Top page
Quantum network is useless
Quantum supremacy or advantage is fake.
Quantum teleportation is meaningless.
Quantum entanglement is illusion.
(Fig.1) The largest numbers factored so far by (still-useless) quantum computers is only 21 = 3 × 7 using fake (slower) Shor algorithm based on a single-world calculation

The current encryption system and keys such as RSA are based on two prime numbers or semi-primes, which are said to be cracked by (still-unrealized) quantum computers which may implement multiple simultaneous calculations of Shor's algorithm at once using (fictional) superposition = a dead-and-alive cat states or parallel worlds ( this p.4 ).
The point is all the current quantum computers are unable to correct errors, so they can Not calculate any meaningful values nor give right answers. ← Useful factoring by quantum computers or executing Shor algorithm is impossible (forever). ← There is No evidence of quantum superposition or parallel worlds causing quantum advantage.
So far, the largest numbers factored by the (still-useless) quantum computers are only 21 = 3 × 7 and 15 = 3 × 5 ( this-1st-paragraph, this 3rd-paragraph, this 4~5th-paragraphs ) using the fake modified version of Shor's algorithm (= called "semi-classical or Kitaev's (fake) Shor's algorithm" this 9, this 2-3rd paragraphs, this p.6 ).
↑ This fake Shor algorithm can carry out only one task at once using only one single world (= implement one task, reset, and recycle each quantum bit or qubit, this 14th-paragraph, this p.2 6th-paragraph,Fig.1.B-D this Figure.3,4,6,7 ) instead of implementing the dreamlike simultaneous quantum calculations which are required for faster factoring in true Shor's algorithm.
The most recent research is also about fake Shor's algorithm called compiled Shor's algorithm just only 5 error-prone qubits for factoring 21 (= real Shor algorithm for factoring 21 needs 26 errorless qubits, which are impossible to realize ), showing No advantage over the above other fake Shor algorithm of qubit recycling (= this-p.3-compiled Shor's algorithm, p.10-concluding remarks ).
This overhyped news-lower-summary says -- Fake slower Shor
"Researchers successfully demonstrated a quantum attack.. by breaking a 5-bit key (= just 5-bit key is useless ) using a modified (= Not real ) Shor's algorithm on IBM's 133-qubit quantum processor (= using only 15 qubits, this-p.3 )... Classical post-processing of the quantum results correctly identified the secret key."
↑ A classical computer is needed, because today's quantum computers alone are useless, unable to calculate anything.
Methods other than the Shor's algorithm are optimization or quantum annealing (= minimization finding the lowest energy state ) which is useless, just publicity stunt (= already-known answers encoded in the lowest-energy state ), too error-prone to give right answers.
So the so-called post-quantum cryptography anticipating such an illusory quantum computers' threat or speed-up is completely meaningless ( this 4th-last~ 2nd-last paragraph, this 4~5th-paragraphs ).
Actually such dubious post-quantum encryption keys were easily cracked even by ordinary laptops or classical computers. ← The post-quantum encryption is useless, meaningless and just a waste of time.
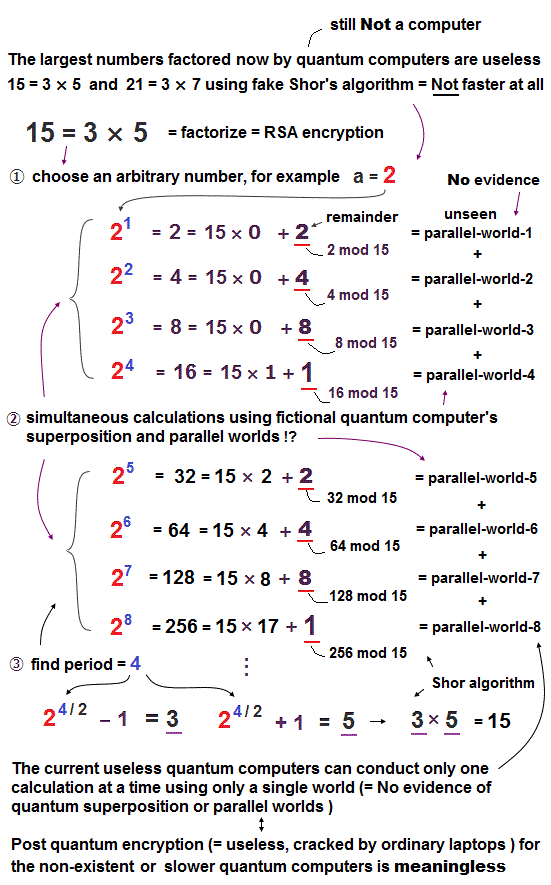
As shown in the upper figure, when we try to factor 15 = 3 × 5 using Shor's algorithm, we first choose an arbitrary number (= for example, choosing "2" here ).
And then, we conduct multiple calculations like 21 divided by 15 gives the remainder of 2 (= 21 mod 15 = 2 ), 22 divided by 15 gives the remainder of 4, 23 divided by 15 gives the remainder of 8, 24 divided by 15 gives the remainder of 1,.. and find the period number (= 4, in this case ) which means the number of terms periodically giving and repeating the same remainders ( this p.7-12, this p.96 ).
↑ These simultaneous calculations giving multiple different remainders in Shor's algorithm need to be done by using (still-unrealized) quantum computer's fictional superposition ( this Step.6, this p.9, this p.2-last-paragraph ) or parallel worlds ( this last-paragraph, this 19-20th paragraphs, this last-paragraph ) in order to factor large numbers faster and break the current encryption key system ( this 10th-paragraph ).
↑ In order to unrealistically carry out these multiple different simultaneous calculations for factoring large numbers using Shor algorithm on the same common quantum bits or qubits, not only qubits but also the external devices emitting microwave pulses for manipulating qubits have to be unrealistically split into multiple different parallel worlds ( = one microwave pulse must split into multiple microwave pulses existing in different parallel worlds to simultaneously calculate different parallel-world numbers by manipulating qubits existing in different parallel worlds ), which is impossible also in the original quantum mechanical rule.
Using the period "4" allegedly found by performing multiple (parallel-world) calculations, we can obtain two prime numbers (= 24/2 - 1 = 3, and 24/2 + 1 = 5 ) composing 15 = 3 × 5 ( this p.13-14 ).
↑ Contrary to the media-hype baselessly saying like "Quantum computers will be exponentially faster", the current useless quantum computers can Not carry out these simultaneous quantum mechanical calculations (= giving multiple different remainders using different parallel worlds simultaneously by Shor algorithm is impossible in the current useless quantum computers ), instead, they can only do one single simple task using fake slower Shor's algorithm needing the help of traditional classical computer or algorithm ( this p.3-first-paragraph,p.23-2(b) ).
It means thinking about the post-quantum encryption prepared for the fictional quantum computers' power of simultaneous calculations using imaginary parallel worlds is nonsense, and just a waste of time and money.
(Fig.2) Using fragile photons or very weak classical lights as quantum information, which is easily destroyed by eavesdropper, is impractical
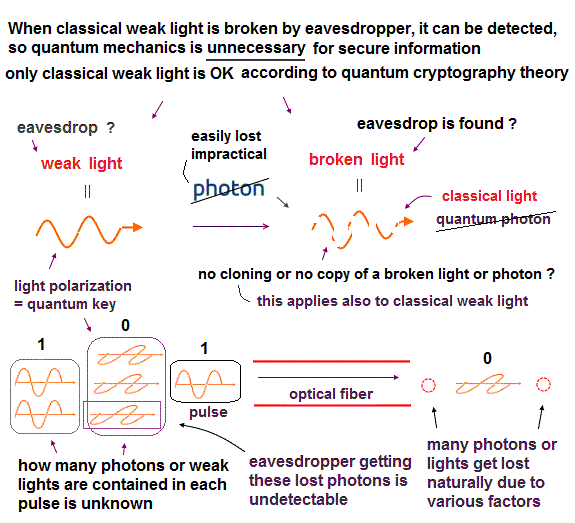
Quantum network, information, cryptography and key distribution (= QKD ) use a very fragile photon or very weak light wave as a carrier of quantum information (= ex. vertically-polarized light = 0, horizontally-polarized light = 1 ), which is completely useless ( this p.2-left-last-paragraph, this or this-lower-challenges ), less secure ( this-last-paragraph ).
↑ Because fragile photons or weak light is easily lost and cannot be amplified ( this p.1-left-1st-paragraph ) nor sent over long distance ( this p.4 ).
And a fictional photon is just a weak classical light wave ( this p.2-4th-paragraph, this p.6-lower ) whose intensity surpasses the detection threshold of the photodetector.
This p.1-left-introduction says -- fragile information
"Despite recent experimental demonstrations of
entanglement distribution in quantum networks with fiber,
and free-space communications, the fragility
of quantum information in the face of noise remains as the
major barrier to the physical realization of scalable, useful
quantum networks."
This-middle-Poor results (4/16/2025) say
"Designing the network architecture of a quantum network is challenging. The no-cloning theorem might be a reliable safeguard against copies, but it also eliminates the possibility of signal duplication and amplification. The overall effect is that quantum networks are prone to information loss and limited ranges of only a few miles."
This recent overhyped quantum internet (3/12/2025) is just about (impractical) software.
↑ This-research paper's p.9-right-NV QDevice implementation says "The two-node network used in this work ... separated by 3 m " ← Just 3 meter
separation between two unstable NV-center atoms is far from practical quantum network.
In 2016, researchers managed to send only one quantum information (= one weak light or one photon ) per hour over 404 km ( this-p.6-3rd-paragraph says only 3.2 × 10-4 bps = only 0.00032 photon bits per second = only one photon information per hour was sent, which is too slow and impractical ).
Quantum communication using existing infrastructure (4/23/2025) is also hype, useless, where quantum information was sent over only 254 km, which is shorter (= worse ) than 2016, so quantum network technology is No progress, rather regressing.
Quantum cryptography research was started in 1970s ( this-p.2 ), so even after more than 50 years of fruitless researches, quantum cryptography is still useless, deadend.
Quantum repeater, satellites are also impractical forever.
This-challenges in quantum cryptography- 3rd~4th-paragraphs (2024) say
"photons can be affected by temperature changes or electromagnetic fields. This can cause errors in quantum communication, making information less secure."
"Quantum systems face challenges like photon loss and decoherence, making long-distance communication tough. Thus, sending secure keys becomes harder with distance. Researchers are trying to solve this by using (useless) quantum repeaters and satellites. However, physics laws still restrict the maximum distances practically achievable"
Even the recent research in 2024 sent such fragile quantum information or photons over only 25km with No progress.
This recent overhyped quantum teleportation research over just 30km ( this 11th-paragraph ) is useless, because quantum teleportation and entanglement need ordinary classical communication to send real information (← they just measured only less than 80 counts in 4-photon coincidence detection for 900s over 30km, which is too few and too slow to be practical, due to massive photon loss, this p.7-Fig.3 ).
(Fig.C) Classical weak light is easily disturbed by eavesdroppers. ← The eavesdroppers can be detected ? ← No quantum mechanics nor a photon is needed in the secure (impractical) quantum key distribution.
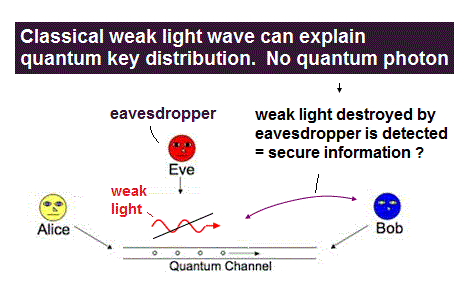
In the mechanism of 'secure' quantum key distribution or cryptography, when an eavesdropper tries to steal this fragile photon's information, the photon or weak light is easily destroyed or changed by the eavesdropper, which destroyed photon or light can be detected as a sign of eavesdropper ( this 2nd-paragraph, this 1st-paragraph, this 4th-paragraph ).
The 2-3rd paragraphs and lower challenges of QKD on this site say
"In a Quantum Key Distribution system, the transmitter, usually called Alice, encodes the key into.. photon (= weak classical light ) polarization or phase...'0' or '1'. Alice then sends the quantum states (= of fragile photons ) through an optical fiber or free-space transmission channel to the receiver, usually called Bob."
"This disturbance means that an eavesdropper, usually called Eve, cannot gain any information about the key without introducing errors that Alice and Bob will detect" ← Classical weak light can explain this quantum key mechanism (= classical weak light disturbed by eavesdropper also causes detectable errors ). Quantum mechanics is unnecessary.
"Current QKD systems have limitations to operate reliably beyond a few hundred kilometers due to channel loss and noise over long distances." ← Quantum network using fragile photons only to detect eavesdroppers (= meaningless security ) becomes impractical, cannot be used over long distance after all.
(Fig.2') Secrete key rate = probability of sending quantum information or photon to destination drastically decreases with distance (= sending photons over 100 ~ 200km is almost impossible due to massive photon loss ).

This fake secure quantum cryptography is useless, because if some eavesdroppers or other noises constantly intercept or influence this fragile quantum information or weak photons (= weak light ), the photons or weak lights are easily and constantly destroyed, and sending quantum information itself is impossible.
This quantum key distribution (= QKD ) sending very fragile photons or weak light is impractical, unable to send information stably over long distance ( this p.1-last-paragraph, this 1 distance limitation ).
This 4~5th-paragraphs says -- useless QKD
"quantum theory.. ensures that any attempt at eavesdropping on the channel results in a modification of the qubits (= destruction of fragile photons or weak light by eavesdroppers ), which will be detected by Alice and Bob. Therefore, QKD offers a secure way to exchange cryptographic keys. However, because qubits cannot be amplified, there are physical limitations on the distances between links. Most commercially available systems have a range of around 100km"
So quantum cryptography or quantum key distribution is completely useless, trying to get meaningless security by using easily-broken photons or weak light as information carriers, sacrificing transmitting distance and practicality.
Quantum information comprised of very faint photons or light is easily destroyed and lost.
But quantum mechanical stupid rule unreasonably forbids such fragile photons or weak light from being copied and amplified ( this p.11 ).
So it is impossible to send quantum information over long distance (= successful key generation rate over 200km is extremely low, and almost all photons easily get lost, this p.34 ).
This 2nd-paragraph says -- No amplified
"One of the most significant challenges is to extend the distance of quantum communication to a practically useful scale. Unlike classical signals that can be noiselessly amplified, quantum states in superposition cannot be amplified"
Due to this extremely low success rate of sending fragile photons, it takes extremely long time for a receiver to get information ( this 1st-paragraph ).
This p.5-right-3rd-paragraph says -- easily lost photons
"A central challenge in implementing QKD over
long distances and at high communications rates
is the ‘transmission loss in optical fibres: approximately nine out of ten photons are lost for every
50km of fibre they travel"
".. We saw that quantum information cannot be copied, which makes it challenging to develop repeaters for quantum information. Although it is an active area of research, currently QKD cannot rely on quantum repeaters to send quantum information"
This p.1-introduction-3rd-paragraph says "Current distance record in fiber for QKD (= quantum key distribution ) is 404 km. At a distance of 1000 km fiber, one would detect only 0.3 photons per century (= due to massive photon loss ) even with 10 GHz ideal single photon source (= even when 1010 photons per second or 10 GHz are generated, it takes a century for only 0.3 photons out of them to reach destination over 1000 km, and almost all other photons are lost ),
".. the key rate, however, will still drop down dramatically in long distance. One solution to this challenge is quantum repeater.. its real application still suffers from the limited performance of quantum memory."
(Fig.E) Quantum information is an error-prone, unreliable meaningless technology
The problem is the quantum information or fragile photons sent to the receiver always includes errors (= there is always disagreement between a sender's and a receiver's quantum information ), which can Not be used as legitimate reliable quantum key ( this-lower 4. this 2nd-paragraph ).
This Quantum noise and
error rates say
"Quantum cryptography uses quantum particles, which are sensitive to noise and errors. For example, photons can be affected by temperature changes or electromagnetic fields. This can cause errors in quantum communication, making information less secure."
This-Challenges-2nd-paragraph says
"Research has shown that even small variations in the polarization state of the photons can lead to significant errors in the key generation process.... significant technological challenge."
In order to correct these errors, sending errorless information via the ordinary classical communication (= ex. telephone, ordinary internet.. ) is indispensable after all, which is called "reconciliation ( this p.1-last-paragraph )."
This p.6-last-paragraph says -- classical error correction
"there are typically
still errors in the raw secret key that need to be identified, and the affected bits need to be
corrected (or discarded). Error reconciliation is performed to correct any such errors and to
minimise the amount of information leaked to eavesdroppers on the classical communication"
This middle says
"While in practice, bit error rate (BER) is not necessarily associated with vicious eavesdropping. Detection inefficiency, transmission loss, imperfect entanglement sources and many other factors contribute as false alarms. Error correction is an essential post-processing procedure."
↑ The fact that sending information by classical channel is necessary to correct errors ( this p.2-left-2~3rd-paragraph ) means the alleged "secure" quantum cryptography or quantum key distribution relying exclusively on quantum channel is just a pipe dream.
↑ The only way to completely eliminate errors of the received quantum key or photons is to compare all quantum key bits between sender and receiver through the ordinary classical communication, which makes quantum network through (error-prone) quantum information meaningless.
Incomplete comparison between the sender's and receiver's quantum key cannot eliminate errors completely, so impractical ( this-middle-Output; reconciliated key, this p.35-lower, this p.238 ).
It is far better, cheaper and more useful to use the practical classical communication based on today's RSA encryption system, because the overhyped quantum computers allegedly cracking the encryption is useless forever.
Sending fragile photons or quantum information cannot use the ordinary telephone lines, because noise easily causes errors in quantum information.
They need to prepare different independent fiber lines for different senders and receivers, one-to-one, which needs infinite numbers of lines for many users, hence impractical ( this p.6-left-1. ).
This-middle Can QKD be deployed on a large scale ? says
"its point-to-point nature,.. make its large-scale deployment extremely complex and costly
The alternative of directly linking all nodes that need to communicate is not feasible"
This 5th-paragraph says
"The problem is that the sites that wish to engage in quantum cryptographic communication must be directly connected by a quantum key distribution system.
Widespread real-world deployment of quantum cryptographic communications would require the installation of a prodigious number of quantum key distribution systems directly connecting every site. This is simply not practical."
This 1. says
"because at the moment QKD supports point-to-point connections only." ← quantum internet sending information to many receivers is impossible.
As a result, all the quantum cryptography, key distribution, internet and network are unrealistic, impossible forever, contrary to the hype.
This recent summary (= 2024 ) about the impractical quantum key distribution (= QKD ) says ↓
p.1-2nd-paragraph says "For the vast majority of use cases where classical key agreement schemes are currently used it is not possible to use QKD in practice. Furthermore, QKD is not yet sufficiently mature from a security perspective" ← QKD is useless, Not secure, contrary to hypes.
p.2-4th-paragraph says "In a QKD protocol, quantum states (for example as polarized photons) are exchanged or distributed and measured; then after post-processing, using classical communication over the authenticated channel (= ordinary classical communication is also necessary ),.. Alice and Bob may detect an eavesdropper by comparing parts of their measurement results since a quantum state changes if there is any non-trivial interaction with it"
p.3-2nd-paragraph says -- Not secure
" Claims about
"absolute" or "unconditional" security allegedly offered by QKD can never apply to actual implementations" ← ultra-secure quantum information is just the unfounded media hype.
p.4-1st-paragraph says -- Not long distance
"Signal losses in fibre-optic cables grow exponentially as a function of distance. Therefore, it is currently not
possible to reliably transmit quantum states via fibre-optic cables over longer distances. QKD
demonstrations at present can reach at most a few hundred kilometres".
p.4-2nd-paragraph says -- Impractical QKD
"One possible solution to reach longer distances is the use of quantum repeaters based on quantum
entanglement (= useless ). Quantum repeaters are still the subject of fundamental research and not practical at present.
An alternative is to use satellite-based QKD. However, current implementations mostly target nongeostationary orbits so that the availability of these satellites, which is also sensitive to weather conditions,
is limited to a short timeframe per day" ← satellite-based quantum key distribution is also useless, hopeless.
p.4-4th-paragraph says "Even in cases where QKD might be identified as a good fit, a lot more work is required to have confidence in the security of concrete QKD devices" ← still Not secure.
p.5-2nd-paragraph says "no security proof for a practically relevant protocol has been written up"
(Fig.3') classical light wave's polarization (= horizontal = 1, vertical = 0 ) or wave phase (= late-arriving = 1, early-arriving = 0 ) is used as quantum information bit. ↓
In actual experiments, encoding quantum information of 0 or 1 in the polarization of weak light or a photon is difficult.
So they often use the time-bin or light phase-encoding where the early-arriving light pulse (= corresponding to a bit = 0 ) and the late-arriving light pulse (= a bit = 1 ) are used as carriers of quantum information.
In this experiment ( = p.2-Figure 1 ), they encoded quantum information 0 or 1 in four different weak lights or photons with different phases (= different arriving time ) of 0 phase (= bit 0, basis-1 = polarizing filter-1 ), π/2 phase (= bit 0, basis-2 = polarizing filter-2 ), π phase (= bit 1, basis-1 = polarizing filter-1 ) and 3π/2 phase (= bit 1, basis-2 = polarizing filter-2 ), and could not send this fragile quantum information or weak light over 200 km (= p.5-Figure 5 ), useless.
This-middle-challenges of QKD-key rate constraints say
"Key generation rates in existing QKD systems are quite low, in the order of kilobits per second, which is insufficient for many applications. Improving key rates to megabits per second level is required.", which is impossible to realize in today's impractical quantum key distribution.
The 3rd-last ~ last paragraphs of this hyped news (3/13/2024) say
"Excess noise erodes the rate of the key that can be distributed. Too much noise,.." ← Quantum key distribution suffering too much noise is impractical.
"By using a narrow energy laser as your local oscillator, it acts as a filter for the background noise" ← Classical laser light was used as quantum key.
"Future efforts will (= just speculation, still useless quantum key distribution ) focus on reproducing the experiment's results.."
↑ This research paper ↓
p.5-Fig.7 shows this research just sent weak classical laser light or photons over only 10.4 km optical fiber, which is too short to be practical.
p.6-Fig.10 estimates the secret key rate is only 10-6 (= only one photon or one bit can reach the destination per 1000000 sent photons due to massive photon loss ) over only 200km (= which is just guess, actually more information would be lost ), which is too short distance for practical quantum communication.
(Fig.M) Sending only small numbers of fragile photons or weak lights over only 35 km with massive photon loss and very high error rate (= 30 % ) is completely impractical quantum internet. ↓
The 4th, 10th, last paragraphs of this hyped news (5/15/2024) say
"The Harvard team established the practical makings of the first quantum internet (= hype ) by entangling two quantum memory nodes separated by optical fiber link deployed over a roughly 22-mile (= just 35 km, far from practical internet ) loop"
"A quantum network cannot use standard optical-fiber signal repeaters because copying of arbitrary quantum information is impossible —making the information secure, but also very hard to transport over long distances."
"A two-node quantum network is only the beginning" ← Just sending fragile photon or weak light over short distance (= 35km ) is far from practical internet.
↑ This research paper ↓
p.2-Fig.1 connected two atoms (= nodes A and B ) called silicon-vacancy center in diamond (= SiV ) where different energy levels labeled as ↑e (= up-spin-electron ? ), ↓e (= down-spin electron ? ), ↑n (= up nuclear spin ? ), ↓n (= down nuclear spin ? ) are used as a bit state that can be changed by light (or micro ) wave with different frequencies (= Fig.1b ). ← Fictional electron spin itself is unmeasurable, all they could measure was just atomic energy levels through light wave.
p.2-right says researchers utilized a photon (= just weak light wave ) to adjust and make two distant atomic energy levels (= in nodes A and B ) the same (= when one atomic energy level was spin-up state, the distant atomic energy level was also spin-up state, which they called entanglement that has nothing to do with quantum spooky link ).
p.4-Fig.4 shows -- Error-prone
they sent a photon or weak light over (only) 35km, so that two distant atomic energy levels (= in nodes A and B ) became the same (= spins are up-up or down-down ), which error rate was impractically high = 31% (= fidelity was 0.69, ).
p.14 The success probability of sending a photon over 35km was only 2.0 × 10-5 (= only 2 photons out of 100000 sent photons could successfully arrive at the distant node, and all other photons were lost ).
↑ The success rate of sending photons (= bit information ) over only 35km was only 6mHz (= only 6 photon bits could be sent per 1000 seconds due to massive photon loss, which is too slow and completely useless internet ).
This recent research (4/2/2024) sent fragile photons or quantum information over only 100km with a lot of errors, which is far from a practical network.
↑ This research paper ↓
p.4-Fig.4A shows sending fragile photons or quantum information over 130km was impossible (= SKR or secret key rate became zero in the sending distance 100km ~ 120km ).
p.3-left-2nd-paragraph mentions reconciliation which means classical channel's error correction of quantum information errors (= reconciliation efficiency β = 92.5%, frame error rate or FER = 0.59, this p.2-right-last-paragraph, which was far from errorless quantum information ).
↑ Sending fragile photons or weak lights as quantum information always causes serious errors (= so quantum key is useless ), which must be corrected by ordinary classical communication called reconciliation, so quantum communication is meaningless.
The 7th, 13th, last paragraphs of this hyped new (7/3/2024) says
"deployed fiber of ∼79 km length" ← sending information only 79km is far from practical quantum key distribution.
"Quantum communication uses the quantum characteristics of light" ← just classical (weak) light wave was used as quantum information.
"we are thrilled to demonstrate their potential for many more fascinating experiments and applications in the future (= uncertain future, still unrealized, useless research ),"
↑ This research paper ↓
p.1-abstract says "Utilising the 79 km long link (= shorter than experiments in the past, so No progress ) secret key bits per pulse of 4.8 × 10−5 (= success rate of sending quantum key photon is only 4.8 × 10-5 due to massive photon loss )
Despite longtime research, it is still impossible to send fragile quantum information (= photon or weak light ) over long distance, which means quantum key distribution research is already deadend and hopeless.

Feel free to link to this site.