Home page
Spintronics is deadend
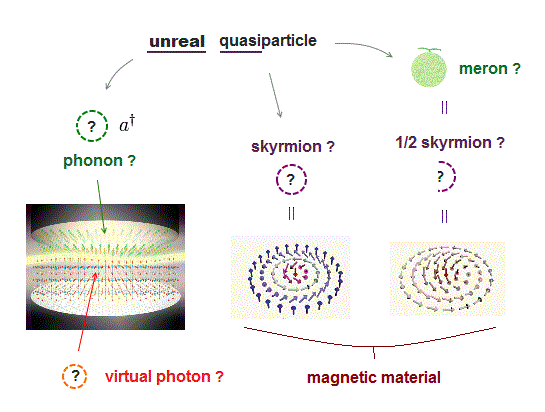
Quasiparticles are unreal
(Fig.1) Skyrmion quasiparticle is just an unstable useless magnetic swirling (= consisting of electron's orbit, Not of unphysical spin ) in magnetic material transiently excited by electric pulse.

Since 1961, quantum mechanics has stuck to fictional impractical quasiparticle model (= unreal particle, this-1st-paragraph ) called skyrmion to express some unstable swirling magnetization patterns (= consisting of electron's orbit, Not of by unphysical spin ) transiently generated (= nucleated ) on materials by electric current pulse under appied magnetic field or laser light.
Impractical quantum mechanics can only describe this fictitious skyrmion quasiparticle using fake effective mass and abstract nonphysical math symbol operators (based on artificial models and freely-fitting parameters irrelevant to quantum mechanical prediction, this-p.7-methods, this-p.6-left ) with No concrete shapes ( this p.4-5 ), which pseudo-models clearly obstruct scientific development.
Half-skyrmion is called meron quasiparticle, which is also a fictional useless particle.
Skyrmion quasiparticle is an unstable, short-lived magnetic swirling whose motion is almost uncontrollable, so useless for any technology such as (racetrack) memory.
To hide the deadend quantum mechanical fictional skyrmion quasiparticle model, a lot of overhyped news tries to connect this useless skyrmion quasiparticle model with some illusory practical application such as data storage, racetrack memory or transistor in vain ( this-abstract-still No skyrmion application, this-lower challenges ahead ).
The 2nd-last paragraph of this hyped news says -- Useless skyrmion
"While practical applications of magnetic skyrmions are likely to be many years off (= skyrmion quasiparticle is still useless ), it is this kind of fundamental research that will enable future (= uncertain speculation ) magnetic storage and spintronics-related devices."
The 4th paragraphs of this (2025) says -- Uncontrollable skyrmion
"Despite these advances, several technical challenges remain before skyrmion-based storage can achieve widespread commercialization. Key hurdles include ensuring the reproducible generation and annihilation of skyrmions (= unstable ), minimizing read/write errors, and scaling device architectures for mass production."
↑ This-challenges and barriers-5th-paragraph (2025) says -- Many challenges
"However, overcoming the intertwined challenges of scalability, stability, and manufacturability will be essential before skyrmion-based storage can transition from research labs to commercial products." ← fictional skyrmion quasiparticle is still useless, far from commercial racetrack memory despite extremely long-time research and a lot of hypes
This p.4-right-1st-paragraph says -- Impractical skyrmion
"many challenges must be overcome before magnetic
skyrmions can be applied to practical products" ← still No practical use
↑ This skyrmion easily breaks (= unstable ) in room temperature ( this-6th-paragraph ). Furthermore, precise creation and control of elusive skyrmion's magnetic state are impossible, hence useless for stable memory devices ( this p.1-right, this p.16(or p.15)-conclusion, p.16(or p.15)-right-upper, this p.1-left-middle ).
This-p.2-1st~2nd-paragraphs (2025) say -- Unstable skyrmion
"This is a significant roadblock to the implementation of skyrmion
based devices as skyrmions will tend to drift to the edges of devices and annihilate"
"Due to the challenges in detection, much of the body of research on skyrmions in synthetic antiferromagnets remains theoretical"
This-challenges and barriers:-2nd~3rd-paragraphs (2025) say -- Useless skyrmion
"Scalability is a fundamental hurdle.... Device architectures must ensure that skyrmions can be nucleated, moved, and read reliably in large numbers without cross-talk or unintended interactions."
"but have Not yet announced pilot-scale production."
"Stability of skyrmions at room temperature and under operational conditions is another major barrier"
Quantum mechanics is useless, cannot predict any physical values including (fictional) spin nor skyrmion quasiparticles.
Quantum mechanics has to rely on ad-hoc artificial equation called Landau–Lifshitz–Gilbert (LLG) euation consisting of magnetization (= M ) and free damping and interaction parameters that can Not predict any skyrmion quasiparticle's behavior ( this-p.8-9-magnetic simulation, this-p.8 ).
This-p.5-right-2nd-paragraph says -- Choosing free parameters
"In this study, we choose three groups of model parameters to simulate those
chiral magnets of MnSi.."
This-p.8-micromagnetic simulations say -- No quantum mechanical prediction
"Material parameters were chosen in order to represent the estimated material
parameters of FeGe.."
(Fig.R) Racetrack memory has to move each bit inconveniently.
The overhyped useless racetrack memory, which has to move each magnetic bits or domain to the static detectors for each bit reading and writing (= so slow, take too much time ), is falsely said to have the potential (= this word "potential" meaning "still unrealized" is constantly used ) to be energy-efficient, faster, smaller memories.
The 3rd-paragraph of this hyped news says -- Impractical moving memory
"In contrast to data bits in hard disk drives, (fictional quasiparticle) skyrmions are movable objects. Their motion along a guiding track in a chip can be induced by a very weak pulse of electrical current. -- the so-called skyrmion racetrack memory. The mobility of skyrmions allows data to move from write to read elements without the need for any movable mechanical parts (= false ) such as read and write heads and spinning hard disk... This capability saves energy (← ? )"
↑ This exaggerated standard explanation for the dreamlike (impractical) racetrack memory (= useless since first proposed in 2004, this-5th-paragraph ) based on fictional skyrmion magnetic skyrmion is completely wrong.
The impractical racetrack memory has to artificially generate and control each unstable magnetic swirling or skyrmion quasiparticle (= bit ) by external electric pulse that needs mechanical electric apparatuses to be placed for each skyrmion bit positions after all ( this-3rd-paragraph, this-4th-paragraph ).
And even when only one magnetic bit (= skyrmion ) is measured in this inconvenient racetrack memory, they need to move all the magnetic bits or (fictional) skyrmion magnetic quasiparticles around it to the detectors' positions, which take much more additional time, space and energy than today's practical faster, energy-efficient DRAM, SRAM (= with static bits, transistors or non-racetrack ) memory.
↑ So the racetrack memory, which has to waste much time and energy for moving skyrmion quasiparticles to detectors, is impractical forever, contrary to hypes.
The 2nd~ paragraphs of this or this (2025) says -- Useless recetrack memory
"racetrack memory faces several challenges that need to be addressed before it can be widely adopted. Some of the key challenges include reducing energy consumption and increasing speed, improving data retention and stability, and addressing scalability and reliability issues"
So racetrack memory (= or skyrmion quasiparticle ) is far from reality now in 2025 ( this-p.1-left ), which fact contradicts a lot of fake news ↓
The 4th paragraph of this fake news (2010) says -- Wrong prediction
"A market-ready device could be available in as little as 5-7 years (= which prediction of practical racetrack memory in 2015 ~ 2017 turned out to be wrong )."
The 4~5th paragraphs of this ( 2008 ) says -- Fake news
"But the IBM team say racetrack memory is still seven to eight years away from commercial use (= which too optimistic prediction of commercialized racetrack memory in 2016 also turned out to be wrong )"
↑ Contrary to these too optimistic misleading predictions, the racetrack memory is still impractical, as this-.1-introduction-2nd-paragraph (2022) says
"One of the main challenges in developing racetrack memory systems is the limited precision in controlling the track shifts,
that in turn affects the reliability of reading and writing the data"
(Fig.1') Skyrmion magnetic quasiparticle is too short-lived to be a stable memory, contrary to hypes.

The 3rd-last and 2nd-last of this say -- Useless skyrmion
"We found that small skyrmions are only stable in very specific material environments,"
"But it will take additional research to make the skyrmion technology commercially viable" ← unstable skyrmion quasiparticle is useless.
This-p.3-3rd-paragraph (2024) says -- Impractical skyrmion
"However, realizing the potential of skyrmion in real applications requires overcoming several
challenging prerequisites including controllable isolated skyrmion generation/deletion, shifting
to a desired position, and reliable detection ( this-p.1-left-2nd-paragraph )
This-introduction-1st-paragraph (2024) says -- Skyrmion disappers
"However, the skyrmions tend to acquire additional velocity deviated from the motion direction due to the Magnus force, called the skyrmion Hall effect, which may cause the annihilation of the skyrmions.. the high density of the skyrmions could lead to misplacement as a result of the interaction between them, reducing the accuracy and completeness of data."
This-p.5-1st-paragraph (= in 2024 ) says -- Uncontrollable skyrmion
"However, some skyrmions change their shape and size when moving
and one of them does not move."
This-introduction-2nd-paragraph (2025) says -- Unstable useless skyrmion
"However, a significant challenge for practical skyrmion-based devices lies in ensuring their robust stability under ambient field-free conditions. In many known skyrmion-hosting materials, skyrmions are stable only within a narrow range of low temperatures or require bias external magnetic fields. Isolated skyrmions in single-layer films are often metastable, prone to collapse or elongate into stripe domains in the absence of a stabilizing field. This reliance on external magnetic fields complicates device integration and increases the power requirements."
↑ Controlling (fictional) skyrmion quasiparticles as stably-moving bits in the racetrack memory is impossible forever.
This p.2-left-last-paragraph says -- Unstable skyrmion
"The positional stability
of skyrmions is a critical issue for both of these applications because a randomly displaced skyrmion can alter
the bit sequence"
This p.2-left-2nd-paragraph (2024) says -- Useless skyrmion
"Despite the potential for competitive technology, the development of a skyrmion quantum processor will face near-term
challenges. On a fundamental level, these include among others the identification of candidate frustrated magnets with low
damping, the microscopic understanding and control of noise
sources,..
On a device-specific level, the deterministic
and precise skyrmion nucleation, the efficient determination
of the fidelity of quantum operations, and robust and reproducible device fabrication are among the pressing issues to be
addressed."
(Fig.H) Useless skyrmion quasiparticle needs fake application.
The 1st-paragraph of this hyped news (or this-1st~2nd-paragraphs ) says
"A team of scientists has taken steps to create a new form of digital data storage, a Racetrack Memory, which opens the possibility (= still unrealized ) to both bolster computer power and lead to the creation of smaller, faster, and more energy efficient computer memory technologies"
↑ This research paper's abstract ( this-2nd-paragraph-link ) says nothing about any practical use such as energy efficient computer memory, contrary to the above hyped fake news.
The 5th-paragraph of this hyped news (5/22/2025) says
"Skyrmions are ultra-small, stable magnetic swirls that can exist in certain materials.., they are being studied as building blocks for future (= still useless ) low-power memory and computing systems"
The last paragraph of this says -- Fake news
"this finding allows for an advanced version of the racetrack memory data storage, "
↑ This-research paper's p.1-abstract says nothing about any practical use such as data storage (= so this skyrmion quasiparticle research is useless ), contrary to the above hyped news.
The last paragraph of this overhyped news says
"this study realized the implementation and reconfiguration of seven kinds of logic functions... promoting the potential (= still useless ) application of magnetic skyrmions-based logic gates"
↑ This-research paper's last-Methods just explained about simulation of fictional skyrmion quasiparticle without conducting experiments (= this research conducted No experiments about skyrmion or any practical use ).
See also this page.
This hyped news (2024) say ↓
1st-paragraph says -- Still useless skyrmion
"A research team.. has created an innovative microelectronic device that can potentially (= still useless ) function as a sustainable, high-performance "bit-switch." This paves the way for future (= uncertain future ) computing technologies"
6th-paragraph says -- Uncontrollable skyrmion
"While skyrmions can be seen under special microscopes and have been manipulated using bulky magnets for over a decade, the absence of electrical control has been a critical impediment to their technological relevance." ← still unable to electrically control skyrmion quasiparticles.
↑ This research paper ↓
p.2-Fig.1-c shows -- Too bulky skyrmion
This so-called skyrmion memory bit is too big or too bulky (> 1μm or 1000nm ) to be practical, compared to today's practical compact memory bit less than 50nm.
↑ This bulky skyrmion switch needed both electric and magnetic field, which needs excessive instruments (= can Not be scaled up ), hence impractical.
This hyped news (12/11/2024) say
5th-paragraph says
"In their work, electric current pulses were applied to a magnetic multilayer stripe... The researchers observed skyrmion motion opposite to the current direction."
Last-paragraph says -- Fake quantum computer
"This study introduces innovative methods for controlling helicity, pushing the boundaries of spintronic device applications such as data storage and quantum computing" ← untrue
↑ This research paper ↓
p.3-Fig.2 (and p.5-measurement of current-driven skyrmion dynamics ) says this research just applied electric current pulse at very long intervals of 980μs (= far slower and longer than today's ordinary SRAM, DRAM memory switch time of less than 60ns ).
And they measured the fictional skyrmion quasiparticke magnetic swirling by seeing change of polarized light reflected by this material (= called MOKE or classical Kerr effect ). ← Additional bulky light-detection devices are also needed, which cannot be scaled up
p.5-left-1st-paragraph says -- No quantum computer
"This research
provides a method for controlling skyrmion helicity reversal, opening
possibilities (= still unrealized ) for the development of advanced spintronics devices that
leverage skyrmion helicity." ← Quantum computing was irrelevant, contrary to the above hyped news
(Fig.2) Phonon quasiparticle meaning sound wave or vibration has No physical shape.
Quantum mechanics is unable to explain the normal thermal (or sound ) vibration of material realistically, instead, it relies on fictitious quasiparticle model called phonon that is expressed just as a nonphysical math symbol with No physical figure or shape ( this p.4 ), which cannot be used as practical tools to build useful nano-devices.
This recent phonon quasiparticle paper ↓
p.1-abstract says "We calculate the superconducting critical temperature TC ab initio considering the full phonon (= fictional quasiparticle ) spectral function." ← No mention of practical application, so phonon quasiparticle is useless.
p.3-right shows phonon quasiparticle is just a unphysical math symbols with No concrete shape.
p.4-right-last~p.5-left-1st-paragraph relied on one-pseudo-electron density functional theory based on artificially-chosen pseudo-potential. ← No quantum mechanical prediction.
p.5-right-2nd-last-paragraph says "We use μ* = 0.16 for the Coulomb pseudopotential" ← choosing free parameters means No quantum mechanical prediction.
The 2-3rd, 7th, 14th, 18th, 28th paragraphs of this hyped news say
"Electrons carry electrical energy, while vibrational energy is carried by phonons. Understanding how they interact with each other in certain materials, like in a sandwich of two graphene layers, will (= just speculation ) have implications for future optoelectronic devices (= vague devices, and just hype, fictional phonon has No practical application )."
"Recent work has revealed that graphene layers twisted relative to each other by a small "magic angle" can act as perfect insulator or superconductor. But the physics of the electron–phonon interactions are a mystery (= quantum mechanics failed to understand phonon quasiparticle )"
"Phonons aren't particles like electrons though, they're a (fictional) quasiparticle. Yet, their interaction with electrons in certain materials and how they affect energy loss in electrons has been a mystery."
"the team wanted to learn more about how electrons lose energy in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene, or MATBG for short."
"especially at ultracold temperatures (specifically below -73°C = impractically-low temperature ). At these temperatures, it's very difficult for electrons to lose energy to phonons, yet it happens in the MATBG."
"As the material is only being studied for a few years, we're still some way from seeing magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene having an impact on society (= still No practical use )"
↑ This research paper ↓
p.1-right-1st~2nd-paragraphs say "In graphene, cooling typically
occurs via the emission of optical and acoustic graphene phonons (= just imagination based on fictional quasiparticle )..
In these systems, a dark exciton (= fictional quasiparticle ) state emerges between van
Hove singularities"
p.3-left-2nd-paragraph says
". In BLG (= nontwisted Bernal bilayer graphene ), the cooling
time increases from 3 to 25 ps as the temperature decreases
from 300 to 5 K, which is expected as it takes longer for hot carriers to couple to phonons at lower temperature due to the reduced phonon occupation. Notably, in MATBG (= magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene ), the
cooling time remains short, around 3 ps, across a broad temperature range (5 to 300 K). This suggests the involvement of
low-energy (fictional) phonons (= an unreasonable leap of logic )"
↑ The time needed to cool graphene from 300 to 5K decreased from 25ps to 3ps depending on the twisted angle between two layers of graphene, which is due to the fictional phonon quasiparticle ? ← Quantum mechanics relying on fictional quasiparticles cannot clarify real mechanism, and No practical use.
p.7-8 This research made No quantum mechanical calculation nor prediction (= No Schrodinger equation nor DFT was used ).
They just used artificially-chosen parameters ( this p.2-3 ).
(Fig.3) ↓ No real magnetic monopole. Berry phase or curvature is just fictitious magnetic field with No real physical meaning and No practical application.
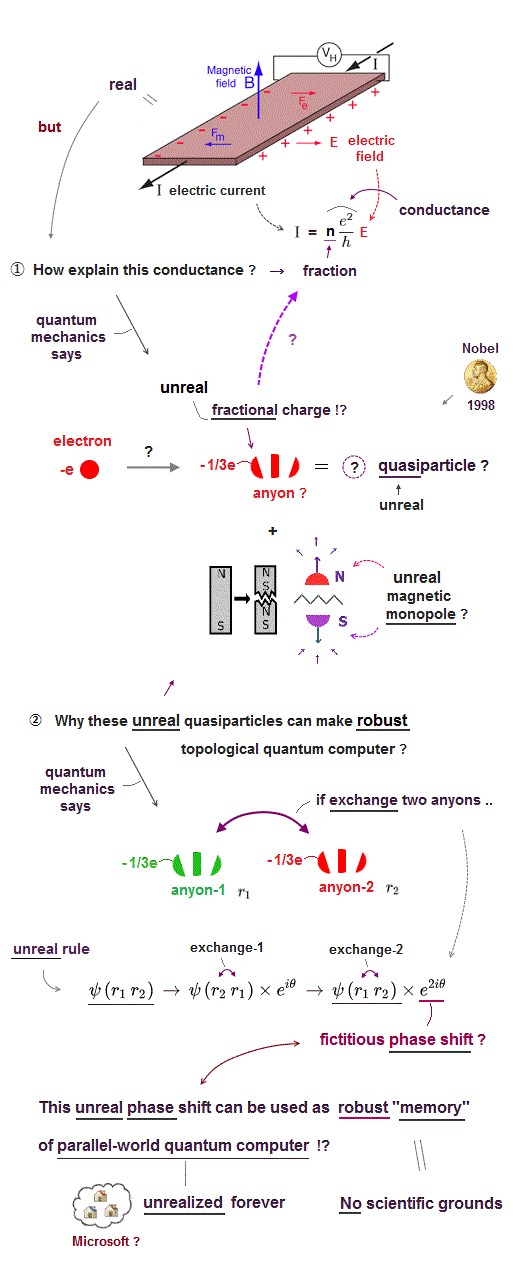
Berry phase is useless fictitious magnetic field.
Magnetic monopole, a hypothetical particle with only one north or south magnetic pole, does Not exist.
Despite this unreal monopole, physicists are trying to use fictitious quasiparticle model to explain and create fake magnetic monopole in various magnetic materials such as spin ice (= unreal spin itself is unseen, only magnetic moment equal to electron's orbital motion can be measured ) in vain.
This fake monopole quasiparticle is Not a real monopole, but just a collection of multiple magnetically-polarized electrons or atoms ( this 4th-last-paragraph ).
Pursuing this fictional meaningless monopole quasiparticle in the current mainstream condensed matter physics clearly obstructs technological innovation, and spawns many unfounded hyped news to hide the unreal and impractical science.
The 1-2nd, 4th, last paragraphs of this hyped news say
"there have been hypotheses of the existence of magnetic monopoles, fundamental particles that are just north or just south. Researchers have Not found them yet"
"Using hematite, the rock equivalent of rust, the researchers discovered that on its surface, peculiar "magnetic configurations (= just magnetic configuration, Not a real monopole )" can emerge. They measured (fictional) quasiparticles – an interaction of sorts that behaves like (= meaning unreal ) a particle for a time."
"These monopoles are a collective state of many spins (= many orbits, correctly ) that twirl around a singularity rather than a single fixed particle (= Not a single real magnetic monopole ), so they emerge through many-body interactions (= fictional monopole quasiparticle just approximately represents a collective magnetic field created by multiple atoms, Not by real monopoles )"
"The measurements were conducted using a diamond needle where the spin of a single electron – its intrinsic angular momentum (= Not by spin but by electron's orbit ) – was used to precisely measure the magnetic field of the material.."
".. Discovering how to manipulate these peculiar quasiparticles might (= just speculation, still useless ) mean better computer technology, with fast and energy-efficient memory logic (= hype, this fictional magnetic monopole has No practical use )."
↑ This research paper ↓
p.3-Fig.1 shows this is Not a real magnetic monopole but just an ordinary molecule consisting of multiple magnetic atoms showing some swirling magnetic field pattern at extremely-low temperature of 4K (= impractically-low temperature ).
p.4-Fig.2 tries to explain some magnetic field pattern by fictional meron quasiparticle.
p.6 No quantum mechanical calculation nor prediction (= No Schrodinger equation nor DFT was used ).
The 5th and 7th paragraphs of this other website say
"Rather, the existence of magnetic monopoles is a collective phenomenon (= Not a single real monopole ) due to the interactions between the atoms and electrons of which spin ice is composed (= fictional monopole quasiparticle is just some magnetic material composed of multiple atoms )."
"The magnetic monopoles are a class of (fictional) quasiparticles that particularly fascinate physicists, while at the same time presenting them with major puzzles. “Quasiparticles exist that appear to be fragments of elementary particles that are normally considered to be indivisible (= quasiaprticle is unreal )".
↑ This research paper on fictional monopole in spin ice ( this ↓ ).
p.1-abstract mentions the fictional fractional electric charge e/3 of quasiparticle, and No mention of practical application of this fictional quasiparticle (= so monopole is useless )
p.1-left mentions 10 (= integer ) Bohr magneton (= μB ) which can be explained by electron's orbit Not by unphysical spin.
p.2-right-(3) fictional magnetic charge Q, which does not really exist.
p.4-6 shows some nonphysical equations with No quantum mechanical calculation nor prediction (= No Schrodinger equation nor DFT was used ).
The current condensed matter physics heavily relies on tons of fictional useless concepts such as Berry phase or Berry curvature which is just fictitious magnetic field (= Not real magnetic field ) generated around imaginary monopole ( this p.1-left, this p.4-1st-paragraph, this p.4-5, this p.1-left ).
This p.12 (or p.32 )-upper says
"The Berry phase is analogous (= No real )
to a magnetic flux, and the quantity... is called the Berry curvature, which is analogous (= Not real ) to a magnetic field.
A good way of thinking about these quantities is to imagine a fictitious
magnetic monopole sitting inside a closed surface."
This p.2-middle-4th-paragraph says
"This phase cannot have any physical
meaning."
↑ As long as the current mainstream physics or quantum mechanics uses these unrealistic concepts, clarifying true atomic mechanism usable for building practical molecular devices is impossible forever.
This recent paper on fictitious Berry phase ↓
p.1-abstract-last just says "Our work provides an opportunity for the study of (unphysical) geometric phases, leading to a variety of observations in light-driven topological phenomena and attosecond solid-state physics (= Not specifying practical use, so the unphysical Berry phase is useless )"
p.2-right-1st-paragraph used fictitious quasi-momentum, and Berry phase is just nonphysical math concept with No physical shape.
p.5-Fig.4 used Circular dichroism HHG spectroscopy, which just measured (classical) laser light response from material ( this p.4 ) for guessing fictitious Berry phase.
This p.6-last-paragraph~p.7 used one-pseudo-electron DFT with PAW (artificially-chosen) pseudo-potential, and The Wannier function-based tight-binding Hamiltonian for fictional Berry phase.
↑ This is Not quantum mechanical prediction, because pseudo-potential and Wannier function must artificially choose various parameters such as energy window ( this p.22, this p.2-right-2nd-paragraph, this-p.11 3rd, last-paragraphs ).
(Fig.6) ↓ The measured real electrons with real mass were intentionally misinterpreted as fictional massless Dirac or Weyl quasiparticles.
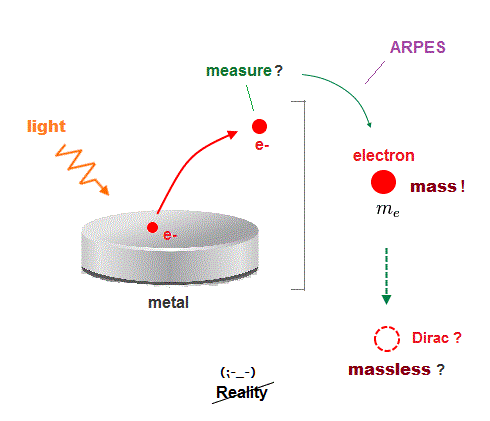
Dirac fermions (or Dirac cone, Dirac semimetal ) and Weyl fermions are all unreal quasiparticles caused by intentionally misinterpreting the measured momentum and energy of electrons ejected by light in the method called ARPES ( this p.4 ).
Majorana fermion is also an imaginary quasiparticle model artificially created to explain some electric conductance (= unreal quasiparticle itself can Not be measured ) and deadend quantum computer.
None of these fictitious quasiparticles have concrete shapes or size, hence, obstructing the real science, which dire facts must be covered up by overhyped news.
The 2nd-3rd, 6th, last paragraphs of this hyped news say
"The mysterious Weyl fermions were, in fact, detected for the first time in 2015; they turned out Not to be free particles like the neutrino, which can move through the universe independently from the rest of the world, but rather '(fictional) quasiparticles' in a solid state."
"Quasiparticles are Not particles in the conventional sense, but rather excitations of a system consisting of many interacting particles"
"According to the laws of relativity, free massless particles must always spread at light speed. This is, however, not the case in solid states: "Even though our Weyl fermions have no mass, their speed is extremely low (= quantum mechanical fictional Weyl quasiparticle contradicts relativity )"
"The Weyl fermions are only dispersed in the material to a minimal extent, meaning they can conduct electrical current almost without loss (= false, No evidence of lossless current ) -- this is of great significance for electronics. They are also likely to be extremely interesting to the field of spintronics,.. Weyl fermions will (= just speculation ) be of interest here due to their particularly robust spin. The particle should also be especially well suited for use in (deadend) quantum computers." ← Overhype, this fictional Weyl quasiparticle has No practical use.
The last paragraph of this recent website on fictional Dirac and Weyl quasiparticles just vaguely says
"The discovery could lead to practical applications in the future (= still unrealized ). “While it’s still early days, this finding could pave the way toward realizing next-generation electronic devices that utilize new fermions,.. They may (= just speculation ) be useful for high-speed devices"
↑ No practical use of these quasiparticles, and only hyped news is rampant.
This research paper on fictional Dirac fermion quasiparticle ↓
p.1-abstract-last says " Thus, graphite presents a system in which massless Dirac fermions, (fictional) quasiparticles with finite effective (= fake ) mass and defect states all contribute to the low-energy electronic dynamics" ← No mention of practical use.
p.1-left-last~p.1-right-1st-paragraph says "Here, we report the first direct observation of massless Dirac fermions coexisting with quasiparticles with finite effective mass in graphite, by using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES)."
↑ This ARPES can just detect real electrons (= e- ) with real mass, which was intentionally misinterpreted as fictional Dirac quasiparticle with fake effective mass due to wrong assumption and free parameters.
p.2-right mentions "quasiparticles that have finite (fictional) effective mass"
Another recent research paper on fictional Dirac quasiparticle ↓
p.1-abstract-last says "Our findings establish the general optical response of massive Dirac fermions (= fictional quasiparticle ), which is closely related to the universal electrodynamics in quantum anomalous Hall state (= No mention of practical use )"
p.1-left says "It has recently been recognized that the nonlinear optical effect and magnetooptical (MO) effect are enhanced in topological materials.."
"When the Fermi level is controlled in between the mass gap, the anomalous Hall response shows the quantized conductance e2 /h, establishing the quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) state" ← Measurement of classical polarized light (= Kerr magnetooptical efect ) and Hall effect based on classical Lorentz magnetic force were used to (falsely) estimate the existence of fictional Dirac quasiparticle.
p.6-right used one-pseudo-electron DFT with full relativistic projector augmented-wave (PAW) pseudopotentials (= artificially chosen, so No quantum mechanical prediction ), and saying "the spin-polarized DFT often overestimates the magnetic exchange splitting"
↑ The current mainstream one-pseudo-electron DFT is useless, wrong, unable to predict any values.
The 4th, 7th, 9th paragraphs of this hyped news say
4th
"Now, a group headed by Zahid Hasan at Princeton University has found evidence that Weyl fermions exist as (fictional) quasiparticles – collective excitations of electrons – in the semimetal tantalum arsenide (TaAs)"
"... This means that TaAs should have Weyl fermions in its bulk and a distinct feature on its surface called a "Fermi arc (= some fictional electron's energy and momentum relation )". Using a standard technique called angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES), the team found evidence of a Fermi arc." ← ARPES can just detect real electrons, Not fictional (Weyl or Dirac) quasiparticles.
7th
"The team fired microwaves at the crystal and measured microwave transmission through the crystal while changing its orientation to the incident microwave beam – and varying the frequency of the microwaves. This allowed the researchers to map out the photonic band structure of the crystal, which reveals which microwave frequencies can travel through the crystal and which cannot. This revealed the presence of “Weyl points” in the band structure, which are indicative of Weyl fermion states"
↑ They just measured (classical) microwave (= Not Weyl quasiparticle itself ) changed by some material, and (mis)interpreted it as fictional Weyl fermion quasiparticle.
9th
"Weyl fermions could (= just speculation ) be very useful because their massless nature would allow them to conduct electric charge through a material much faster than normal electrons (= false, massless is fake effective mass, Not real ) – which could be used to create faster electronic circuits. This property is also shared by electrons in graphene. However, unlike graphene, which is a 2D material, Weyl fermions should exist in more practical 3D materials. Furthermore, Weyl particles are topologically protected (= No evidence of topological protection ) from scattering, which means that they could be useful in quantum computers (= hype, quantum computer is already deadend )."
↑ This research paper's abstract last just vaguely says "Our work opens the field for the experimental study of Weyl fermions in physics and materials science. " ← No mention of detailed practical application, so Weyl fermion quasiparticle is just unreal and useless, contrary to hypes (= topologically-protected or something ).
↑ this supplementary material ↓
p.2-1st-paragraph says "The experimental geometry of SX-ARPES has been described in (29). The sample was cooled down to 12K (= too low temperature to be practical )"
p.2-last-paragraph used one-pseudo-electron DFT with artificially-chosen pseudo-potentials. ← No quantum mechanical prediction.
As a result, it is impossible to put such fictional quasiparticle models to practical use, so academia and the media desperately try to hide this deadend quantum mechanical model by spreading overhyped news with misleadingly colorful particle pictures now.
The 1st and 2nd paragraphs of this overhyped news (1/11/2025) says
"electrons mimic (fictional) massless particles called Weyl fermions."
"This finding could (= just speculation, still useless ) open a breadth of new quantum device platforms for harnessing emergent topological states for novel chiral nano-spintronics and fault-tolerant ( deadend ) quantum computing"
↑ This research paper's p.1-abstract says nothing about the practical use such as fictional quantum computing, contrary to the above hyped news.

Feel free to link to this site.