Home page
Einstein relativity is false
(Fig.1) Two satellite clocks A and B moving around the earth cause twin paradox, which shows Einstein relativity is wrong.

Contrary to the standard explanation, GPS satellite clocks do Not use Einstein relativity which is said to cause time difference between GPS satellite and the earth's receiver clocks ( this-lower-conclusion, this 5~6th-paragraphs, this p.1-introduction ).
This extremely tiny time difference by this (fictional) relativity is meaningless, because the receiver's cheap clocks often cause large time errors (= irrelevant to relativity, this p.2-1st-paragraph ), and the time difference between satellite's and receiver's clocks can be corrected by using 4 satellites without using Einstein relativity ( this p.7, this-maintaining synchronicity-3~4th-paragraphs, this-last-paragraph ).
Furthermore, GPS clocks cause errors by a lot of factors such as atmosphere (= so GPS clock time disagrees with relativistic prediction, this-middle, this-p.2-3,p.6-conclusion ), which must be constantly corrected by being compared with the earth ground station's clocks ( this p.2, this p.4 ) irrelevant to relativity.
This-3rd-last~2nd-last paragraph say
"If it were necessary to accommodate for relativity at different latitudes and altitudes, the calculations would be very complex and would need to be done at the receiver. But they aren't done there: only a fixed time adjustment is made at the satellites for all points on Earth. This fact alone demonstrates that Relativity is irrelevant to the GPS operation.
"Conclusion The presence of Special and General Relativity effects has No bearing on the accuracy of GPS operation. In summary, it wouldn't matter whether clocks aboard GPS satellites ran faster or slower than Earth's clocks or even changed their speed each day."
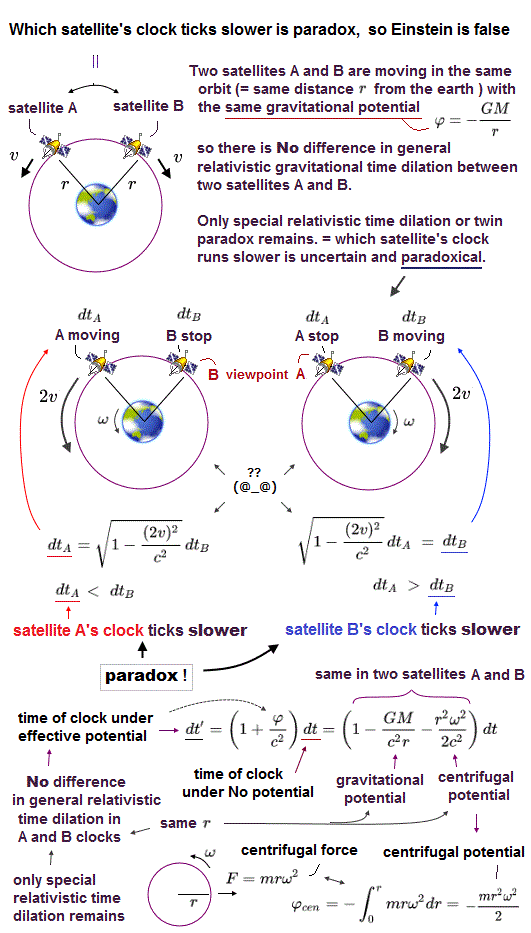
When two satellites A and B are moving around the earth at the same velocity v in the opposite directions at the same height (= distance between satellites and the earth's center is always r ), Einstein relativity causes twin paradox in these satellite clocks.
From the perspective of a satellite B (= B's rest frame ), the satellite A's clock is moving and running slower according to Einstein special relativity.
But from the perspective of a satellite A (= A's rest frame ), the satellite B's clock is moving and running slower.
↑ Which satellite clock A or B is moving and running slower is paradoxical (= called twin paradox ), so Einstein relativity is wrong.
In this case, general relativistic (= gravitational ) time dilation is irrelevant, because the distances between the earth center and two satellites are always the constant r, causing the same gravitational potential and No gravitational time dilation difference between two satellites A and B.
Furthermore, from the perspective of the satellite A (or B), the satellite A (or B ) is free-falling (= called inertial frame ) where the earth's gravity is canceled by centrifugal force, so No general relativistic time dilation is involved in comparing these two satellites' clock time, and only special relativistic time dilation (= moving clocks run slower ) and twin paradox occurs ( this p.2-left-upper, this p.2-left-2. ). → Einstein relativity is wrong.
In fact, Einstein relativity, Lorentz transformation based on the constant light speed c measured by any observers are proved to be wrong by Sagnac effect where the speed of signal emitted by GPS satellites can be faster (= c + V ) or slower (= c - V ) than light speed c by the earth spinning speed V.
From the perspective of satellite A (or B ), all things appear to be rotating around the earth in the opposite direction, which is the rotating (= accelerating ) frame (= rotating coordinate ) involving general relativity.
The 2nd-last paragraph of even this pro-relativistic site admits
"There is more to relativity than the special theory and general theory. There is the Sagnac effect.. The principle of constancy of the speed of light cannot be applied in a rotating reference frame, "

Feel free to link to this site.