Home page
Einstein relativity is wrong
Lorentz magnetic paradox
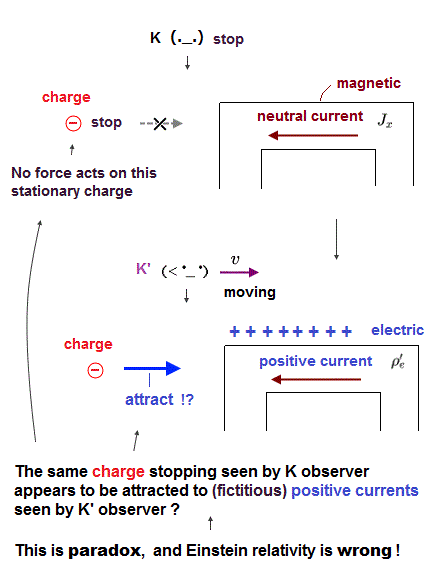
(Fig.1) Neutral electric current seen by a stationary K appears to be positively charged seen by a moving K', which causes paradox in Einstein relativity.

In the Fig.1-left, a stationary observer K (= lab frame ) sees the electrically-neutral wire where negative electrons (= - ) are flowing at a velocity v in the rectangular circuit clockwise (= which corresponds to electric current J moving in the opposite direction or counterclockwise ), and the same numbers of positive nuclei (= +, so neutral ) are stationary.
But as seen by another observer K' moving at the same velocity v as the electrons' current (= moving frame ), this same upper wire (= electrically-neutral seen by the stationary K ) is unrealistically positively charged and the lower wire is negatively-charged, according to the (unphysical) Einstein relativity.
This 2nd, 6th-paragraphs say
"the wire appears to be neutral, with no net electric charge (= as seen by K )."
"In the frame (= different frames mean seen by different observers ) of reference of the charge +Q (= seen by K' ), the wire no longer appears neutral, but appears to have a net positive charge"
This-p.9-last~p.10 say
"In this frame the wire is neutral.... However, in our new frame... the wire carries negative charge"
↑ According to the unphysical Einstein relativity, the neutral magnetic field unrealistically changes into electric field as seen by different observers (= in different frames, this-p.2, this-2nd-paragraph ).
This Einstein relativistic electromagnetism contradicts reality, because the excessive positive charges in the upper wire and negative charges in the lower wire should be attracted to each other and immediately return to neutral wire (= even when seen by the moving K' ) in the real world.
In the upper wire ( this-figure-lower ), the intervals between electrons (= - ) which are stationary as seen by the moving K' observer is wider than the intervals between the same electrons which are moving seen by the stationary K according to the unphysical relativistic Lorentz length contraction (= a moving object or length appears to be shorter, this-12~13th-paragraphs, this-lower ).
↑ As a result, negative charge density is lower when seen by the moving K' (= who sees the stationary electrons whose intervals are wider ) than when seen by the stationary K (= who sees the moving electrons' current whose intervals are narrower or shorter ).
And the intervals between stationary positive nuclei seen by the stationary K gets shorter (= positive charge density increases ) as seen by the moving K' due to Lorentz length contraction of the moving positive charges seen by K' ( this-Figure-24.5.2 and 24.5.3 ).
This-p.2-3rd-paragraph says
"In the electron's reference frame (where the electron is standing still, as seen by the moving K' ), all of the electrons in the
wire now appear to stand still. They are not moving in this reference frame, so the
"The opposite happens to the positive metal ions. They appear to move backwards in the electron’s frame, and so their separations appear length-contracted to the electron. Thus, the electron (= K' observer ) sees a lower density of negative charges, and a higher density of positive charges, which creates an electric field (= unrealistic, this-right-lower ) that attracts the electron"
This Einstein relativistic electromagnetism causes serious paradoxes, so Einstein relativity is wrong.
In Fig.1-left-lower, an external electron (= - ) seen by the stationary K remains at rest, Not attracted toward the neutral electric wire.
But only when seen by the moving K', the same external electron is pulled or accelerated toward the ( unrealistically ) positively-charged electric wire ( Fig.1-right-lower ), which is clearly paradox, disproving Einstein relativity.
↑ This external electron is moving in -x direction as seen by the K' moving in x direction ( Fig.1-right-lower ), so Lorentz magnetic force (= in y or z direction ) perpendicular to the electron's moving direction cannot cancel the paradoxical attraction in x direction acting on the external electron, so this is an unsolvable relativistic paradox (= independent of the famous lorentz force law paradox ) disproving Einstein.
(Fig.2) Neutral current (= charge ρ = 0 ) seen by a stationary K unrealistically becomes positively charged (= ρ' > 0 ) as seen by a moving K' according to Einstein relativity.
According to unphysical Einstein relativistic Lorentz transformation giving relationship between spacetime coordinates seen by different observers, neutral current (= total charge ρ = 0, neutral current density Jx = - J, this-p.1-1.inroduction ) seen by a stationary K unrealistically changes into positively charged (= charge ρ' > 0 ) seen by K' moving in x direction at a velocity of v ( this-p.3, this-p.12-2.5, this-p.10-lower, this-p.12-(2.4) ).
In the real world, these excessive positive charges (= upper wire ) must be naturally attracted to negative charges (= lower wire ) and become neutral soon as seen by any observers K and K'.
So Einstein relativity where K' observers see unreal positively (or negatively ) charged wires contradicts the real electromagnetic theory of positive and negative charges attracting each other, hence false, causing fatal paradoxes.
This-middle-Box 13.6-lower says "how does a current density become a charge density ? I don't know an easy way to explain it"
(Fig.3) Einstein relativity says the neutral wire seen by K is changed into positively-charged wire seen by K', but the electric field Ex (= around the positively-charged wire ) remains zero seen by K', which is paradox.
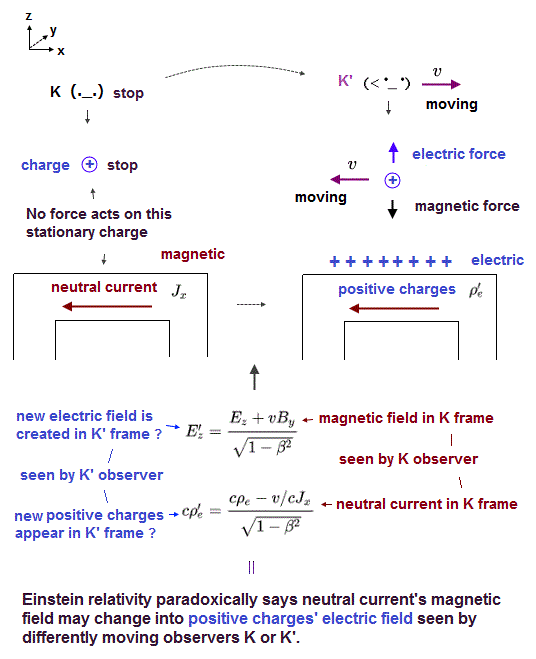
We can prove Einstein relativity is false, causing serious paradox in electromagnetic fields.
In Fig.3-left, an external positive charge (= + with charge e ) stops, feeling No electric nor magnetic forces from the electrically-neutral current (= causing only magnetic field not exerting magnetic force on the static charge, and No electric field ) as seen by a stationary K.
But in Fig.3-right, as seen by K' moving in x direction at a velocity of v, the same external positive charge appears to be moving in the opposite -x direction at v, so this external positive charge experiences Lorentz magnetic force (= evB' ) from the electric current wire, and starts to move in -z direction only when seen by the moving K' observer.
↑ This external positive change is Not moving in -z direction as seen by the stationary K, so to cancel this paradoxical Lorentz magnetic force occurring only when seen by the moving K', the neutral wire seen by K must unrealistically change into positively charged as seen by the moving K' according to the unphysical Einstein relativity ( this-p.2 ).
As a result, these Lorentz magnetic (= evB' ) and electric force (= eE' ) caused by new unphysical positive charges acting on the external positive charge (= e ) cancel each other (= evB' = eE ), and the external charge is not moved in -z direction when seen either by the moving K' or the stationary K ( this-Figure 3.4.3~, this-p.11 ).
↑ So the neutral wire seen by the stationary K (= seen by different observers in different frames or coordinates ) needs to be unrealistically positively-charged, which causes another fatal paradox, to cancel Lorentz magnetic force as seen by the moving K'
This-16th-paragraph says
"what was once magnetic fields have now changed into electric fields.... The magnetic force and electric force on the nuclei cancel out."
But Einstein relativity paradoxically says the zero electric field (= Ex or E|| = 0 ) in x direction on the side of the neutral wire seen by K should remain the same zero (= Ex = Ex' = 0 or E|| = E||' = 0 ) even on the side of the positively-charged wire seen by K' ( this p.14, this p.14-5.15 ).
↑ The electric field in x direction (= Ex or E|| ) remains the same zero (= even near the positively-charged wire ) as seen by the stationary K and K' moving in x direction in the relativistic Lorentz transformation of electromagnetic field ( this-p.10 ).
↑ This is clearly contradiction (= because the electric field E should be changed from 0 in the neutral wire to positive in the positively-charged wire, contrary to the Einstein relativity ) showing Einstein relativistic theory is false.
↑ Actually, other electric fields Ey and Ez in y,z directions except x around the positively-charged wire are changed from zero (= neutral wire causing magnetic field By, Bz = non-zero, while the initial electric fields Ey, Ez are zero ) in K frame (= seen by K ) to positive (= E'y and E'z in K' frame become positive, changed from the original neutral magnetic field B in K frame, this p.14, this p.14-5.15 ) in K' frame , which is contradiction.
↑ Only the electric field in x direction (= E'x ) remains zero (= electric fields E'y and E'z in other directions become positive, paradoxically ) even around the positive wire seen by the moving K'.
This disproves Einstein relativity.
Some people claim that neutral current remains neutral as seen by any moving observers even in Einstein relativity ( this-p.5-2nd-paragraph ), which is just wrong ( this-p.1-abstract ), inconsistent with Lorentz length contraction and the official relativistic Lorentz transformation of electromagnetic field
To avoid this Einstein relativistic paradoxes such as Lorentz magnetic force, kinetic energy, de Broglie wave, twin paradox, we have to admit the real medium and reject Einstein relativity.
↑ Because if only the electrons moving relative to the medium cause Lorentz magnetic force (= or kinetic energy, de Broglie wave ) irrelevant to observers' motion, the fatal Lorentz magnetic and electric force paradoxes (= and kinetic energy, de Broglie wave paradoxes ) seen by different observers in Einstein relativity can be avoided.
Disproving Einstein relativity means disproving quantum mechanics.

Feel free to link to this site.