Home page
QED is wrong.
Dirac hydrogen atom
Particle physics is unreal
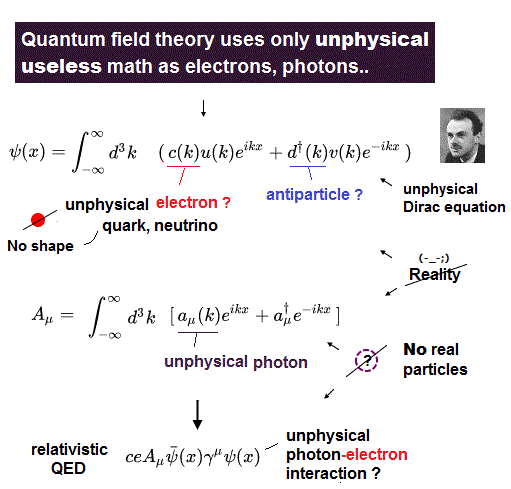
(Fig.1) Relativistic quantum field theory = Dirac equation is unreal.

Relativistic quantum field theory (= QFT ), quantum electrodynamics (= QED ) and today's useless particle physics, all of which are based on the unphysical Dirac equation ( this-p.9, this-p.10-2.4 ), were artificially created by combining the unphysical quantum mechanics and paradoxical Einstein special relativity ( this-p.3 ).
↑ The outcome of this unphysical current mainstream physics combining quantum mechanics and Einstein relativity is the unrealistic "extra-dimensional theory or everything" or string theory.
The point is these quantum field theory, QED, particle physics are useless, unphysical, unable to express electrons and light (= or fictional photons ) as real particles except as the unphysical math operators ( this-p.7-10, this-p.3- ).
Quantum field theory and QED consisting of Dirac equation and wrongly-modified Maxwell equation can only describe each electron, (illusory) antiparticle and photon as an unphysical abstract math symbols (= with No real particle shape ) and matrices without real particle shapes ( this-p.9-10, this-p.36, this-p.17 ).
This unphysical Dirac equation is today's particle physics mainstream equation used to express all electrons, (illusory) antiparticles, quarks, neutrino called fermions, all of which are just nonphysical math symbols with No real particle shapes ( this-p.3-14, this-p.1-8 ).
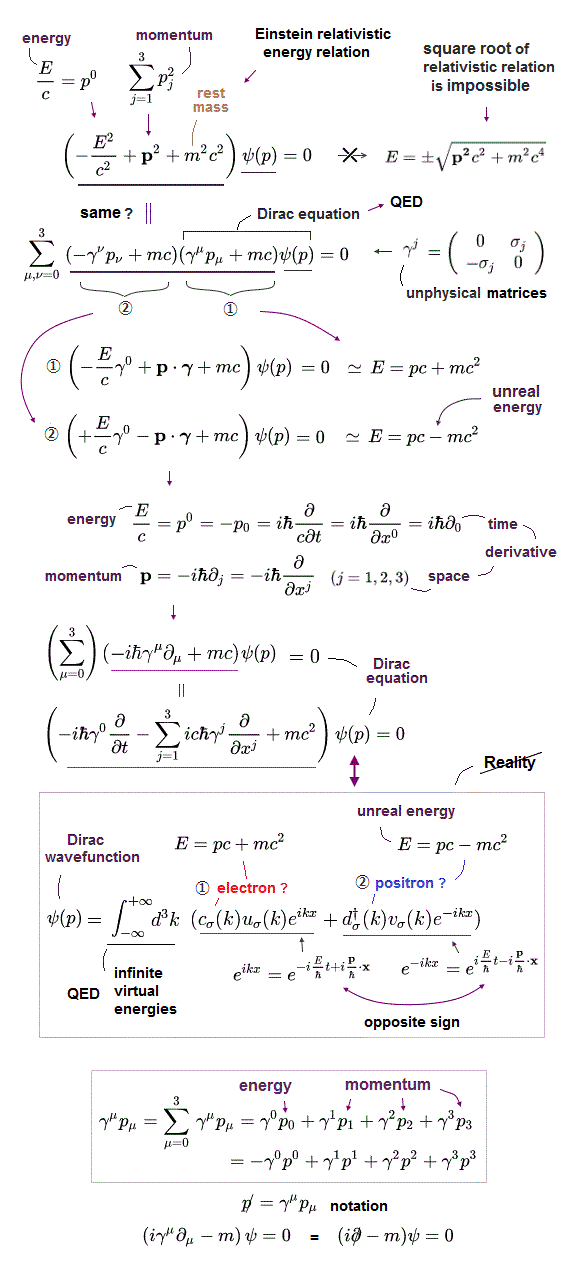
(Fig.2) Paradoxical Einstein relativistic energy (= E ), momentum (= p ), mass (= m ) equation is divided into relativistic Dirac equation consisting of unphysical 4 × 4 γ matrices.
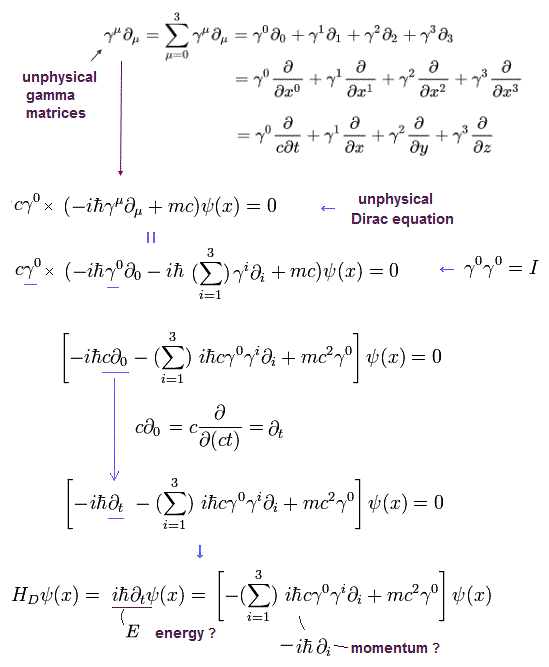
(Fig.3) Unphysical γ matrices ↓ wrongly treated as "(electron) spin" used in relativistic Dirac equation.
Einstein's paradoxical relativistic energy (= E = p0/c ), momentum (= p1 = px, p2 = py, p3 = pz ), mass relation is an inconvenient quadratic equation.
To combine this (paradoxical) Einstein energy equation with quantum mechanics, physicists need to express the relativistic energy E as the time derivative, and the momentum p as the space derivative operators related to de Broglie wave contradicting Relativity.
Klein-Gordon equation is the direct expression of this Einstein relativistic energy equation by using the quantum mechanical differential operators.
The current mainstream Dirac equation was obtained by dividing the quadratic relativistic energy (= Klein-Gordon ) equation into two linear equations by using the unphysical 4×4 gamma matrices ( this-p.22-26, this-p.29-30, this-p.2-5 ).
↑ These unphysical γ matrices including Pauli σ matrices which are related to kinetic energy (= as shown in γ or σ matrices attached to momentum p ) are wrongly treated as spin ( this-p.6-11, this-p.5-6 ) in Dirac equation, which abstract math lacking real particle picture is irrelevant to the real phenomena, though.
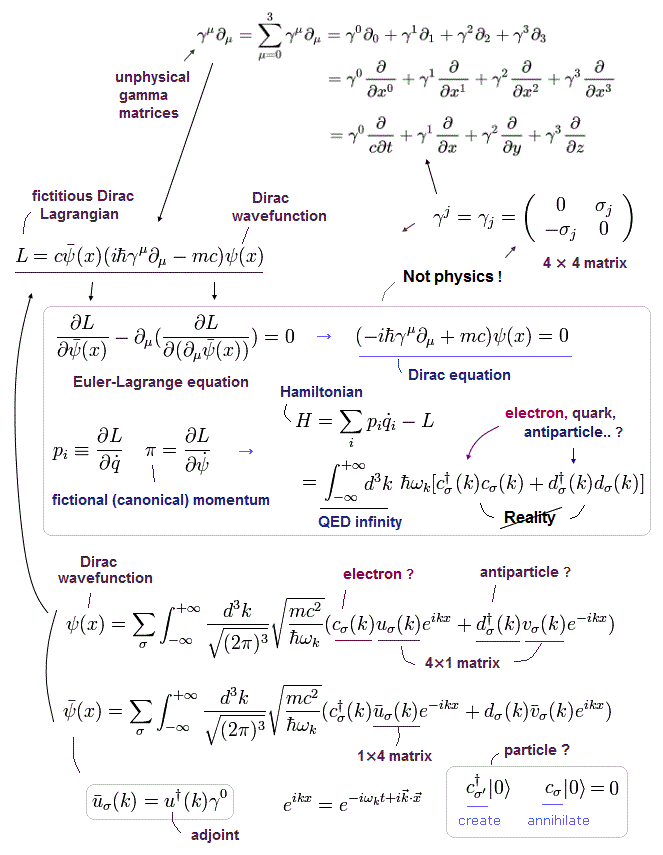
(Fig.4) Artificially-created Lagrangian (= L ) of Dirac equation.
Relativistic quantum field theory based on Dirac equation is obtained by dividing the simple Einstein energy-momentum equation into linear equations with the help of unphysical γ matrices.
This relativistic Dirac equation expresses particles such as electrons, antiparticles, quarks.. only as unphysical math symbols (= a†, b† c† d†.. ) with No shape ( this-p.19, this-p.24-p.30, this-p.14-p.15 ).
And these (anti-)particle math operators are attached to the unphysical 4 × 1 spinor matrix such as u and v treated as artificial spin wavefunction ( this-p.22-p.37, this-p.13 ).
↑ All these definitions of unreal particles in relativistic Dirac equation are artificial, irrelevant to the real world.
(Fig.5) Lagrangian (= L ), which was artificially created, irrelevant to quantum field theoretical prediction → Euler-Lagrange equation → unphysical Dirac equation ?
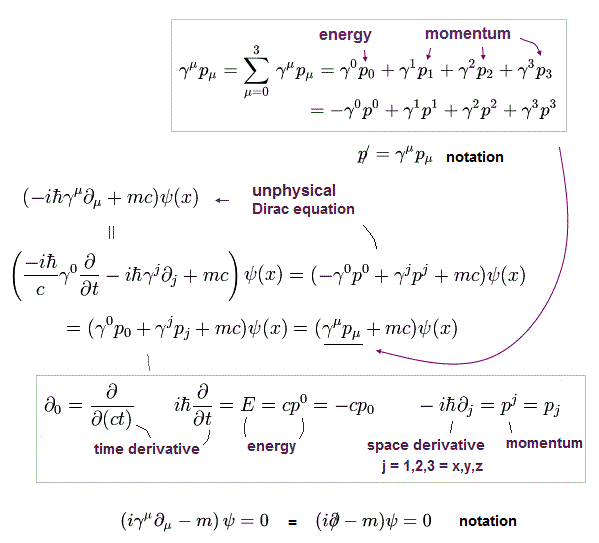
Quantum field theory tries to imitate classical mechanical (unphysical) Lagrangian (= L ) to artificially obtain relativistic Dirac equation and Hamiltonian through (modified) Euler-Lagrange equation.
Fig.5 shows the artificially-created Lagrangian (= L ) of the unphysical relativistic Dirac equation lacking real electron picture.
Relativistic quantum field theory, QED, particle physics rely on these artificially-created concepts called Lagrangian L (= "artificially-created" means No power to predict anything ) to justify their derivation of Hamiltonian (= H, total energy ) and (Dirac) energy-equation, though Lagrangian (= action ) itself has No physical meaning ( this-p.1-last ).
This website uses (-1. +1, +1, +1) relativistic metric notation.
Physicists claim substituting the artificially-created Dirac' Lagrangian equation (= L ) into (artificial) Euler-Lagrange equation ( this-p.12 ) leads to the unphysical Dirac equation.
↑ The point is all these (Lagrangian) equations were artificially created (= Not derived from quantum mechanical theory ), irrelevant to prediction of relativistic quantum field theory or quantum mechanics.
(Fig.6) Artificially-created Dirac Lagrangian (= L ) → Legendre transformation → Dirac's Hamiltonian (= total energy ), which is a useless equation.
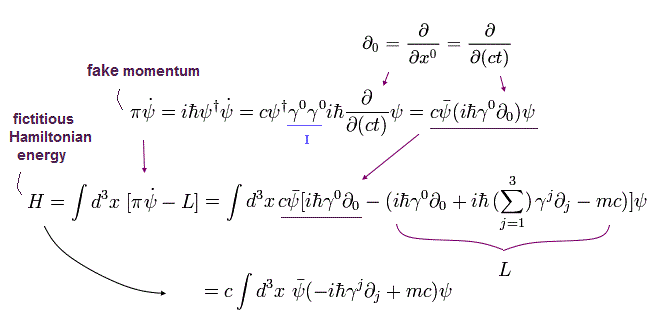
Quantum field theory tries to imitate classical mechanical Hamiltonian (= total energy ) obtained from the artificial Lagrangian through Legendre transformation ( this-p.9-p.10 ).
From the artificially-created Dirac's Lagrangian (= L ) irrelevant to relativistic quantum field theoretical prediction, they obtained Dirac equation's Hamiltonian H (= total energy ? ) via Legendre transformation using this, this (= adjoint Dirac spinor ) and γ matrix ( this-p.17, this-5.466 ).
(Fig.7) Artificially-created Dirac equation's Hamiltonian cannot describe Pauli principle, which is just unphysical math relation called anticommutation.
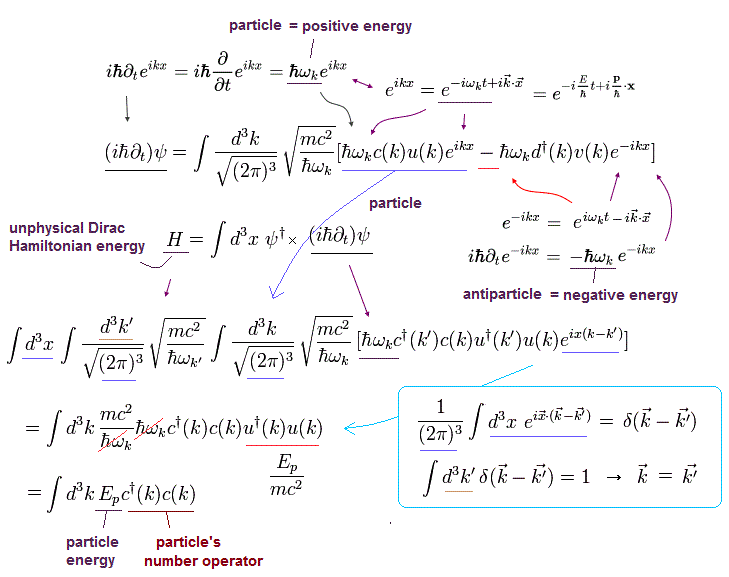
From the artificially-created Dirac equation's Hamiltonian (= total energy ) equation and unphysical math operators (= on this page, c, c† represent electrons, d, d† represent antiparticles ), Pauli principle is said to be obtained ( this-p.3-6, this-p.1-8 ).
As shown in Fig.7-lower, to obtain the antiparticle's energy E d†d (= instead of dd†, which meaningless order of unphysical particle operators is very important for Dirac equation ), the anticommutation relation (= d d† = -d†d ) is necessary ( this-lower, this-p.2-5 ).
Relativistic quantum field theory illogically claims this abstract meaningless anticommutation relation expresses Pauli principle, just because exchanging (anti)particles' unphysical math operators (= c, c†, d, d† ) changes the sign ( this-p.4 this-p.7, this-p.2-3 ).
↑ unphysical anticommutation = d d† = -d†d → if d = d† (= if two particles occupy the same space ? ), → d d = -d d → d = 0 (= Pauli principle ? this-p.56, this-p.2-upper, this-p.1-2 ) ← nonsense.
As I said, all these equation (= Hamiltonian, Lagrangian ) are just artificially-created, irrelevant to prediction of relativistic quantum field theory or QED based on Dirac equation which is just an unphysical math unable to explain the real world's phenomena.
(Fig.8) Photons of relativistic quantum electrodynamics (= QED ) are just unphysical math symbols lacking real particle picture.
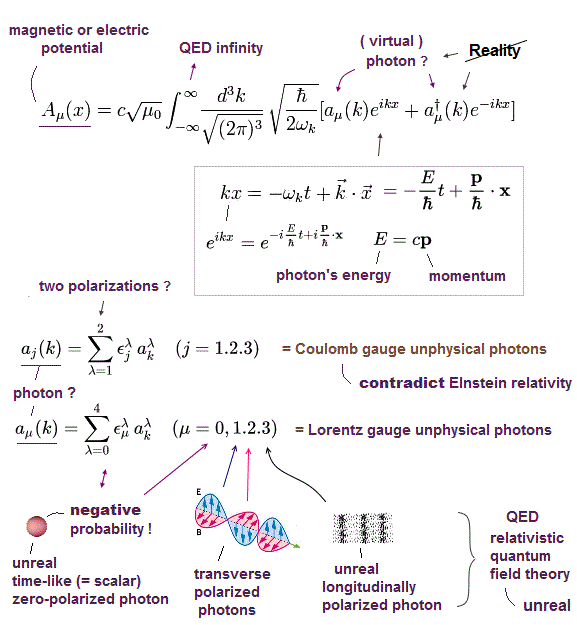
According to Maxwell equation incompatible with Einstein relativity, electric (= E ) and magnetic (= B ) fields can be expressed by electric or magnetic vector potential (= A this-p.1-2 ).
Relativistic quantum field theory or QED tries to express an illusory photon as the unphysical math symbol (= a, a† ) lacking real particle picture inside this electromagnetic vector potential A ( this-p.10-12, this-p.12 ).
Real light (or photon ) must be transversely polarized.
But the relativistic QED is unrealistic, needing unphysical virtual photons with non-existent longitudinal polarization ( this-p.3-2 ) and scalar photon ( this-p.5-left-lower ) with unreal negative probability or energy ( this-p.50(or p.49)-last-sentence, this or this-p.10-6.50, this-2nd-paragraph ).
This-p.28-last-paragraph says -- Unreal polarization
"virtual photons can be (unrealistically) longitudinally polarized."
This-p.16-2nd-paragraph says -- Unreal virtual photons
"When charges are present, the (unreal) longitudinal and scalar photons (= unreal negative probability ) provide the
Coulomb interaction between the charges and thus appear as virtual particles ( this-p.8 )"
Fictitious photons are obtained by quantization of electromagnetic field in Maxwell equation in relativistic quantum field theory or QED where photons are just nonphysical math operators lacking shape (= a†, this-p.1~p.12, this-p.6-10, this-p.9-10, this-p.9~ ).
In quantum field theory or QED, the time derivative (= ∂t ) expresses the relativistic energy E, and the space derivative (= ∂x ) expresses the relativistic momentum p by acting on exponential function of eikx ( this-p.2 ).
Photons are said to satisfy the massless relativistic energy (= E ) and momentum (= p ) relation (= mass m = 0 ), which corresponds to the massless relativistic Klein-Gordon equation ( this-p.9, this-p.9-upper, this-last ) incorporated into classical Maxwell equation.
(Fig.9) In static electromagnetic field, the time derivative of electromagnetic field (= vector potential A ) is zero, which means photons' energy and momentum in static electromagnetic field are zero, which paradoxically cannot move charged particles.
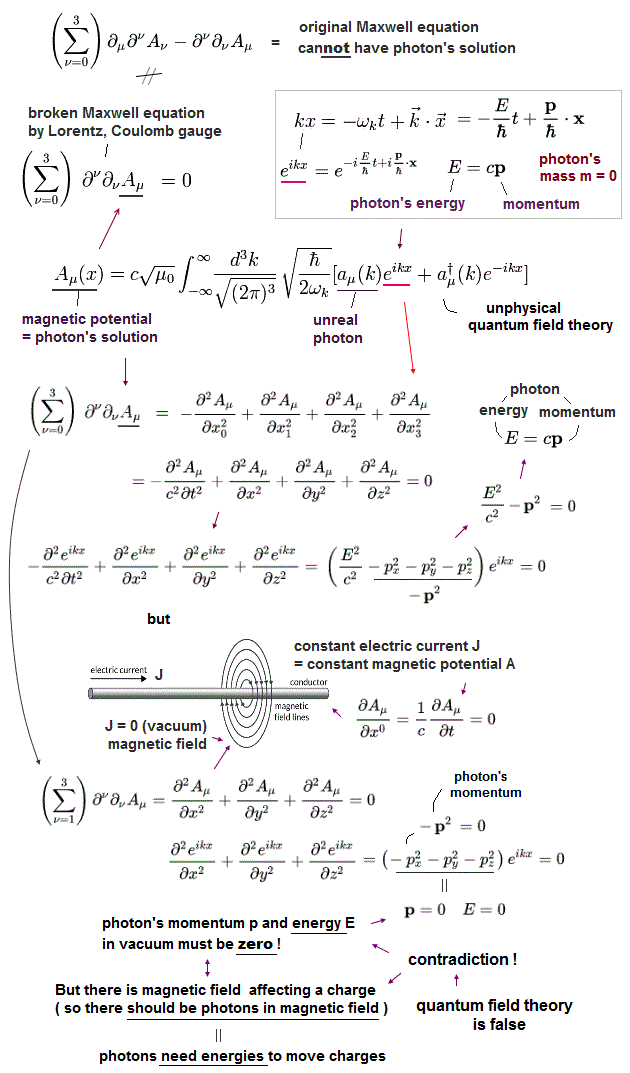
Actually, the relativistic quantum field theory or QED contradicts the real electromagnetic field expressed by Maxwell equation.
In the quantum field theory or QED, the time derivative (= ∂t ) of electric or magnetic potential (= A ) means the relativistic energy E (= photons correspond to massless Klein-Gordon equation, this-p.5, this-last ).
In the static electromagnetic field, this time derivative of electromagnetic field (= fictitious photon's energy ) or (magnetic) potential is zero, which means (virtual) photons' energy E (= ℏωk, this-p.11-(31)(32) ) and momentum p (= expressed as the space derivative ) included in the static electromagnetic field must be unrealistically zero.
↑ This unrealistic zero relativistic energy or momentum contradicts the fact that even static electromagnetic field exerts the force and moves the charged particles (= meaning the static electromagnetic energy and momentum, which have the power to move charged particles, are Not zero ).
(Fig.10) QED relies on unphysical photon (= A )-electron (= ψ ) interaction expressed by nonphysical math symbols
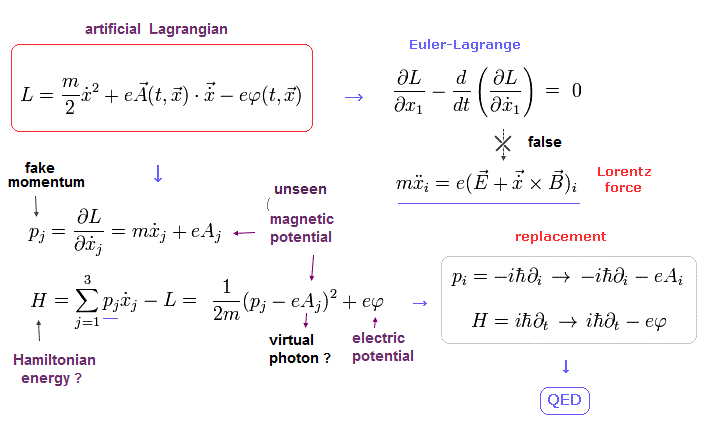
The unphysical relativistic quantum field theory or QED relies on the abstract electron-photon interaction relation consisting only of unphysical math symbols of illusory photons (= A ) and electrons expressed by Dirac equation ( this-p.4-5 ).
The point is this relativistic QED is based on wrong math to derive this (illusory) interaction relation between (virtual) photons (= vector potential A ) and electrons (= Dirac spinor ψ ).
↑ The unphysical QED interaction between a (fictitious) photon and electrons is expressed just by putting the meaningless math symbols of photon (= A ) and electrons (= ψ ) side by side, which abstract relation cannot clarify real detailed mechanisms.
QED's reliance on wrong math means all QED calculations such as anomalous magnetic moment and Lamb shift are also wrong and illegitimate.
(Fig.11) Artificial Lagrangian L consisting of electric potential (= φ ), magnetic potential (= A ) and charged particle's velocity (= v ), mass (= m )
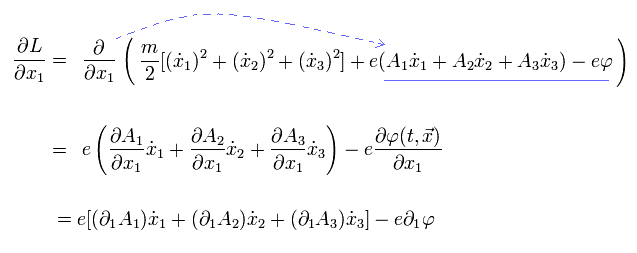
The upper Fig.11 is an artificially-created Lagrangian (= L ) for deriving the (unphysical) interaction between (virtual) photons (= magnetic potential A or electric potential φ ) and electrons (= charge e, velocity of v, mass m ) in QED
(Fig.12) QED wrong math trick wrongly mixing the static x in vector potential A (= ∂A/∂x ) with the irrelevant moving charge's velocity v = ∂x/∂t in dA/dt.
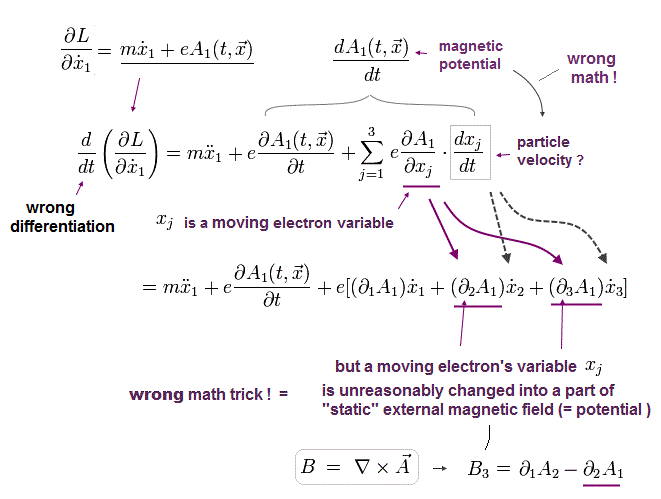
In substituting the artificially-created Lagrangian L into Euler-Lagrange equation, they deliberately use the wrong math trick disproving quantum field theory and QED.
In Fig.12-square, the time derivative of the magnetic potential (= dA/dt = this external magnetic potential A does Not contain particles ) is wrongly divided into the static space derivative of A (= ∂A/∂x = this x should Not be related to the moving particle's position x of ∂x/∂t = v. ← but they wrongly treat these two different x as the same x ) and the moving charged particle's velocity (= v = ∂x/∂t ), which causes the serious paradox, so false.
↑ The external magnetic field or magnetic potential A (= Not charged particles ) must paradoxically contain fictitious charged particles' speed v, which unreal wrong trick is needed in QED's photon-electron interaction.
See this-middle, this-p.3-lower, this-(6), this-p.3-(18)
(Fig.13) Artificial-created Lagrangian (= L ) can obtain electromagnetic force ?
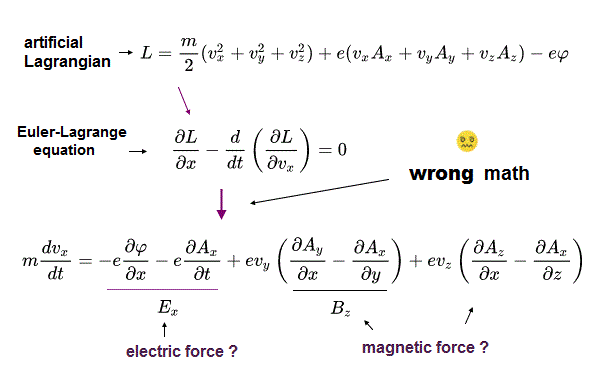
By inserting the artificially-created Lagrangian (= L ) into Euler-Lagrange equation, they (wrongly) claim the electric (= E) and Lorentz magnetic (= B ) force expressed as electric or magnetic vector potentials on the charged particle (= charge e, mass m, velocity v ) can be obtained by using wrong math trick.
(Fig.14) Artificially-created QED Lagrangian is wrong, unable to express the static electromagnetic field.
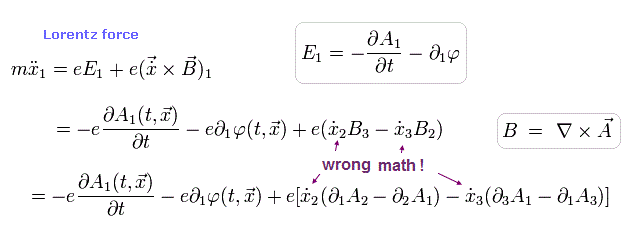
In case of the static magnetic field where the time derivative of the magnetic potential is zero (= dA/dt = 0 ), the artificially-created electromagnetic Lagrangian L cannot obtain the real (electro-)magnetic field (= B ) due to the wrong math trick.
As shown in Fig.14-lower, in the static magnetic field (= dA/dt = 0 ), the real magnetic field Bz consisting of two magnetic vector potentials of Ax and Ay cannot be obtained ( this-p.4 ).
(Fig.15) Relativistic quantum field theory or QED is wrong, relying on wrong math trick to derive its illusory photon-electron interaction.
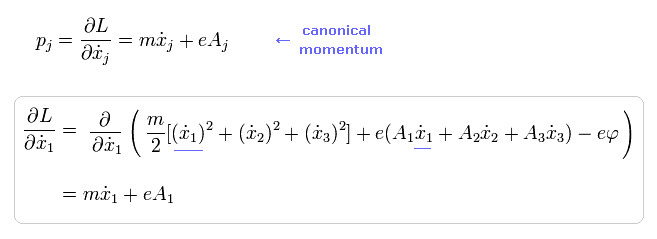
From the artificially-created electromagnetic Lagrangian L and Hamiltonian H replacing the momentum p → p-eA (= A is magnetic potential, momentum p is the space derivative, this-8.3.1.1 ) based on wrong math, physicists tried to obtain the illusory interaction between virtual photon (= A ) and Dirac's electron (= ψ ) in QED ( this-p.2.p.10-C, this-p.1-p.6, this-p.24, this-last, this-p.1-last ).
QED relying on this wrong math for deriving artificial electron-photon interaction relation means all (dubious) calculations of QED such as anomalous magnetic moment and Lamb shift are wrong, too.

Feel free to link to this site.