Home page
Einstein is wrong
Sagnac, Bell spaceship paradox
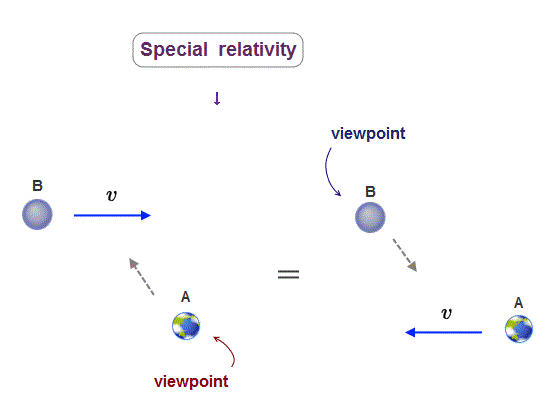
(Fig.1) Einstein's twin paradox; which clock A or B is moving and running slower is paradoxical and different as seen by different observers.

According to paradoxical Einstein relativity, there is No absolute frame (= or no ether nor medium ).
So which things are moving is uncertain and changed depending on which observers seeing them (= all motions are relative ).
↑ This Einstein relativity lacking the absolute frame (= medium ) violates conservation of energy and momentum, so Einstein relativity is wrong.
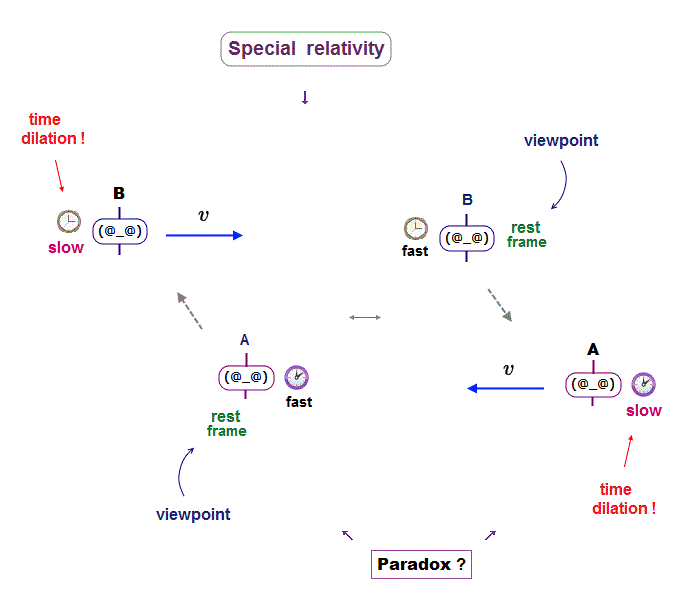
According to the unphysical Einstein special relativity (= paradoxical Lorentz transformation ), a moving clock is said to tick slower than a stationary clock. ← illusory pseudo-science
In Fig.1-upper, a clock-A is moving toward a clock-B at rest. ← The moving clock-A runs slower than the stationary clock-B according to special relativity.
But from the viewpoint of the clock-A , the clock-B appears to be moving toward the clock-A, hence, the clock-B must run slower than the clock-A (= Fig.1-middle ).
↑ This means which clock A or B runs slower is paradoxical and unknown (= called twin paradox ), which shows Einstein relativistic theory is false ( this-p.5-4.conclusion ).
On this page, we show this twin time paradox is a a real fatal paradox, and can Not be solved in either special relativity (= using No acceleration, so just avoiding solving true twin paradox ) or general relativity that needs unreal (Rindler) black hole horizon seen only by accelerating observers.
Contrary to hypes, the paradoxical Einstein relativistic theory is useless, Not applied to any phenomena such as GPS clock time (= relativistic time dilation is too small to measure reliably, this-p.2-3,p.6-conclusion ) and illusory muon's lifetime, as shown in Sagnac effect disproving relativity.
General relativistic time dilation is illusion in gravitational redshift that can be explained by ordinary classical Newtonian energy conservation law.
(Fig.2) Real twin paradox disproving Einstein relativity in clocks in a rotating loop. Which clock S or C is moving or ticking slower is paradoxical.
In the upper Fig.2, Clocks-S on a loop rotating at a velocity of v is ticking slower than the clock-C at rest according to special relativistic time dilation.
But as seen by the rotating clock-S, the clock-C at rest appears to be moving in the opposite direction, so the clock-C ticks slower than the clock-S.
↑ Which clock S or C is moving and running slower is paradoxical, which rotating twin paradox is real, unsolvable, disproving Einstein relativity ( this-p.40 or p.39 ).
All clocks S on a rotating loop are symmetrical, moving and running at the same speed, which means there is No clock time difference in different positions along the loop.
And the rotating clock-S can return to the original stationary clock-C position to compare their paradoxical times (= only one set of clock-S anc clock-C is needed with No problem of clock synchronization and No need to measure clocks' time in two different positions ).
↑ The clock-S (or clock-C ) sees the other clock-C (or clock-S ) moving and running slower, so which clock S or C is moving and ticking slower is paradoxical, disproving Einstein relativity.
General relativity tries to solve this special relativistic time dilation (= a moving clock ticks slower ) by fake gravitational time dilation (= caused by unreal Rindler black hole ) of clocks in different positions ticking differently based on fake gravitational potential experienced by accelerating observers.
But in the above rotating twin paradox, all clocks along the loop are symmetrical and ticking at the same speed, which means when the clock-S (or clock-C ) ticks slower as seen by clock-C (or clock-S ) at one point, which same relation continues all along the loop, until they return to see each other again and see their paradoxical times.
↑ This rotating twin paradox is real, unsolvable, disproving Einstein relativity.
Special relativistic time dilation is based on Lorentz transformation derived by Michelson-Morley experiment conducted on the earth rotating around Sun.
So clocks in the above rotating loop corresponds only to special relativity, and general relativity based on (fake) gravitational or acceleration time dilation is irrelevant.
As a result, the above rotating twin paradox is real, cannot be solved by general relativity.
Which clock S or C is rotating or running slower is paradoxical, disproving Einstein relativity.
↑ The above rotational (= circular ) twin paradox is real, unsolvable.
Because there is No problem of synchronization nor simultaneity in the above rotational twin paradox where we can use only one clock-S (or clock-C ) to measure two separate times (= clock-S seeing clock-C can return to the original clock-C's position to measure their paradoxical times arbitrary times ).
↑ To (wrongly) solve this rotating twin paradox, each clock-S must have two different (fantasy) parallel-universe times (= each clock-S needs to have two differently-running times in two different parallel universes to try to solve this unsolvable rotational twin paradox ).
For example, this paper on the wrong solution p.3-left-3rd-last-paragraph says
"Lisa at angle 0 and Selma at
angle 2π are at the same place. But their clocks will not
agree."
↑ An clock in the same place (= angle of 0 and 2π ) in a rotating loop must unrealistically have two differently-passing times using two fantasy parallel universes to solve the above (unsolvable) circular twin paradox.
For example, as seen by the stationary clock-C, the clock-S-one (= Lisa ) in a rotating loop ticks slower, but as seen by the rotating clock-S-two (= Selma, Not clock-S-One in the same S position ), the clock-C ticks slower (= A clock-S has two parallel-world times of the "slower clock-S-one" and the "faster clock-S-two" unrealistically ).
↑ This wrong solution relying on two different clock times in one place with one same motion contradicts the original Relativity (= a clock-S in one place in a loop should tick at one particular speed based on Relativity, Not two different speeds, which can be confirmed by observers inside and outside the loop. )
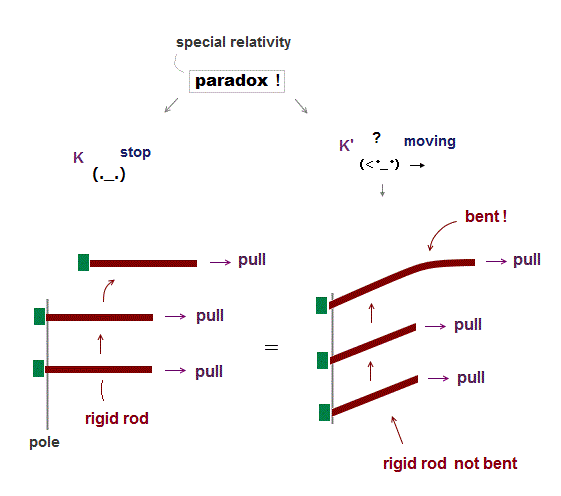
(Fig.3) Special relativity cannot solve twin paradox. General relativity also cannot solve twin paradox, because an accelerating observer must see unreal Rindler black hole and violate energy conservation.
As shown in Fig.2, when a clock-A is rotating and returning to the original place of the stationary clock-B, which clock A or B is moving and ticking slower is paradoxical.
↑ This rotational twin paradox is real, unsolvable, disproving Einstein relativity.
So textbooks tend to show only (wrongly-)solvable twin paradox where a clock-B departs from the stationary clock-A, accelerating and moving in a linear motion to return to the original clock-A position (= Fig.3-upper-right ).
↑ This linear twin paradox can be (wrongly) solved by using general relativistic (fake) gravitational (= acceleration ) time dilation and unreal Rindler black hole.
As shown in the upper Fig.3, a twin-A remains on the earth from which a twin-B departs, moves in the spacecraft in a linear path, and returns to the earth.
Seen by the unmoving twin-A's clock on the earth, the moving twin-B's clock runs slower.
But as seen by the twin-B, the twin-A on the earth appears to be moving, so the twin-A's clock must run slower.
↑ Which twin-A's or twin-B's clock runs slower is paradoxical, which is called twin paradox.
The twin-B in the spacecraft must be accelerating and decelerating to return to the earth in a linear path, so the frame seen by the twin-B is the "accelerating frame" that needs general relativistic pseudo-gravitational time dilation that is said to resolve this twin paradox ( this-2nd-last-paragraph, this p.3, p,4-(8) ) with the help of unreal Rindler black hole.
Einstein relativity unrealistically says only an accelerating twin sees fake-gravitational field caused by artificial black hole called Rindler horizon ( this-p.4-3rd-paragraph ), which causes new irreparable black hole paradox and violates energy conservation law (= as seen by twin-B, smaller energy to launch a rocket can move the earth and whole universe needing far larger energy, which violates total energy conservation ).
As a result, twin paradox is a real, unsolvable paradox ( this-p.1-abstract ) disproving Einstein relativity, contrary to an incredible amount of misleading hyped explanations including youtube ( this-p.3-left-2nd-paragraph ).
To solve the true twin paradox, we must consider the viewpoint of the accelerating twin-B in spacecraft, which needs general relativity.
But this general relativistic solution needs the unreal black hole called Rindler horizon that causes new irreparable ( time-stopping ) paradox, so can Not solve twin paradox.
So physicists started to ( wrongly ) say the special relativity without acceleration (= called inertial frame ) can resolve the twin paradox.
In these false special relativistic solutions, they use the 3rd-person moving at the constant speed instead of the accelerating twin-B, which is Not the original twin paradox ( this wrong solution-11~12th-paragraphs use the 3rd-person Albert moving at a constant speed instead of the accelerating twin Sam ).
This typical wrong special relativistic solution used the stationary twin-A's viewpoint (p.6 = Earth's RF ) and the 3rd-person's moving at the constant, non-accelerating speed (p.7 = this RF instead of accelerating Space twin ) who sees the twin-B (= Space twin ) return to the earth at a speed higher than twin-A (= Earth twin ), so the twin-B spacecraft's clock always moving faster ticks slower.
As a result, the special relativity without acceleration also can Not solve twin paradox, and Einstein relativity is proven wrong.
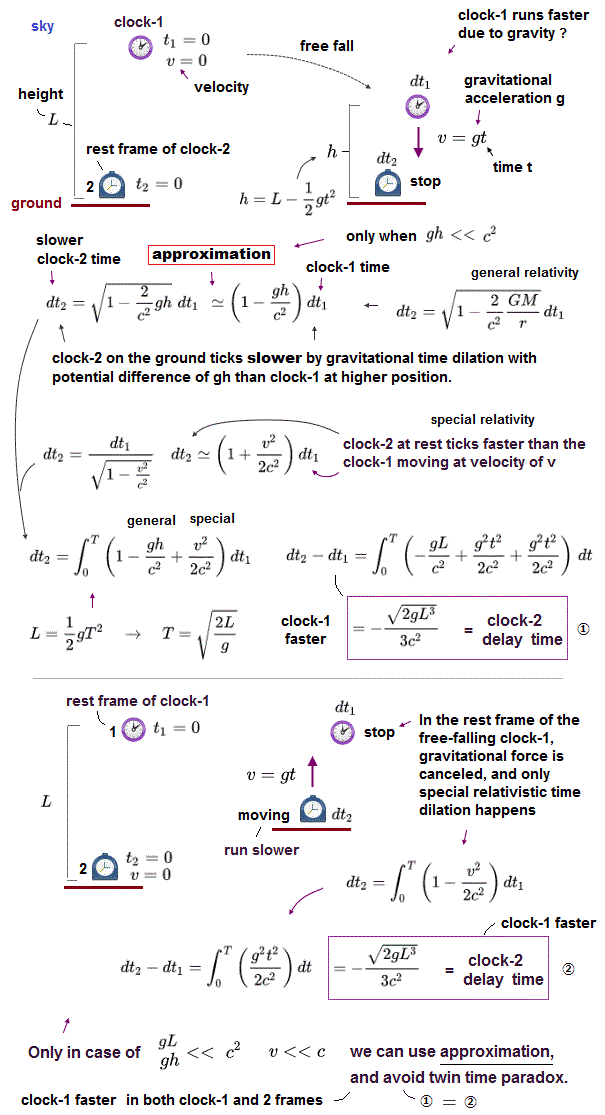
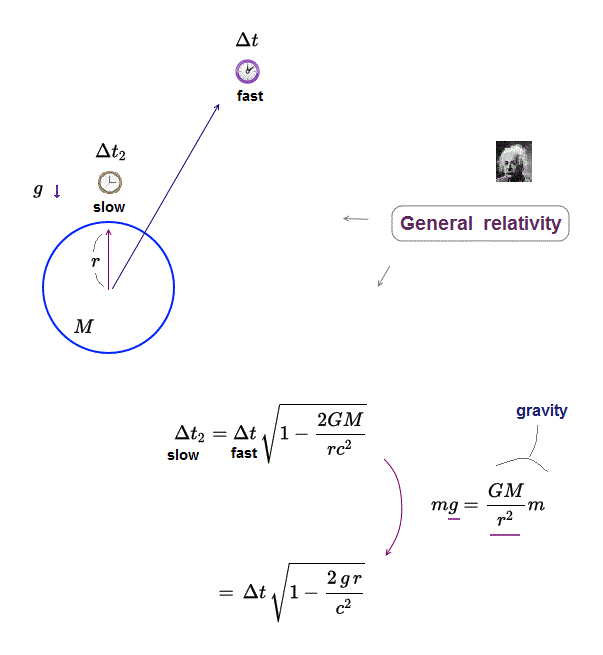
(Fig.4) Clock-A on the ground runs slower than clock-B at a height of L under gravitational acceleration g according to general relativity.
According to general relativity, clock-A on the ground (= closer to a massive star or earth ) ticks slower than clock-B at a height of L under gravity of acceleration g.
This gravitational time dilation is related to the gravitational potential (= φ = -GM/r, this p.3,p.5 ) equal to acceleration g × the distance (= height ) L = -gL (= Δφ, this p.3, this 2nd-last-paragraph ).
↑ Clocks in stronger gravitational fields (= lower gravitational potentials ) tick slower, according to the paradoxical Einstein general relativity.
The problem is that this general relativistic gravitational (= acceleration ) time dilation is also paradoxical (= so wrong ), causing unreal imaginary (or negative ) time (= going backward to the past ? ) like inside an unphysical black hole, when the distance L between these two clocks is very long.
Gravitational redshift can be naturally explained by the ordinary classical Newtonian energy conservation law, Not by the paradoxical gravitational time dilation ( this-p.1-right-2nd-paragraph ).
As a result, twin paradox caused by a moving clock ticking slower in special relativity is a real fatal paradox that can Not be fixed by the (paradoxical) general relativity (= gravitational or acceleration time dilation )
(Fig.5) As seen by an accelerating clock-A, fake gravitational time dilation happens ?
In the upper Fig.5, clock-A is accelerating (= by some force except for gravity ) at g toward a stationary clock-B under No gravity.
According to Einstein general relativity or equivalence principle, as seen by the accelerating clock-A, all things appear to be accelerating at fake gravity (= acceleration of g ) in the opposite direction, which causes (fake) gravitational (= accelerating ) time dilation related to this fake gravitational potential = gL (= L is distance between clocks A and B, this-(1)~lower, this p.5-upper, this-2nd-last-paragraph, this p.3-lower~p.4, this-p.9 ).
This-p.2-right-3~p.3-left says
"The accelerated worldline suffers an
increasing rate of time dilation, somewhat like gravitational
time dilation where increasing height in the gravitational potential results in increasing time dilation"
"an accelerated frame of reference undergoes time dilation similar to gravitational time dilation"
This-p.6-2nd-paragraph says
"That is, clocks at larger z' in the accelerated frame run faster than clocks at smaller z',
relative to clocks in the inertial lab frame"
The 1st, 2nd, 11~12th paragraphs of this site say
"we can treat a uniformly accelerated frame as if it were an inertial frame with the addition of a uniform pseudo gravitational field"
"The one thing we need here is that time runs slower as you descend into the potential well of a pseudo force field."
"No mystery: uniform pseudo-gravitational time dilation depends on the "gravitational" potential difference"
↑ This fake gravitational force seen by accelerating observers due to Einstein equivalence principle is false, violating energy conservation law (= as seen by observers accelerated by small energy, all things around the world unrealistically appear to be accelerated with far larger energy ).
(Fig.6) ↓ The same man-A says paradoxical things as seen by different observers.

According to the paradoxical Einstein relativity, an accelerating observer sees all things around him appear to be accelerating in the opposite direction by fake gravity caused by artificial (Rindler) black holes (= or horizon, this-2nd-paragraph ) .
↑ This causes fatal paradox (= so twin paradox is real ) disproving Einstein relativity.
In the upper Fig.6, a clock-A is accelerating (= by some force except gravity ) toward a stationary clock-B under No gravity.
↑ As seen by this stationary clock-B, a man-A says (= or take a note of ) "There is No massive star nor a black hole here (= at any times including the past )"
But as seen by the accelerating clock-A, the clock-B and all other things appear to be accelerating in the opposite direction by fake gravity caused by an artificial Rindler black hole or horizon.
↑ So as seen by the accelerating clock-A, the same man-A says (= or takes a note of ) "I can touch a massive star or a black hole (= accelerating all things around the clock-A needs massive stars or very heavy black holes for total momentum conservation )".
↑ Inside this artificial black hole, the clock time unrealistically goes back to the past (= due to unreal negative time ) when the black hole should Not exist (= there is No black hole before the clock-A starts to accelerate ), so this artificial massive black hole or star (= needed to generate artificial gravity to accelerate all things ) seen or felt by the accelerating clock-A is paradox.
↑ The same man-A (= existing in the place inside the artificial black hole = L > c2/g all the time since the past ) says (or takes a note of ) the different paradoxical things (= the same man-A says he can touch massive star = black hole or not ) as seen by different observers, which is clearly relativistic paradox disproving Einstein.
This fake gravity caused by fake black hole seen by accelerating observers or clocks necessary to solve twin paradox is wrong, violating energy conservation law.
↑ Small energy or fuel to move a small rocket can unrealistically rotate the whole bigger earth (= needing far larger kinetic energy ) as seen by twin-B, which does Not conserve energy (= which means there is only one absolute frame conserving the total energy, which fact disproves Relativity lacking the absolute frame ).
So twin paradox is unsolvable, Einstein relativity is proven wrong.
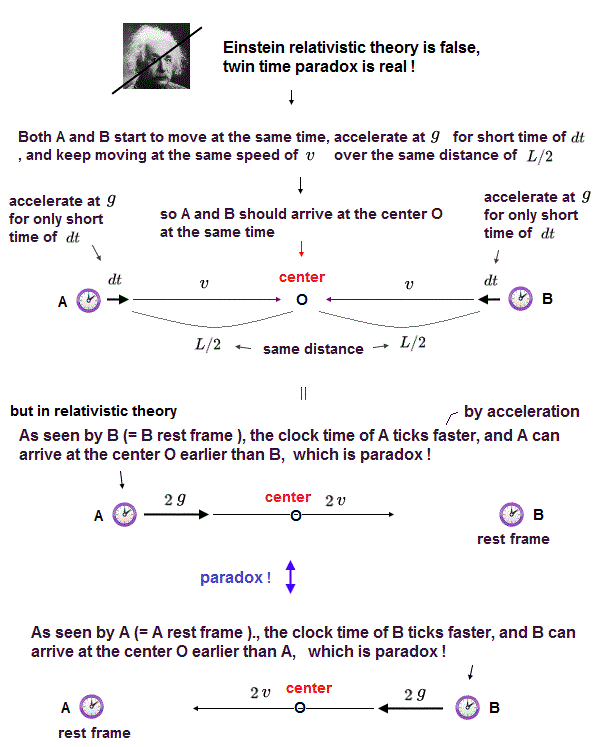
(Fig.7) Clock-A starts to accelerate at g (= by force except for gravity ) at the distance L from clock-B. ← This clock-A moving at a speed of v (= gt g is acceleration, t is time ) ticks slower ?
In the upper figure, a clock-A at rest starts to move or accelerate at a acceleration of g at distance L from a clock-B (= this force causing acceleration g is applied only to clock-A in this case, so No gravitational field nor no gravitational time dilation in this frame ), while the clock-B keeps stopping.
The velocity v of this clock-A at a time t is v = gt, which gives the total special relativistic time dilation of the moving clock-A by integrating it with time from t = 0 to t = T where T is the time when the clock-A reaches the clock-B (= figure.7-lower ).
↑ In this case, the
(Fig.8) From the viewpoint of the (accelerating) clock-A, clock-B appears to be accelerating toward the clock-A at fictitious gravitational acceleration of g, which causes pseudo-gravitational time dilation canceling twin paradox ?
When the clock-A starts to move and accelerate (= acceleration of g ) at distance of L from clock-B toward the clock-B at rest, from the viewpoint of the clock-A, the clock-B appears to be accelerating toward the clock-A by the fictitious gravitational acceleration of g.
↑ From the viewpoint of the accelerating clock-A, all things including the clock-B appear to be accelerating at g in the opposite direction, which corresponds to the fake gravitational field influencing all things according to (unphysical) Einstein general relativistic equivalence principle.
First, as seen by the clock-A, the clock-B appearing to be moving (= accelerating ) at velocity v = gt (= t is time ) runs slower according to special relativistic time dilation (= upper figure ① ).
Second, as seen by the (accelerating) clock-A, all things appear to be accelerating at fake gravity (= acceleration of g ), which causes (fake) gravitational (= accelerating ) time dilation related to this fake gravitational potential = gL or gh (= L or h is distance between clocks A and B, this-(1)~lower ) as shown in the upper figure ②.
↑ In this fake gravity (= acceleration from clock-B to clock-A ) seen by the accelerating clock-A, the clock-A at the lower fake gravitational potential runs slower by the amount of the fake gravitational potential (= - gh/c2 ) according to general relativity.
By combining these special (= moving clock-B runs slower in this ① ) and general relativistic time dilation (= by fictitious gravity in this ② ), the clock-A runs slower after all, like the clock-A moving frame (= compare the total time dilation of clock-A of the last of Fig.7 and Fig.8 which are the same. ← No twin time paradox ? ).
↑ There appears to be no (twin) paradox, because both in clock-A's moving and stationary frames, the clock-A always runs slower by the same amount of time.
But this fake gravitational time dilation where clocks tick differently in different positions only when seen by the accelerating clock-A causes new irreparable paradox such as black hole and violation energy conservation law.
So twin paradox is real, unsolvable. which disproves Einstein relativity.
(Fig.9) Twin paradox in linear motion needs unreal black hole's fake gravitational time dilation, while rotational twin paradox cannot be solved by fake gravity. ← Einstein relativity is proven wrong.
In twin paradox where one clock or twin is moving and accelerating in a linear path, only the accelerating clock or twin sees unreal (Rindler) black hole's fake gravitational time dilation to cancel special relativistic time dilation (= moving clock ticks slower )
In the rotational twin paradox, one clock is rotating along one loop at the same speed with No acceleration, and returning to the original place to compare their paradoxical times with the other stationary clock.
↑ All clocks along the loop are symmetrical, ticking at the same pace, so No fake gravitational time dilation is involved to solve this rotational twin paradox.
Actually, this rotational twin paradox is equal to Michelson-Morley experiment conducted on the earth rotating around Sun with only special relativity.
So this rotational twin paradox is real, unsolvable, disproving Einstein relativity.

Feel free to link to this site.