relative ?
"this is the relativity in the theory of relativity: all motion is relative. If Einstein rode past me on his bicycle, I could only say that he is moving from my perspective. From his perspective, he could rightly claim that he was fixed still and that I was the one in motion."
This Einstein relativity lacking the real absolute frame causes kinetic energy paradox and violation of energy conservation, which needs paradoxical gravitational wave.
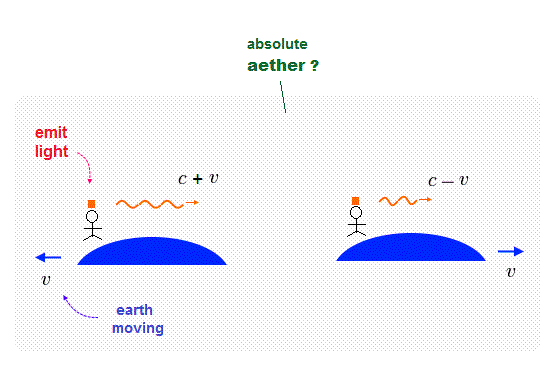
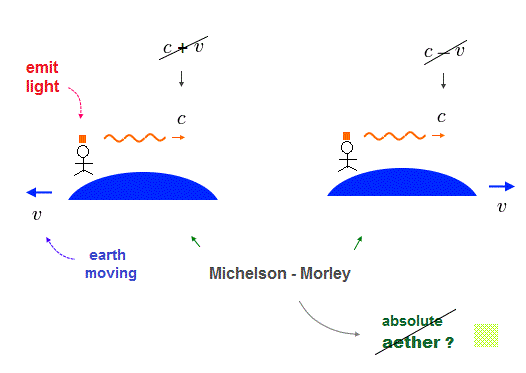
This unrealistic Einstein relativity with Lorentz transformation was derived by wrongly interpreting Michelson-Morley experiments that showed light was measured to always travel at the constant light speed c on the earth rotating around Sun, which fact disproved the absolute aether or lumniferous medium that is independent of the earth rotating around Sun ( this-p.1-last ).
↑ But this Michelson-Morley experiment did Not deny the light medium moving with the earth. ← Inside that earth medium the light can be measured to always travel at the constant light speed c in any directions like the constant sound speed in the air medium.
↑ This realistic light medium moving with the earth can perfectly explain stellar aberration, interference, refraction of light and electron's de Broglie wave without paradoxes such as kinetic energy and electron's de Broglie wave.
Einstein relativity claiming light is measured to always travel at the constant light speed c independent of observers and light sources ( this-p.3-p.6 ) is false.
Signals emitted from GPS satellite are observed to travel faster (= c + v ) or slower (= c - v ) than light speed c by observers on the earth spinning speed of v in Sagnac effect disproving Einstein relativity ( this-3. conclusion ).
↑ Only the medium moving with the earth (= which can explain Michenson-Morley experiments ) but that medium independent of the earth spinning (= which can explain faster-than-light Sagnac effect ) agrees with all the experiments.
Einstein relativity unrealistically claims the moving clocks tick slower than the stationary clocks.
Einstein relativity lacks the absolute frame, so which clocks are moving and ticking slower is paradoxical and changed as seen by different observers, which is called twin paradox.
Contrary to textbooks, this twin paradox is real, disproving Einstein relativity.
When the clock-S is moving and rotating in a circular path with respect to the stationary clock-C, the clock-C (or clock-S ) sees the other clock-S (or clock-C ) moving and ticking slower.
↑ Which clock S or C is moving (= rotating ) and ticking slower is paradoxical (= clock-S can return to the original clock-C position and compare their paradoxical clock times ).
Michelson-Morley experiment deriving this special relativistic twin paradox was conducted on the earth rotating around Sun, so this rotating twin paradox involves only special relativity, and general relativity cannot fix this real twin paradox.
Einstein relativity lacking the medium (= aether ) needs unreal virtual photons with imaginary mass contradicting Einstein relativity to explain electromagnetic force ( this-p.3 ).
↑ All of these paradoxes clearly show Einstein relativity is false.
Contrary to a lot of overhyped fake news, Einstein relativity is useless for any technologies such as GPS and PET, just leading to unreal extradimensional unified theory.
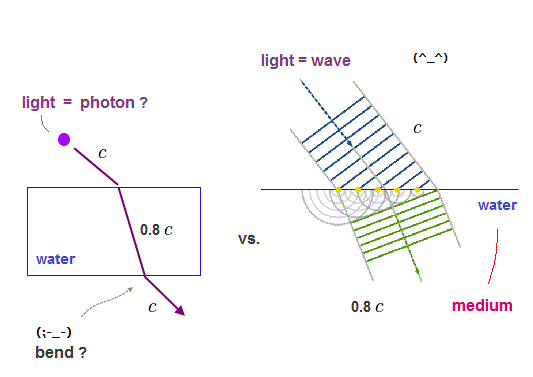
(Fig.A) Snell's law proves stellar aberration is seen also in the light medium moving with the earth (= ether drag ).
Contrary to wrong textbooks' explanation, the stellar aberration (= light emitted from a distance star appears to be inclined by the earth's motion ) can be observed also by the light medium moving with the earth (= compatible with Michelson-Morley experiment, too ).
As shown in the upper figure, the light emitted from a distant star appears to be traveling in the outer space slightly faster than light, as seen by the earth moving at a speed of v.
When this light enters the medium moving with the earth, the light speed becomes the constant c.
According to Snell's law, the ratio of the light angles (= singθ1/sinθ2 ) is approximately 1 due to the almost same light velocities in the outer space and the earth medium.
As a result, the light path remains inclined (= θ2 is not zero ) also in the earth medium that can observe the stellar aberration.
↑ If textbooks' (wrong) idea that the ether dragged by the earth cannot explain aberration ( this-p.2, this middle ) is right, The angle θ2 must be zero, which means the light speed inside the earth medium must be unrealistically zero (= which is Not the case ), so the aberration is compatible with the ether (= medium ) moving with the earth, after all.
This-p.3-Discussion says "The empirical aberration evidence supporting the dragged ether theory is thus overwhelming."
(Fig.V) Einstein relativity rejecting the real medium needs unreal virtual photons with imaginary mass, which disproves Einstein.

Einstein relativity rejecting the light medium paradoxically needs fictional virtual photons with imaginary mass to explain electromagnetic force and photoelectric effect ( this-p.16 ).
Without the medium, an electron can emit or absorb only unreal virtual photons with imaginary mass (= m2 < 0 ) paradoxically disobeying Einstein relativistic energy-mass relation called off mass shell ( this-p.3, this-p.4-6, this-5th-paragraph ).
The reliance on these unreal virtual photons disproves Einstein relativity and the unphysical relativistic quantum electrodynamics (= QED ) giving only meaningless infinities that must be illegitimately removed by renormalization ( this-p.4-5 ), which ad-hoc QED trick, which cannot predict any physical values, was criticized by many physicists ( this-1st-paragraph ).
(Fig.T) Einstein relativity is wrong, needing unreal quantum mechanical parallel universes in two slit interference.
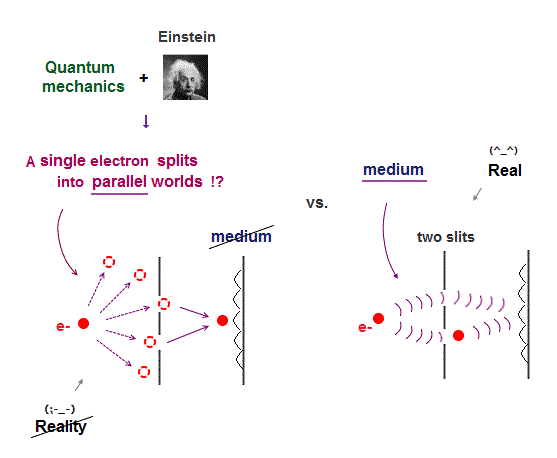
A single particle such as an electron is known to interfere with itself in two-slit experiments.
We can naturally say an electron generates real de Broglie wave in the medium causing interference (= de Broglie wave instead of a single electron can pass two slits realistically ).
But in the unphysical Einstein relativity rejecting the medium (= aether ), a single electron has to split into multiple (fictional) parallel universes (= one electron unrealistically splits into two slits ) to interfere with itself by the paradoxical quantum mechanical wave-particle duality.
↑ As a result, disproving Einstein relativity rejecting the real medium by fatal paradoxes is equal to disproving quantum mechanical wave-particle duality in fantasy parallel universes.
Real de Broglie wave (= whose wave phase is moving with a moving electron ) disproves the unphysical quantum mechanical static probability wavefunctions that cannot be changed nor moved.
Interference of an electron definitely needs some external medium, because the electron alone (in the vaccuum containing nothing ) cannot push itself to cause destructive or constructive interference patterns.
↑ Because even when the electron tries to push itself, the electron is pushed back from itself due to action-reaction law, which total force on the electron is zero, which cannot push the electron from destructive interference area toward the constructive interference area.
(Fig.P) Light refraction due to different light speeds in different mediums cannot be explained by Einstein relativity rejecting the medium or a unreal photon particle.
Light is clearly wave traveling and interfering in the medium as shown in Light refraction caused by the difference in light speeds in different mediums according to Huygens principle.
Einstein relativity rejecting the light medium (= aether ) needs an unreal photon particle that cannot explain light interference nor refraction (= a photon particle can only collide with each other without interference ).
Because in the light refraction, a (illusory) photon particle has to unreasonably slow down and accelerate at some definite angles by some fictional forces, each time it enters different mediums, which also contradicts Einstein relativity of the constant light speed c.
(Fig.K) An electron-1 paradoxically has kinetic energy (and de Broglie wave ) emitted as light as seen by a stationary K, or no kinetic energy (= no de Broglie wave nor emitting light ? ) as seen by a moving K'

Einstein relativistic theory rejecting the medium (= luminiferous aether ) has No absolute frame in the space where what objects are moving or stationary are changed depending on which observers seeing them.
So according to the paradoxical Einstein relativity, an electron-1, which is moving at speed of v emitting light energy and generating de Broglie wave interference as seen by the stationary K, paradoxically appears to stop with No kinetic energy (= but emitting and losing light wave energy ! ), Not generating de Broglie wave interference (= de Broglie wavelength changes depending on the particle's velocity ) as seen by K' moving at the same speed as the electron-1.
↑ These paradoxes in kinetic energy and de Broglie wave clearly disprove Einstein relativity.
Because as shown in photoelectric effect, the electron's kinetic energy is absolute energy (= contradicting relativistic energy ) that can be converted into light wave energy related to light frequency.
The observer K' moving with the electron paradoxically sees the stationary electron with No kinetic energy losing light energy and accelerating, which clearly violates energy conservation law, disproving Einstein relativity.
↑ To solve this fatal relativistic paradox in kinetic energy, physicists introduced the contradictory idea called Unruh effect where the empty vacuum paradoxically emits light (= meaning the vacuum filled with light medium or ether or unreal virtual particles, this-5th-paragraph ) when observers start to accelerate, which clearly disproves Einstein saying the vacuum is empty with No energy ( this-1~2nd-paragraphs ).
↑ Actually, this Unruh effect is unrealistic, too small to observe ( this-3rd-paragraph, this-p.1-left-1st-paragraph, this-1st-paragraph ) , so this relativistic kinetic energy paradox cannot be solved even by this artificial Unruh effect seen by accelerating observers.
↑ Einstein relativity is false, violating energy or momentum conservation law.
The only legitimate solution to this relativistic kinetic energy (= light-emitting ) paradox is that an electron moving relative to the real light medium has kinetic energy to emit light energy and generate de Broglie wave interference (and Lorentz magnetic force ) regardless of observers, which rejected Einstein relativity.
(Fig.E) Einstein relativity is false, cannot conserve energy nor momentum.
Einstein (general) relativity lacking absolute frame (= which objects are moving is uncertain and changed as seen by different observers in Relativity ) is false, cannot conserve energy nor momentum.
In the upper figure, a small stationary stick is accelerated by small energy and gain small kinetic energy (= ① ).
↑ As seen by the accelerated small; stick (= ② ), all heavier objects in the whole world around the stick appear to be accelerated and gain far larger kinetic energy.
↑ This is clearly violation of energy conservation law disproving Einstein relativity, because the smaller energy accelerating the small stick can unrealistically accelerate all heavier objects in the whole world around the stick.
↑ These unrealistically accelerated heavier objects with far larger kinetic energy could be converted into far larger light energy, violating energy conservation law, which does Not happen in the real world.
There is only one real absolute frame (= ① ) conserving energy and momentum, which means Einstein relativity lacking the real absolute motion or ether is wrong.
(Fig.R) An electron and a proton increase their kinetic and relativistic energy, but the total (relativistic) energy of a hydrogen (= H ) atom decreases due to the lower potential energy in the medium (= Not particles' kinetic energy ), which fact disproves Einstein.
Einstein relativistic (kinetic) energy mc2 is unreal, increasing or decreasing as seen by different observers, violating energy conservation law, because Einstein lacks the real absolute frame or ether.
Einstein relativistic energy is wrong, because it needs the potential energy ( this-3rd-paragraph ) stored in the medium disproving Einstein relativity rejecting the medium.
In the upper figure, an electron and a proton separated by an infinite distance (= with zero Coulomb potential energy ) are stationary (= No kinetic energy ) with only the rest mass energy of m0c2.
When this electron and the proton attract each other and form a hydrogen (= H ) atom, their kinetic and relativistic energy related to the particle's velocity increases (= an electron starts to be moving around the proton inside a H atom due to Virial theorem ).
But the total (relativistic) energy of the H atom decreases due to the lower Coulomb attractive potential energy between an electron and a proton ( this-p.4 ).
↑ This is paradox, because the total relativistic energy of the H atom decreases due to the potential energy in the medium which Einstein rejected, around the electron and the proton whose kinetic energy increases.
Actually the mass energy equation of mc2 was first derived by classical Maxwell theory (= with the medium = No need for paradoxical Einstein relativity ), which was illegitimately copied by the paradoxical Einstein relativity. later ( this-p.3~ ).
(Fig.Q) Einstein relativistic theory rejecting the real medium causes unphysical quantum mechanical wavefunction or parallel universes.
As shown in fatal relativistic paradoxes such as Lorentz force, twin, length, kinetic energy, de Broglie wave, faster-than-light-Sagnac effect, mc2 energy Not conserving energy, contradictory gravitational wave, black hole, Einstein relativity is officially proven wrong.
The fact that Einstein relativity rejecting the medium (= ether, this-p.10 ) is wrong means the electron's de Broglie wave is real wave generated in the real medium (= agreeing with stellar aberration ), which disproves quantum mechanical unphysical wavefunction or wave-particle duality against reality, too.
Real de Broglie wave whose wave phase is constantly changing with a moving electron disproves the unphysical quantum mechanical static probability wavefunctions that cannot be changed nor moved.
Einstein relativistic theory introduced the paradoxical Lorentz transformation or time dilation by trying to explain the constant light speed c on the earth without the real medium (= aether ) in space.
So in this unphysical Einstein relativistic world without the real medium in space, physicists have to unrealistically treat each electrons as a particle and wave simultaneously called wave-particle duality.
Quantum mechanics based on this paradoxical Einstein relativity claims a single electron (unrealistically) splits into many different places by (fictional) quantum superposition or parallel universes to interfere with itself in two-slit experiments ( this-2nd-last-paragraph, this-4-5th-paragraphs ).
↑ If Einstein relativity is wrong, we can naturally explain this contradictory wave-particle duality and two-slit-experiment of a single electron's interference by separating a real electron particle and real de Broglie wave generated around the electron.
An electron cannot influence or change its own motion due to action and reaction law (= even when the electron pushes itself, the electron is pushed backed by itself by the same amount of force, so the electron cannot move ) in two-slit interference experiment of a single electron or stable quantized orbits.
↑ Some external medium except the electron needs to push the electron from destructive into the constructive interference area, which medium disproves Einstein relativity.
A photon particle is illusion just light wave ( contradictory virtual photons are unreal ) in the medium.
Due to paradoxical Einstein relativity rejecting medium, physicists unable to separate a real electron particle and real de Broglie wave generated in the medium have to use unphysical quantum mechanical probability wavefunction or contradictory wave-particle duality.
This quantum mechanical ( paradoxical ) probability wavefunction is unrealistic, based on unscientific superposition where each electron must exist in all places at once in fantasy parallel universes until measured, like in two slit experiments of a single electron or a photon.
Physicists can Not determine each electron's position (= uncertainty principle ) in this unphysical quantum mechanical probability wavefunction that always includes impossible negative kinetic energy area.
Furthermore, quantum mechanical electrons in s orbitals are said to have (unreal) zero orbital angular momentums, which means those electrons moving in linear orbits (= zero orbital angular momentum ) always crash into nuclei, and their de Broglie wave causes destructive interference, and become unstable.
↑ All these paradoxical unphysical quantum mechanical probability wavefunction can be replaced by real atomic model based on real electrons (= non-zero angular momentum, so not crashing into a nucleus ) and de Broglie wave.
Quantum mechanical wavefunction has to rely on unphysical exchange energy (+ paradoxical superluminal electron spinning ) based on pseudo-kinetic energy change caused by the wavefunction interference (= hampering science due to shapeless wavefunction ) to express Pauli repulsion, which can be naturally replaced by real de Broglie wave interference.
Einstein relativity is wrong due to its fatal paradox.
So the hydorgen's excited energy levels' small energy splitting between 2p3/2 and 2p1/2 energy states called fine structure is caused Not by the (paradoxical) relativistic spin-orbit magnetic energy ( this p.6 ) in quantum mechanical Dirac hydrogen, but by real Bohr-structure without spin.
This p.14-4th and last paragraphs says -- Real Bohr model
"Sommerfeld's fine-structure formula was spectroscopically confirmed for
H and for hydrogenic ions (He+,
Li2+, ...) to the highest precision—the greatest triumph
of the old quantum theory"
"Over a decade later, after the electron spin had
been discovered, relativistic quantum mechanics
(Dirac 1928) obtained the fine-structure formula (Gordon 1928) along a very
different route....
yields the same energies as Sommerfeld’s formula"
This-3rd-last-paragraph says -- Dirac copied Sommerfeld
"When Dirac developed relativistic quantum mechanics, the relativistic Coulomb problem proved to be exactly solvable ...But the resulting formula for the energy levels was truly a surprise: The new answer was precisely the old Sommerfeld formula !"
This realistic Bohr-Sommerfeld model relies on Maxwell's authentic mc2 energy (= classical Maxwell theory first proved the energy E stored in the medium has mass m equal to E/c2 ) that was copied as the paradoxical relativistic mass later by Einstein.
Einstein relativity is paradoxical and wrong, which means all relativistic quantum theories such as QED, quantum field theory and standard model using paradoxical virtual particles with imaginary masses are wrong, too.
Today's only theory of everything allegedly unifying Einstein relativity and quantum mechanics is fictional extra-dimensional string theory ( this-4th-last-paragraph ), which is also wrong, if Einstein relativity is wrong.
Actually, these unphysical QED and particle physics are completely useless, just wasting huge taxpayer's money in unnecessary gigantic colliders.
(Fig.P1) Different clock times in different positions.
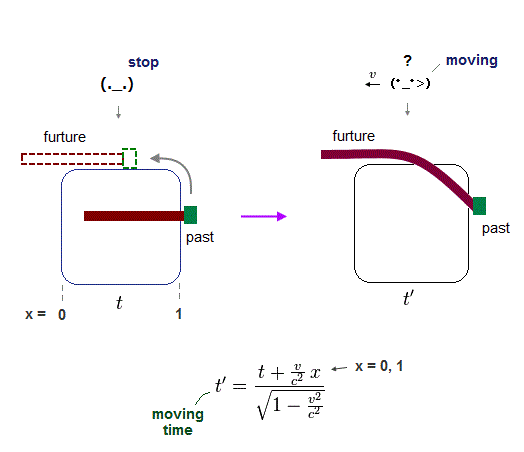
Here we present a typical example of fatal paradox in Einstein relativity.
In Einstein relativity, a moving ovserver has an unrealistic power to bend even a rigid rod without touching it , no matter how hard the rod is, as seen in Lorentz contraction.
A rigid rod is moving upward at first and then turn to the left horizontally along the rigid square rail in the upper figure.
External forces are always applied to any positions of the long rod uniformly, in both leftward and upward directions (= at first, the rod cannot move to the left, blocked by the vertical rail on the right side. )
Surprisingly, as seen by a moving observer, this originally-straight rigid rod appears to be bent complexly, as seen in the upper figure right.
According to relativistic Lorentz transformation, events occurring in different positions (= x = 0, 1 ) at the same time (= t ) seen by stationary observer occur at the different times (= t' ) seen by a moving observer !
By inserting two positions x = 0 and 1 (= same time t by stationary observer ) into Lorentz tansformation, we find a moving observer sees the left end of rod turning to the left earlier than the right end of the rod.
Hence, a moving observer tends to see the future event of the left end of the rod and the past of the right end of the rod. which appears to bend the rod like in the upper figure right.
This occult world is Einstein special relativity.
(Fig.P2) "Block" changes the rod "future" direction.
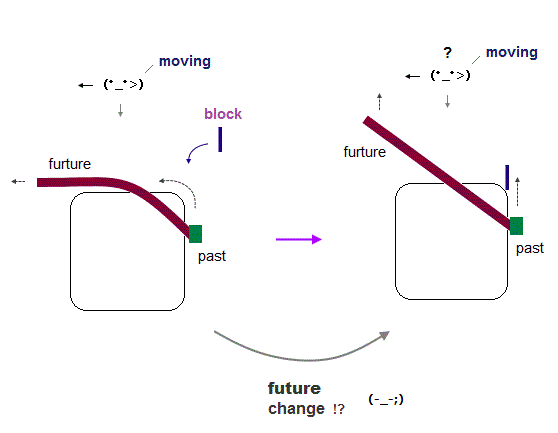
So in Einstein fantasy relativistic world, a rigid rod "can" foresee the future !
In the upper figure, the right end of the rod (= still existing in the past ) has Not arrived at the turning point, but the left end of the rod (= existing in the future ) has already turned to the left at the turning point.
If someone suddenly puts a new block onto the turning point, the whole rigid rod (= including left and right ends of the rod ) cannot move leftward (= the whole rigid rod cannot turn to the left ), meaning the left end of the rod already turning leftward suddenly changes its past event and its direction (= as if moving upward from the beginning without turning to the left at the turning point ) without touching the rod !
This is paradoxical and impossible, because the right end of the rod (= past ) has Neither arrived at the turning point nor known whether a block is there or not.
But the left end of the rod can automatically predict the future event (= can know whether a new block is put at the turning point without touching it ), and make a decision whether it will bend (= moving leftward ) or bend back (= moving upward without turning leftward ) !
This is one of fatal paradoxes of Einstein relativity which theory proved to be wrong just by this paradox.
Here we suppose external force is always applied to any points of the rod uniformly, so the moment the rod arrives at the turning point without a block, the whole rod starts to turn to the left without delay simultaneously.
See Einstein is wrong in electromagnetic field.
See Einstein relativity de Broglie wave paradox
See Einstein relativity contradicts kinetic energy.
See Relativistic mass is unreal.
See Twin paradox is real, Einstein is wrong.
See GPS doesn't use relativity.
(Fig.U) Driving force to expand universe is dark energy ← NOT diluted ? Unreal negative pressure ?
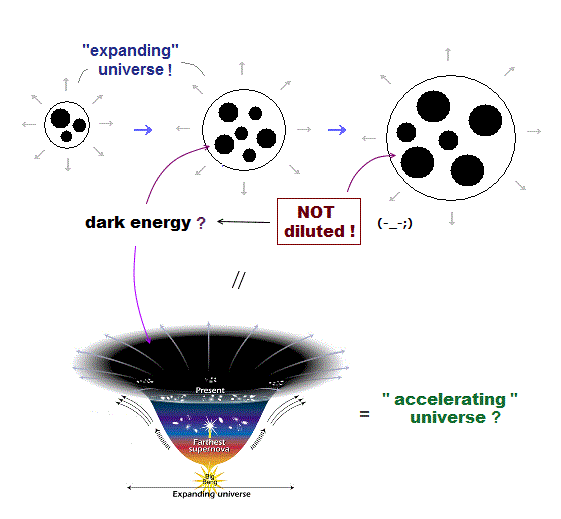
Big Bang and expanding universe are just fantasy.
There is No evidence indicating our universe is expanding so rapidly, as seen in the fact that our solar system is Not expanding at all.
The current cosmology claims the entire universe is expanding by fictional dark energy with unreal negative pressure, which is said to be Not diluted even by the space expansion ( this 2nd-paragraph ). ← Dark energy is Not a real thing !
They baselessly conjecture that universe is expanding only from the fact that light emitted from more distant stars is redshifted (= longer wavelength ), which can be more naturally explained by lights from more distant stars tend to lose their energies, elongate their wavelength by being scattered by more dusts and or by oscillating other molecules while light is traveling an extremely long distance.
The most conclusive evidence of fantasy Big Bang is said to be an uniform cosmic microwave background (= CMB ) which is unrealistically misinterpreted as a remnant of the beginning of our universe.
But it's impossible for each microwave to keep an intact state of very ancient light wave from the early universe for as long time as 13.8 billion years !
So it is more natural to think that the uniform cosmic microwave filling all space is an evidence of uniform light "medium (= slightly oscillating at 3 K )" filling space.
The current astronomy focuses only on fictional science saying this cosmic microwave may indicate fantasy parallel universes. ← nonsense.
Astronomers often cite "Olber's paradox (= why night sky is dark )" as a reason for the (fictional) expanding universe or BigBang, but this Olber's paradox does Not justify the expanding universe at all.
According to Olber's paradox, if the universe is static and infinite filled with luminous objects (= stars ), every sight line from the Earth will eventually intersect a bright object, it means the night sky will be bright, hence, the universe should be finite and expanding (= BigBang ) to solve this paradox and make the night sky dark.
And they misleadingly claim that even if dusts or debris in the space could absorb the light, they heat up and eventually reradiate the same light towards the Earth (← this is wrong ), hence the existence of dusts doesn't solve this Olber's paradox ( this resolution ).
↑ But this logic of expanding universe intentionally avoids the case where many dusts and objects in the space block and reflect the light back to the stars, as seen in the solar eclipse ( this 5th-paragraph ).
In conclusion, Olber's paradox is caused by forgetting the case of light reflection, and the expanding universe and BigBang are false.
See Gravitational wave is unreal

Feel free to link to this site.