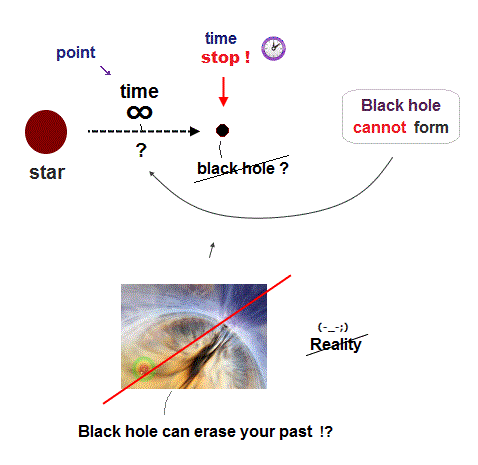
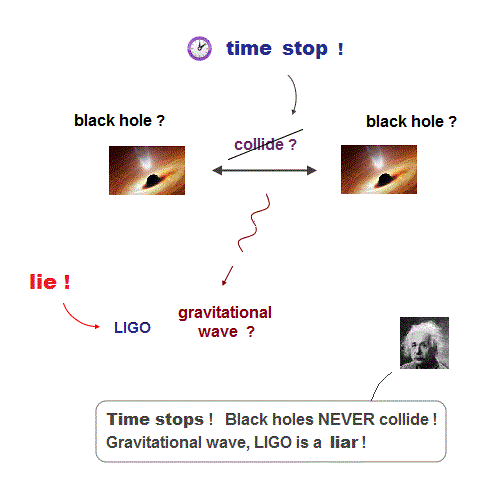
(Fig.1) Time stopping on black hole prevents its formation.

Despite extremely long time research, black hole is still useless, because imaginary black holes are too far away from the earth to reach and confirm directly.
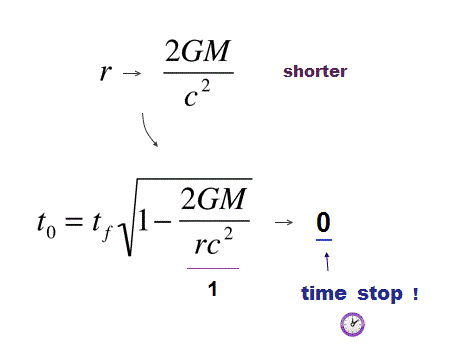
First, black hole cannot be formed. A clock time is said to magically slow down and stop by strong gravity at points close to black hole's surface called event horizon, as seen by outside distant observers ( this p.21 ) on the earth ( this-lower, this p.15-16 ).
The current mainstream theory claims that black holes were formed by a massive star collapsing and becoming compressed by its own gravity into black hole.
↑ But as the star becomes denser and closer to black hole, its clock time becomes significantly slower, and it would take almost infinite time to form black hole on which the time must completely stop seen from the outside observers (= hence, many researches claiming black holes were detected or photoed from the outside earth's telescopes are wrong ).
The last paragraph of this site says
"theoretical Black Holes with Event Horizon (where time stops) do Not exist"
Stopping time means the collision of two black holes allegedly generating gravitational wave is also impossible, too.
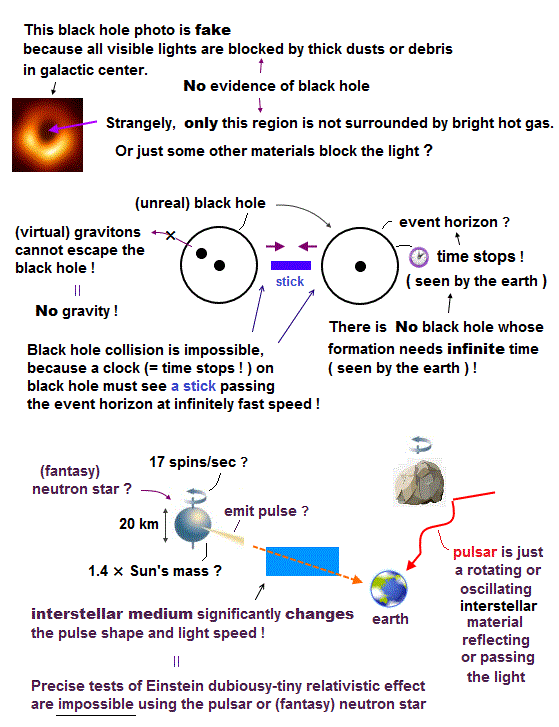
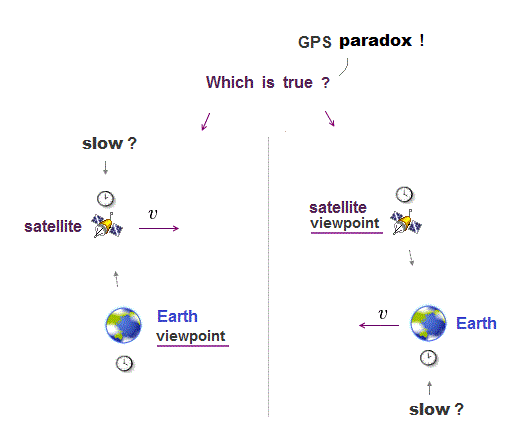
(Fig.2) A stationary stick appears to move faster than light as seen by an observer on the black hole whose time stops ? ← paradox !
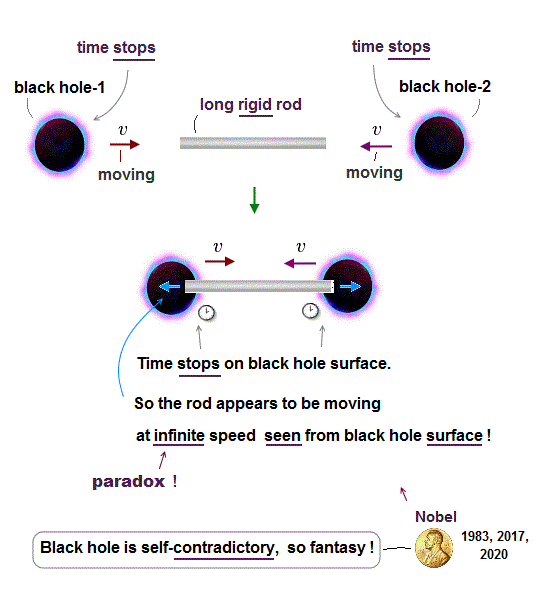
In Fig.2, a black hole is approaching a stationary stick at a velocity of v.
When the stationary stick passes the event horizon of the black hole whose time stops, an observer on the event horizon paradoxically sees the stick passing at infinite (= much faster-than-light ) speed.
Because the stick appears to move even on the event horizon whose time stops, which contradicts Einstein relativity prohibiting faster-than-light motion.
↑ A black hole always attracts the stationary stick only in the left direction, so the stick does Not start to move in the right direction, and the stick appears to move at infinite speed as seen by the observer at rest relative to the event horizon whose time stops.
(Fig.3) Gravitons must be unreal virtual particles moving faster than light to escape black holes, which contradict Einstein relativity.
The current mainstream "theory of everything" called string theory allegedly unifying Einstein relativity and quantum mechanics claims that (virtual) gravitons mediate gravitational forces.
But if so, these gravitons emitted from the black hole must pass through the event horizon where the time stops, which means gravitons also must stop at the surface (= event horizon ) of the black hole, and cannot escape into the outside of the black hole, hence, black hole cannot exert gravitational force on any outside objects. ← this means all the current researches trying to measure the strong black hole's gravity from the outside earth's telescopes are meaningless.
Some people say that gravitons may not exist, which causes another problem of No connection between black hole and gravity outside of the black hole.
Other people say the gravitons are Not real particles but just virtual particles which can unrealistically move faster than light contradicting Einstein.
↑ As a result, the black hole is self-contradictory and unreal, as Einstein himself theoretically rejected the existence of black hole.
(Fig.4) Black hole picture is fake.
Black hole, which absorbs everything, cannot be seen directly. Though the current physics claims the existence of black hole can be proved by watching the motion of stars allegedly orbiting around unseen black holes, it is untrue.
Because even stars around black holes in the galactic center cannot be seen hidden by very thick and dense clouds of dust and gases ( this 4th paragraph ).
So the recent ( dubious ) black hole picture is fake or artificially-created, because No visible light can be detected near black hole due to very thick dusts. ← Not a real photo of unseen black hole.
This 4th-paragraph says
"These “photos” do Not, of course, directly show a black hole,.. They actually record portions of the flat pancake of hot plasma swirling around the black hole at high speeds.. its accelerating particles emit radio waves." ← Then why does this hot bright plasma avoid surrounding only the front of black hole's photo (= black part ) accidentally ? ← this is strange.
This original paper says (p.5-2nd-paragraph, p.8-right-lower)
"Every imaging algorithm has a variety of free parameters
that can significantly affect the final image. We adopted a twostage imaging approach to control and evaluate biases in the
reconstructions from our choices of these parameters (= black hole photo is an artificial image based on freely-chosen parameters and algorithm for constructing artificial images )."
"it is more difficult to rule out alternatives to black holes in GR, because a shadow can be produced by any compact object with a spacetime characterized by unstable circular photon orbits. ← It means there are possibilities that other irrelevant objects just blocking the light (= so seen "black" ) were mistaken for (fictional) black hole's shadow."
(Fig.5) A black hole must be massive and small, but the size of a black hole cannot be known, so No evidence of black holes.
To discover a black hole, we have to know both the mass and size of a black hole, which must be an extremely dense and small (= Just "massive" cannot prove a black hole, which can be replaced by a massive large non-black-hole star ).
For example, the radius of such a dense black hole with the same mass as the Sun or Earth must be extremely small = 3.0 km, or only 9mm.
The present astronomy relies on the ungrounded assumption that the rapid brightness fluctuation of X ray allegedly emitted from black hole may tell us how small the black hole is ( this 2~3rd-paragraphs, this 3rd paragraph, this p.1-3rd-paragraph ).
This 3rd-last paragraph claims
"To make rapidly varying X-rays, the unseen companion must be small ! The fluctuation timescale gives us the maximum possible diameter of the object. Since the speed of light is finite, it takes a given amount of time for light to travel across the object... The quicker the fluctuations are, the smaller the object (= black hole ) must be."
↑ But the rapid fluctuation of the brightness of X rays can occur due to rapid fluctuation of materials or hot gas around the black hole like the solar flares, which is completely irrelevant to the (unknown) black hole size ( this p.2-last-paragraph ) like the fake black hole picture ( this-middle-2) ).
↑ There is No legitimate way to know the size of a unseen black hole (= the black hole's size is only ungroundedly guessed from the mass ), which means No evidence of black hole.
Sagittarius A at a galactic center of the Milky way is said to be a supermassive black hole whose mass is about 4 million times bigger than the Sun.
↑ If there is a massive star whose radius is about 160 times longer than Sun's radius, and with the same density as the Sun, this bigger star can have the mass of 4 million times the Sun (= 1603 = 4 million times the size of Sun ), and mimic the Sagittarius A's black hole, though it is Not a black hole. ← It means the black hole, which can be replaced by an ordinary big star, is unnecessary.
The star allegedly closest to this black hole is called S4714 whose pericenter distance from the black hole is 12.6 AU (= 12.6 times the distance between Sun and Earth = 1.8 × 109 km ).
↑ Inside this closest star S4714 orbit (= whose orbital radius is 1.8 × 109 km ), there is a space enough for the massive star, whose radius is 160 × Sun's radius = 7 × 105 × 160 = 1.1 × 109 km (< 1.8 × 109 km of the closest star's orbital radius ), mimicking the Sagittarius A black hole with the same density as the Sun.
(Fig.6) Black hole picture is fake.

In only (fictional) black holes near the earth such as Sagittarius A in our Milky way galaxy, astronomers can use the (dubious unseen) orbiting stars around the black holes to roughly estimate the masses of black holes using Kepler law, various ad-hoc models and fitting parameters ( this p.2-left-2nd-paragraph, this p.3-fig.1 ).
But the galactic centers are covered by very thick dusts and debris, so we cannot observe any stars' motion around the black hole, because No visible light can penetrate these thick layers of dust (= so photos of unseen black holes are impossible ).
Astronomers try to "imagine" (fictitious) star's motion based on infrared rays with longer wavelength, which are emitted from everywhere not only stars (= hence, distinguishing stars orbiting around the black hole using this infrared rays is impossible ), in order to estimate the black hole's mass.
↑ Furthermore these (imaginary) stars' motions allegedly around the unseen black hole are often unnatural and unrealistically irregular (= stars become irregularly faster and slower, which are Not real orbits ), which means all these (unseen) orbits of stars around black holes are fake and unreliable.
This method based on stars around black holes cannot be used in more distant black holes where measurement of precise motion of stars around distant black holes is impossible. Of course, the size of black holes cannot be known.
In more distant black holes, they try to rely on much more unreliable method called "reverberation mapping" where they roughly estimate the orbiting radius (= directly unmeasurable ) of unspecific clouds around a unseen black hole from the time delay or lag between the time when light is emitted from near black hole and the time when this light is reflected from the (unmeasurable) surrounding clouds called broad line region (= BLR ).
↑ But the light (= allegedly emitted from distant black holes ) is naturally reflected from many particles and gases (= Not only the cloud of broad line region ) in the dense space in the galactic centers around black holes, and this method must rely on some unknown ad-hoc freely-adjustable parameters ( this p.1-right ). Hence, the precise estimation of the alleged (unmeasurable) distant cloud's motion and radius for obtaining the distant black hole mass only from this light reflected from unknown clouds is impossible.
Almost all (dubious) black holes are so far away that we can Not even observe stars' motion around the (unseen) black holes.
Recent (doubtful) claim of discovering most distant black hole by Webb space telescope relies only on very unreliable ad-hoc interpretation where some hydrogen emission (= Hβ ) line may tell us rough masses of unseen black holes instead of seeing stars around them ( this p.14 6.1 black hole mass ), though this interpretation has No physical grounds.
↑ The rough (unreliable) estimation of the unseen, unmeasurable distant black holes' masses based only on line luminosity and width of hydrogen atomic lights = Balmer Hα (= wavelength 656 nm = 6560 Å ), Hβ (= wavelength 486 nm = 4860 Å ) lines allegedly emitted from hot gases around the unseen distant black holes is impossible due to hot gases or starts around (imaginary) black holes or galactic centers continuously emitting many kinds of lights with many kinds of wavelengths as continuous spectral lines (= hot stars' temperature is 5000 ~ 10000 K, which emits continuum spectral lines or bright lights with wavelengths from 100 ~ 1000 nm ) which background lights easily mask the hydrogen Balmer H lines (+ lights scattered and modified by interstellar medium ), make it impossible to estimate based on light wavelength.
This research ( this p.4-5=using artificial parameters, p.6-4.2=discrepancy between theory and observation ) also depends on the ambiguous the hydrogen's Hα spectral line as a means of (baselessly) guessing the unseen distant black hole's mass using various freely-adjustable parameters, and found the discrepancy (= contradiction) between theory and observation. ← No reliable evidence of black hole
All other methods also depend on various ad-hoc models and freely-adjustable fitting parameters ( this p.12-lower ) with No direct evidence of Einstein black hole.
(Fig.7) Black hole is too far away from the earth to confirm as real.
From these doubtful unseen star's motion allegedly around the (imaginary) black hole, physicists try to estimate Einstein relativistic effects such as tiny gravitational redshift (= about 200km/s = far smaller than the classical redshift by normal Doppler effect as seen in ordinary sound wave, this last-paragraph, this 2nd-paragraph ), which dubious tiny gravitational redshift is often indistinguishable from the far-larger (= nonrelativistic ) Doppler effect's redshift influenced by star's velocity = 7650 km/s or redshifts by light's energy loss (= Compton scattering or a part of light energy is absorbed into other atomic electrons ).
First of all, gravitational red or blue shift is due to ordinary classical gravitational energy conservation law irrelevant to Einstein relativistic time dilation.
The tiny redshift calculation is done by fitting various artificial parameters (= so Not agreeing with Einstein relativistic prediction, this p.3, this p.3-right-lower ), though these stars' motions with unrealistically irregular velocities are unreliable.
↑ It is impossible to confirm Einstein tiny, tiny gravitational time dilation (= causing fatal twin paradox, so unreal ) or red-shift around the distant (imaginary) black hole surrounded by a thick layer of dust which blocks almost all lights such as visible lights ( this 7th-paragraph ).
↑ Astronomers tried to guess Einstein (imaginary) gravitational time dilation by seeing the slight wavelength change of unspecific and unreliable infrared light ( this 6th-paragraph ) or K-band such as very-low energy hydrogen Brackett-γ(= Brγ) line with 2.1661 μm wavelength (= only 0.5 eV ), which was allegedly emitted by the transition from high energy level n = 7 → n = 4 (instead of observing some strong specific atomic lines such as visible or ultraviolet lights, this p.2 observations, this p.1-right, this p.2-right-2nd-paragraph ).
↑ Knowing the original infrared light's (unspecific) wavelengths for estimating gravitational time dilation or red-shift is impossible, because many kinds of lights with various wavelengths from high-energy γ rays to low-energy infrared lights are flying everywhere around galactic centers (or black holes ), which are indistinguishable from the tiny infrared light's wavelength change.
The space around black holes are filled with very high-energy particles moving at light speed (= energy is greater than 106 eV ) causing larger classical Doppler shift's wavelength change and high-energy light at hot temperature, which can easily mask the extremely-weak hydrogen's infrared Brγ line (= only tiny 0.5 eV energy ) and make it impossible to measure the tiny relativistic redshift of the weak infrared light's slight wavelength change in the circumstances filled with a lot of lights with much higher energies.
↑ The infrared red lights they used for estimation of the dubious gravitational redshift have about 2 μm wavelength ( this 2.1 K-band ). ← Many stars such as Sun emit these infrared lights with various continuous wavelengths whose wavelength's slight change (= tiny redshift ) cannot be identified or distinguished.
(Fig.8) Gravitational lens is just light bent by dust, Not by (illusory) gravitational time dilation.
Gravitational lens is said to be one of relativistic effects where light emitted from distant light sources (= background ) such as bright galaxies, stars or quasars are bent by the strong gravity (= due to unphysical relativistic time dilation or redshift, rejected by twin paradox ) of the foreground galaxies, unseen black holes or ad-hoc ghost-like dark matter.
They insist when the background star, the center of foreground galaxy and the earth are rarely and perfectly aligned in one line, the background star's image or light is seen as ring called Einstein ring around the foreground galactic center or black hole as phenomena of gravitational lensing.
↑ But it is too unnatural and coincidental that the distant (= background ) star and the center of some irrelevant foreground galaxy are just perfectly aligned in one line to the earth.
So it is more natural to say that the light emitted from some background star or galaxy is scattered or reflected by various gases, dusts and interstellar medium around the foreground galaxy, and this scattered light coming to the earth is observed as light ring instead of the paradoxical Einstein relativistic effect ( this p.2, p.8-right ).
Actually, part of Einstein ring is often dark, completely blocked by some dusts or interstellar medium, and centers of galaxies or areas near black holes are often filled with thick clouds of dusts and gases.
So gravitational lens is Not a proof of Einstein general relativity but just light scattering by interstellar medium or gases.
Some people say the gravitational lens is achromatic, different from chromatic refraction.
But as shown in very rare rainbow formation, the chromatic refraction separating lights with different wavelengths is rare, often prevented by the light scattering (= so achromatic refraction is common ).
Einstein general relativity claims light is slightly bent by fantasy gravitational time dilation by massive stars or Sun. But this bent light is much more easily and naturally explained by light refraction (or light scattering ) by dust and molecules around stars.
↑ Einstein general relativity often deliberately ignores the far more influential atmosphere or air (= gas ) medium around the earth or massive stars which can more easily modify the light speed, wavelength, frequency and atomic motions.
The refractive index of the air (= 1.0003 ) means the light speed c is significantly slower by the air medium to c/1.0003, which atmospheric influence (= 0.0003 ) is far more influential than the tiny relativistic gravitational effect or time dilation (= allegedly only 45 microseconds/per day = 24×3600 = 86400 sec/day, so relativistic effect is far smaller = 45×10-6/86400 = only 5 × 10-10 and more negligible than the air medium's influence of 0.0003 ).
Some astronomers try to roughly estimate the unseen black hole's mass by using this (imaginary) gravitational lens, but it is impossible to observe the precise Einstein ring around the galactic center or black hole covered by very thick dust and debris.
So they have to rely on some ad-hoc speculative lens models with unknown background stars' positions and artificially adjust many free parameters (= including unmeasurable dark matter parameters ) to (baselessly) deduce the masses of distant (fictional) black holes ( this Fig.2, 3.3~4.3=various models, table.6= dark matter model parameters, this p.5-left, this p.12-lower ), which artificial models are Not the proof or test of Einstein relativity.
↑ In order to explain unusual gravitational lens in the space without black holes (= this gravitational lens is caused by light scattering in the interstellar medium, Not by Einstein relativity ), they are forced to artificially create ad-hoc convenient concept of unseen dark matter, which can be explained by the real medium in space, as shown in even Einstein paradoxically trying to restore ether which he rejected before.
The perihelion for Mercury is said to move only 0.012 degrees for 100 years due to doubtful Einstein relativity which effect is too tiny to believe (= there are many other factors irrelevant to Einstein relativity such as many-body complicated forces working among various shaped planets causing such a negligibly-tiny orbital change for 100 years ), and we don't need too small Einstein relativistic effect for our daily life at all.
GPS, which is said to be the only application of Einstein relativity, does Not need Einstein, which is just useless and wrong.
Contrary to the media-hype such as "Einstein relativity was right again", the (illusory) expanding universe based on the hypothetical dark energy is irrelevant to Einstein relativity.
This-2nd~4th-paragaphs say
"In 1917, Albert Einstein inserted a ( artificial ) term called the cosmological constant into his theory of general relativity to force the equations to predict a stationary universe"
"But lately scientists have revived Einstein's cosmological constant to explain a mysterious force called dark energy that seems to be counteracting gravity -- causing the universe to expand at an accelerating pace."
↑ So this artificial conmological constant terms are freely-adjustable parameters that can freely change from stationary to expanding universes, irrelevant to Einstein relativistic prediction.

Feel free to link to this site.