Home page
Einstein relativity is wrong
Wrong papers defend Relativity
(Fig.1) GPS, Michelson-Morley (= Gale-Pearson ) experiments showed light speed is changed by the earth rotation and disproved Einstein relativity.

Einstein relativistic Lorentz transformation is based on the postulate that light speed must be always the constant c when measured by any moving and stationary observers ( this-middle ).
The speed of light emitted by GPS is observed to be faster or slower than the light speed c, depending on the earth (= observer ) rotating speed, which is called Sagnac effect disproving Einstein relativity claiming the observed light speed must be always the same c regardless of any moving observers ( this-abstract, this-abstract, ).
This-last-8.conclusion-2,4th paragraphs says -- Einstein relativity wrong
"These non-constant light speed values c±v
induced by the rotation of the Earth contradict the ( relativistic ) postulate of light speed constancy"
"It is clear therefore that GPS technology very easily demonstrates that light speed is not constant and hence that the light speed invariance postulate which leads to the Lorentz Transformation and special relativity is invalid"
According to Einstein relativity, these observed faster-than-light GPS signals must have unreal imaginary mass and imaginary time ( v > c ), which disprove Einstein relativity.
Also in Michelson-Gale-Pearson experiment, they measured two lights traveling at faster or slower than light speed c through a rectangular hollow pipe circuit rotated by the earth (= As seen by the detectors rotated with the pipe rotated by the earth, light traveling through the pipe was observed to travel faster or slower than light, depending on the pipe's rotating speed ).
↑ All these GPS and Michelson-Gale experiments clearly contradict Einstein relativistic theory claiming the same constant light speed c must be measured irrelevant to motion of the earth or observers. ← Textbooks tend to hide this inconvenient truth ( this p.3-discussion~p.4 ).
All ad-hoc general and special relativistic solutions to GPS observing the faster or slower than light speed in Sagnac effect are wrong, unable to explain why the light speed is affected only by the earth's spinning, and Not affected by the earth rotating around the Sun.
This p.1-lower, p.3-conclusion says -- Einstein is wrong
"in the global
positioning system (GPS)... From these light travel time differences
these researchers deduced light speeds c - v eastward and c + v (= faster than light speed c ) westward relative to the surface
of the Earth where v is the speed of rotation of the Earth’s surface at the particular latitude"
"one-way light speed is Not the same in all directions as required by the light speed constancy postulate of special relativity."
Only the real medium moving with the earth (= but this medium unfixed to the earth spinning like free atmosphere ) can explain the why speed of light emitted by GPS is changed only by the earth's spinning, Not by the earth moving around Sun (= constant light speed c in Michelson-Morley experiment ) in addition to aberration.
Like the atmosphere, only near the earth's surface, the medium colliding with buildings or something appears to (= actually Not ) be dragged by the earth spinning, which explains the faster or slower-than-light signal emitted from GPS distant from the earth's surface.
The light medium can also explain Michelson-Gale experiment where the rotating vacuum rectangular loop measured the light traveling faster-than-light in the light medium which is not dragged in the loop's rotating (= tangential ) direction by the hollow rectangular loop's wall.
↑ This inconvenient truth is hidden by textbooks and the overhyped media repeating empty phrases "Einstein was right again !"
(Fig.2) Light speed c is changed only by the earth rotation (= spinning ), which cannot be explained by Einstein relativity.

GPS, Michelson-Gale experiments (= conducted in the vacuum ), Sagnac effect clearly showed the light can travel faster (= c + v ) or slower (= c - v ) than the light speed c when measured by the observers moving at a velocity of v ( This p.1-lower, this p.3-discussion ), which disproves Einstein relativity and Lorentz transformation based on the same light speed c regardless of motions of light sources and observers ( this-Einstein's two postulates ).
↑ If Einstein "relativistic" motion is right, the observed light speed must be changed not only by observers' or earth's motion ( this-6th-paragraph ) but also by the velocity of the light source = GPS satellite (= emitting light ). But paradoxically the speed of light c is not affected by the light-source = satellite speed ( this p.18-19, this p.4 ) which only causes Doppler shift (= light wavelength change ).
↑ If the light speed c is faster or slower due to the velocity of light sources such as satellites and atoms, the speed of light emitted by atoms (= which can move at almost light speed c ) can be very
We can easily prove light measured by the moving detectors can be faster or slower than light speed c (= in this case, according to Einstein relativity, objects or light moving faster than light have unreal imaginary mass in relativistic mass of v > c or imaginary time ) which disproves Einstein relativity.
Even the recent published papers officially admit the light speed measured by the moving observers is anisotropic (= faster or slower than light speed c depending on observers' or the earth's motion, which contradicts Einstein relativity, this-lower-8.conclusion ).
This-p.7-2nd-paragraph (2024) says -- Faster than light
"the one-way speed of light is anisotropic (= faster or slower than light speed c ) in
inertial frames, which agrees with the experimental results (= disagreeing with Einstein relativity with the constant speed c, this-1st-paragraph )"
This-p.6-6th-paragraph says -- Relativity is wrong
"In other words, the SRT (= special relativistic theory ) correctly applied to a rotating Sagnac Interferometer does Not predict the Sagnac Effect."
There are still wrong papers still claiming the faster or slower-than-light signals actually observed in a rotating loop and GPS are illusion by using imaginary idea that one place in a rotating loop may have three differently-ticking clocks (= contradicting the original relativistic postulate ) as if three parallel universes..
Due to Sagnac effect experimentally measuring faster-than-light speed contradicting Einstein relativity, they start to use fake general relativity saying the contradictory thing: the light speed is the constant c only with respect to the stationary earth (= admitting one absolute frame or aether stationary with respect to the earth contradicting Einstein relativity prohibiting absolute frame or faster-than-light, this p.6-upper, this p.3-lower~p.4 ).
This-p.5-left, p.9-conclusions say general relativity or GPS system chooses the earth-centered inertial (= ECI ) frame as one absolute frame (= contradicts Einstein relativity, which is disproven ) that can measure the constant light speed c (= in other rotating frames, faster or slower-than-light speed is measured )
The reliance on fake general relativity to justify the contradictory faster-than-light signals is wrong, because Michelson-Morley experiment on which special relativity is based was conducted on the earth rotating around Sun, which means a rotating loop uses only special relativity, which fatal paradoxes cannot be fixed by general relativity.
They try to use fake general relativity to admit the light observed by the rotating earth can travel faster or slower than light-speed c (= in this case, a thing or light moving faster than light has unreal imaginary mass-energy and imaginary time ) depending on the rotating direction (= anisotropic ) by using fictional Coriolis force speed-up or slow-down conveniently changed by the light's moving direction.
This-p.4-6 conclusions say
"the speed of light varies by c ± ωr (= faster or slower than light ) in one or the other
direction around the disk.... the apparent variation of
the speed of light is... gravitational Coriolis time dilation (= No such thing as Coriolis time dilation conveniently changing the light speed faster or slower depending on the light's traveling directions even in official relativity though )"
Einstein relativity falsely tries to admit light can travel faster or slower than light by the earth spinning in Sagnac effect (= which clearly disproves Einstein relativity, though ).
But the earth is also rotating around Sun or galactic center at a speed much faster than the earth spinning, so the light speed observed on the earth must be affected by the earth rotating around the Sun or galactic center, which light speed change cannot be detected (= as shown in Michelson-Morley or GPS ), paradoxically.
As a result, both special and general relativity are proved to be wrong, cannot explain why light speed is changed only by the earth spinning, Not by the earth rotating around Sun.
These Sagnac effect (= light speed is changed by observer's motion ) is one of ordinary classical mechanical effects ( this p.1-right-2 ) contradicting Einstein relativity (= due to light speed c changed by observers' velocity ), contrary to the misleading word of the relativistic Sagnac effect ( this-lower-conclusions ).
This p.8-5-conclusion-2nd-paragraph says -- Relativity is wrong
"The positive result of the Sagnac experiment is significant. The experiment was
sufficient proof that the velocity of light can be added to or subtracted from in accordance
with the classical law of addition of velocities but in contradistinction to the relativistic law
which makes the velocity of light absolute and independent of motion of the observer or the
source of light"
This Sagnac effect and Michelson-Gale-Pearson experiments are consistent with the light medium (= aether ) moving with the earth (= light speed is the constant c inside this earth medium. ← this can perfectly explain aberration, too ), but this earth medium is not fixed to the earth spinning (= light speed is changed only by the earth's spinning, as seen in Sagnac effect. this p.6 ).
Actually, the atmospheric air moving with the earth can move independently of (= not fixed to ) the earth spinning (= air molecules are moving in various directions at very fast speeds, as seen in super-rotation ), because the earth gravity attracts the atmospheric air molecules only in vertical direction, irrelevant to the spinning (= horizontal ) direction.
Only near the earth's surface, the atmosphere and the medium colliding with buildings or something appear to be dragged (= actually Not ) by the earth's spinning, which can explain why signals emitted from satellites distant from the earth's surface are measured to be faster or slower than light speed c by the earth's spinning.
Michelson-Gale experiment is known to detect the light traveling through the rectangular hollow pipe clockwise or anticlockwise faster or slower than light, because the whole pipe is slightly rotated by the earth spinning while the light was traveling inside it.
Michelson-Gale experiment used the rectangular hollow vacuum pipe (= surrounded by the solid wall ) inside which the light medium substance's velocity is balanced and uniform, which can detect the faster or slower-than-light speed changed by the earth rotation (= affecting the rectangular pipe's rotation ), violating the relativity.
↑ This rectangular circuit's shape doesn't change, and the north and south pipes' velocities are different due to different earth's spinning speeds at different latitudes, so in this Michelson-Gale experiment, the rectangular hollow pipe slightly rotated by the earth, which did not drag the medium inside the hollow pipe in tangential (= rotational ) direction, which could detect the light traveling faster or slower than light speed inside the pipe by the detectors attached to the pipe rotated by the earth spinning.
The hollow rotating ring path does not change or accelerate the light medium's velocity (= or light speed ) in the tangential (= rotational ) direction (= because the wall of this rotating vacuum ring tube doesn't push the medium in tangential direction ), which can detect light speed difference between clockwise and anticlockwise seen by the observer rotating with the ring, which disproved Einstein relativity with the constant light speed c seen by any moving observers. ← Optical fiber case also disagrees with relativity ( this 7th, last-paragraphs ).
(Fig.3) Lights traveling clockwise and anticlockwise reach S (= S attached to the loop light path rotating at v clockwise ) at different times (= faster or slower than light ), which Sagnac effect contradicts Einstein relativity with the constant light speed c.

In Sagnac effect using optical gyroscopes, two beams of light emitted by a light source S travel clockwise (= red light-2 ) and anticlockwise (= blue light-1 ) inside the loop light-path circuit rotating at a velocity v clockwise, and return to the S (= this S is attached to the rotating loop ) at different times.
From the perspective of the S observer rotating at v clockwise with the loop, the light-1 travels anticlockwise at a faster than light speed c+v, and the light-2 travels clockwise at a slower than light speed c-v.
All points along the circular loop are symmetrical, so all clocks along the rotating loop tick at the same pace, which can be easily monitored and confirmed by the outside clocks.
So in a rotating loop, as seen by the rotating S, the light travels at the constant uniform speed of faster or slower than light all along the loop, which clearly disproves Einstein relativity.
As seen by the S rotating at a velocity of v, light-1 and light-2 emitted from S travel the same distance of 2πr (= r is the loop radius which is not Lorentz length contracted by the S rotating in tangential non-radial direction ), and return to the same S at different times at different speeds of faster (= c + v ) or slower (= c - v ) than the light speed c.
This or this-p.13-(2.5.4) says "light travels with velocities c-v (= slower than light ) and c+v (= faster than light ) for the co and counter rotating beams"
This Sagnac effect (= this faster-than-light motion was experimentally confirmed in the vacuum this 7th-paragraph ) can be naturally explained by the ordinary classical mechanics irrelevant to relativistic theory ( this p.2-p.3 ).
(Fig.3') Things traveling faster-than-light must have unreal imaginary time, imaginary energy, which unreal concepts disprove Einstein relativity.
Sagnac effect where light signals are observed to travel faster (= c + v ) or slower (= c - v ) than light speed c depending on the observers' speed of v (= the rotating S detector or earth ) disproves Einstein relativity that claims the observed light speed must be always constant c ( this-abstract, this p.2-last-conclusion, ).
According to Einstein relativistic mass-energy relation and time, any things moving faster than light (= v > c ) must have unreal imaginary mass, imaginary relativistic energy, and imaginary time (= square root of 1-v2/c2 in Lorentz factor becomes unreal imaginary, when v > c ).
↑ These unreal imaginary energy and imaginary time of the faster-than-light signal show Einstein relativity is wrong in Sagnac effect.
Light observed to travel slower than light in a rotating loop also has unreal zero relativistic energy E due to the zero rest mass (= m0 = 0 ) of a photon (= or light ), which contradicts the fact that even such light (= slower-than-light energy ) can be detected in a rotating loop in Sagnac effect.
This-p.11-2nd-paragraph says "Selleri suggests that the SRT (= special relativistic theory ) should be abandoned and that the isotropy of the speed of light exists in only one privileged reference frame"
(Fig.4) S attached to the loop rotating at a speed v measures lights traveling faster (= c +v ) and slower (= c - v ) than light speed, disproving Einstein relativity.
In the upper Fig.4, S and the loop are rotating at a velocity of v clockwise, and S emits light-1 counterclockwise and light-2 clockwise at the same time ts = 0 (= ts is time measured in the rotating S clock ) or t = 0 (= t is the time measured in stationary clocks outside the loop in the inertial frame ).
When the outside stationary clock time is t = t1, the rotating or moving S clock time is slightly slower or time-dilated ts = square root of (1-v2/c2) t1 due to the moving clock running slower.
↑ The rotating S clock's time can be easily monitored and confirmed by the outside clocks (= actually, this rotating clock causes serious twin paradox disproving Relativity, because as seen by the rotating S, the outside stationary clock appears to be moving and ticking slower. ← This twin paradox doesn't change the fact that the faster-than-light speed is observed in this rotating loop, which also disproves Einstein ).
Light-1 travels 2πr (= r is the radius of the loop ) as seen by the rotating observer S, because the the radius r seen by the rotating S is unchanged, not Lorentz length contracted (= because S moving in the tangential direction, Not in the radial direction ), which also causes Ehrenfest paradox disproving Einstein relativity.
Some people says the circumference may be slightly elongated as seen by the rotating S by the inverse Lorentz length contraction, which does Not change the fact that the faster or slower-than-light speeds can be observed by this rotating loop, which also disproves Einstein relativity.
As a result, the rotating S measures the light-1 traveling faster than-light ( > c ), as shown in this, which contradicts Einstein relativity ( wrongly ) claiming the light speed must be always the same c as measured by any moving observers.In the same way, this rotating observer S measures light-2 traveling slower-than-light speed ( < c ), which also contradicts Einstein relativity.
According to Einstein relativistic mass, light traveling faster than light speed c must have unreal imaginary mass (or unreal imaginary energy ), and light traveling slower than light must have unreal zero energy (= due to photon's zero rest mass ), which contradicts experimental results.
As a result, Einstein relativity is proven wrong.
(Fig.5) Which clock inside or outside the loop is moving and running slower is paradox, disproving Einstein relativity
See rotational twin paradox is real, unsolvable, disproving Einstein relativity.
There are wrong papers falsely claiming Sagnac effect still detects only the constant light speed c even in a rotating loop.
(Fig.6) General relativistic fictional Coriolis time dilation conveniently changed by the object's moving direction allows the paradoxical faster than light, causing unreal imaginary relativistic mass. → Einstein is false.
In a rotating loop and GPS signal measured by the spinning earth, the faster or slower-than-light signals are actually observed, which disproves Einstein relativity based on the postulate that the constant light speed c must be always observed by any moving observers.
Special relativity is based on the constant light speed measured in Michelson-Morley experiments conducted on the earth rotating around Sun.
↑ So Sagnac effect based on the rotating loop should use only special relativity (= Michelson-Morley experiment on the earth rotating around Sun ), and general relativity is irrelevant and unable to fix the faster-than-light Sagnac effect paradox.
The observer S rotating at a velocity v = rω (= r is the loop's radius, ω is the loop's angular velocity ) measures light traveling faster or slower than light depending on the light's traveling direction, which disproves Einstein relativity claiming the observed light speed must be always the constant c regardless of any moving observers.
General relativistic ( gravitational or acceleration ) time dilation depends on (pseudo-)gravitational potential φ causing clocks in different positions r or h (= r is distance from the star or rotating center ) with different (pseudo-)gravitational potential to tick at different speeds ( this-p.15 ).
↑ General relativistic time dilation should depend only on positions r or h, Not on velocities of particles, which basic Einstein relativistic rule is violated in this illegitimate general relativistic interpretation of the faster-than-light Sagnac effect.
The ordinary general relativistic time dilation can Not be applied to the rotating loop (= using only special relativity as shown in Michelson-Morley experiment ) where all clocks along the rotating loop tick at the same pace symmetrically (= which synchronization can be easily monitored and confirmed by the outside stationary clocks ) with the same (centrifugal) potential that is the same in all places of the same radius r ( this-p.17-5.9 ).
↑ So there should be No general relativistic time dilation in the rotating frame (= as seen by the rotating observer S ) in positions along the loop with the same r from the center ( this-middle ), and only special relativistic irreparable time dilation paradox of moving clocks running slower remains, which disproves Einstein relativity.
So fake general relativity paradoxically admits the faster or slower-than-light speeds by introducing the ad-hoc new concept called "Coriolis pseudo-gravitational potential" that paradoxically speeds up or slows down the light speed depending on the light's traveling direction even in the same light's positions r ( this-p.4-5 ), which contradicts the original general relativistic time dilation that depends only on positions, Not on the light's traveling direction.
This paper ↓
p.1-right-says -- No relativistic solution
"there are still different interpretations of
Sagnac experiment in the framework of the GTR (= general theory of relativity )." ← still No solution to Sagnac effect even in general relativity.
p.3-right-(32)(33) says -- Unreal Coriolis force
"Equivalently we can say that there is a “gravitational” potential... which generates the the Coriolis tidal force "
p.4-left-(34)(35) falsely insists lights traveling in the opposite directions (= ±v = ±c ) experience different time dilations (= one light is faster, the other light is slower, = dτ1 and dτ2 ) even in the same place along the loop.
p.4-6 conclusion says -- Faster than light
"it seems
that the speed of light varies by c ± ωr (= faster or slower than light speed c ) in one or the other
direction around the disk....
by using the gravitational Coriolis time dilation"
↑ First of all, there is No such thing as Coriolis potential, because Coriolis force is always perpendicular to the thing's moving direction, which can Not generate potential energy (= potential energy equals force × thing's moving distance in the same non-perpendicular direction, this-last-paragraph ), as seen in the fact that there is No potential of Lorentz magnetic force exerted on particles moving in the direction perpendicular to magnetic field.
As a result, the (fake) general relativistic Sagnac effect allows the rotating observer S to measure light traveling faster (or slower ) than light, whose relativistic mass or energy (and time ) must be unreal imaginary, which imaginary time and energy clearly contradict not only Einstein relativity but also reality.
↑ And this (fake) general relativistic solution to Sagnac effect paradoxically admits the absolute light aether stationary with respect to the earth ( this-p.1-right-lower~p.2-left ).
Also in cases where the radius of the loop is very large r → ∞ and angular velocity ω → 0 to keep the same loop's or S rotating speed rω, which corresponds to the linear motion of special relativity (= actually, rotating system also uses only special relativity ), the linearly-moving S still can measure light traveling faster or slower than light, disproving Einstein relativity ( this-middle~lower ).
↑ The difference in times (= Δt = 4πr2ω/c2 ) required for light-1 anticlockwise and light-2 clockwise to return to the rotating S (= or S is linearly moving when r → ∞ ) becomes infinite (= Not zero, so two lights-1 and 2 travel at different speeds of faster or slower than light speed c ) also in case of special relativity of r → ∞, ω → 0, rω = constant ( this-p.2-(6) or p.3-(20) = Δt = 4πr2ω/c2 → ∞ ).
↑ So Sagnac effect paradoxically allowing faster or slower than light speed corresponds also to linear motion or inertial frame, Not limited only to the rotating system or observers, hence, the claim that only general relativity can explain Sagnac effect (after special relativity failed to explain the observed faster than light Sagnac effect ) is false.
Furthermore, light emitted from GPS satellite is observed to travel faster or slower than light only when seen by the earth spinning, Not by the earth rotating around Sun nor galactic center (= as shown in Michelson- Morley experiment measuring the constant light speed in any directions ), which contradicts this relativistic interpretation of Sagnac effect applied to any rotating systems that cannot distinguish the earth spinning and the earth rotating around the Sun.
The only legitimate explanation agreeing with the observed Sagnac effect without any contradictions is the light medium unfixed to the earth spinning (= detecting Sagnac effect where light speed is changed by the earth's spinning ) moving with the earth (= compatible with Michelson-Morley experiment and aberration ).
(Fig.7) Relativity claims the light speed with respect to the stationary medium (= rotating with S ) must be always c/n (= n is refractive index of the medium ), which is wrong.
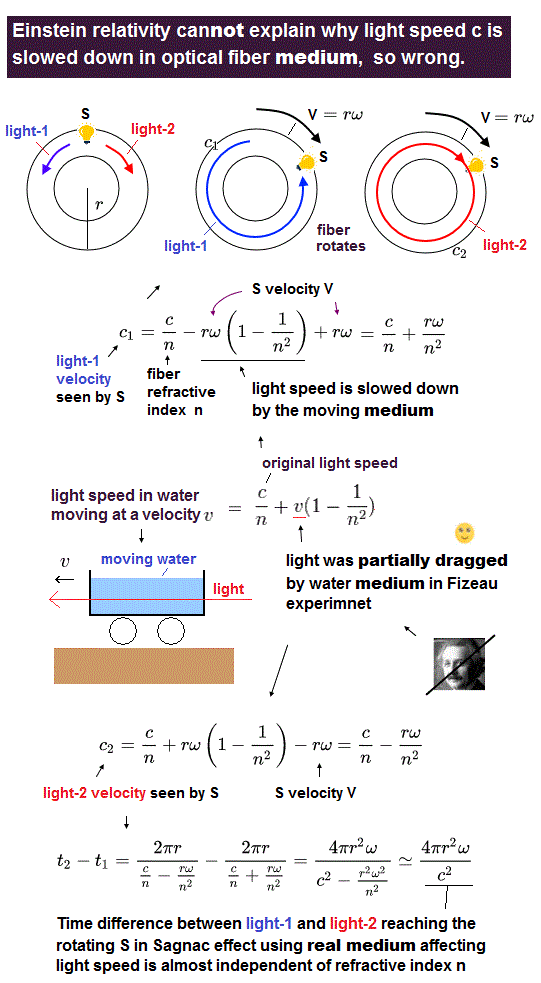
In Sagnac effect using optical fiber with refractive index n, the light speed is heavily influenced by the light medium in the fiber, which also confirms the light medium (= aether ) moving with the earth.
Fizeau experiment showed the light speed c is slowed down to c/n (= n is water's refractive index ) in water medium, and the light is partially dragged by the moving water medium.
↑ Einstein relativity or its Lorentz transformation can Not explain why the light speed c is suddenly slowed down to c/n inside the water medium, so false.
As shown in Fig.7, the difference in time needed for light-1 (= traveling anticlockwise ) and light-2 (= traveling clockwise ) to reach the S rotating clockwise at a velocity of v = rω (= r is radius of the circular path, ω is the angular velocity of the path ) is almost independent of the refractive index n ( this p.6, this-last ), which can be explained by the real medium theory partially dragging light of Fizeau ( this p.13-lower, this p.2 ).
↑ Transparent medium (= molecules ) such as optical fiber and water allows almost all the earth's light medium (= aether ) to pass through it, and partially affects the light speed.
The fact that two lights reaching the rotating S inside the rotating optical fiber medium at different times means the light speed is Not uniform in the rest frame of the (optical fiber) medium which contradicts the relativistic interpretation of Fizeau experiment where light speed must be always the same c/n in the rest frame of the medium whose refractive index is n ( this p.16-upper, this p.6-(25)(26) ).
Disproving Einstein relativity rejecting the medium means disproving quantum mechanics based on unphysical wave-particle duality or parallel universes.

Feel free to link to this site.