Home page
Sagnac effect disproves Einstein
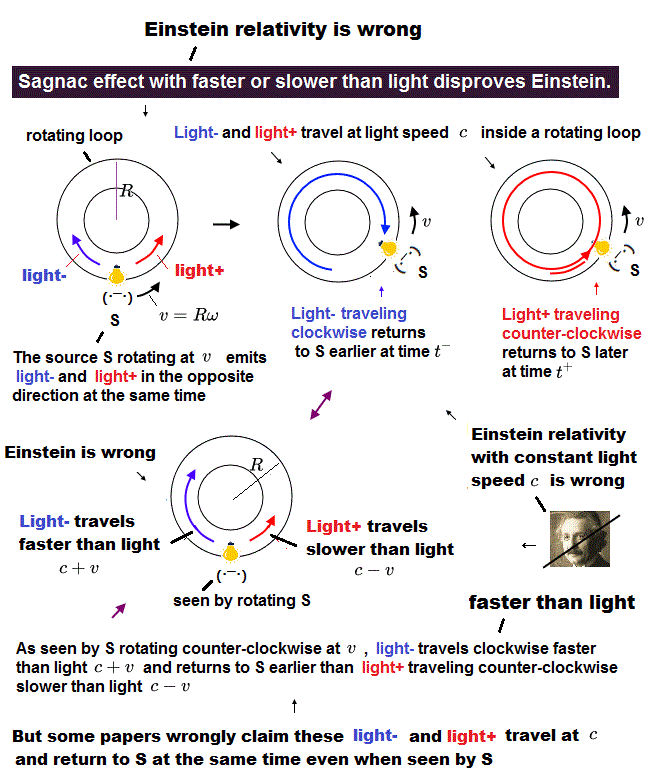
(Fig.1) A rotating S measuring faster or slower than light disproves Relativity

Textbooks and the media hide the inconvenient truth that Sagnac effect in GPS observing the speed faster or slower than light definitely disproves Einstein relativity claiming light must always be measured to travel at constant light speed c by any moving observers.
In the upper Fig.1, the light source (+ detector ) S is rotating counter-clockwise at the velocity v = Rω (= R is the radius, ω is the angular velocity of the loop light path rotating with S ).
This S rotating at v counterclockwise emits light- clockwise and light+ counterclockwise at the same time.
Light- traveling clockwise at the light speed c can return to S at time dt- earlier than light+ traveling anticlockwise returning to S at a different time dt+ (= this time difference in when light- and light+ return to S can be confirmed also by the outside observers ).
↑ As seen by the S rotating at a speed of v counterclockwise, the light- travels clockwise faster than light (= c + v ), and light+ travels counterclockwise slower than light (= c - v ), which clearly disproves Einstein relativity based on the postulate that any moving observers must always measure light traveling at the constant light speed c.
Some papers wrongly claim both these light- and light+ emitted from the rotating S may return to S at the same time by traveling at light speed c as seen by S (= so Einstein relativity is right ? No. ), which claim clearly contradicts the fact that these light- and light+ return to S at different times, which can be easily confirmed.
As a result, in Sagnac effect a rotating loop can clearly measure lights to travel faster or slower than light, which disproves Einstein relativity.
(Fig.2) The rotating S observes light- (or light+ ) travel faster (or slower ) than light.
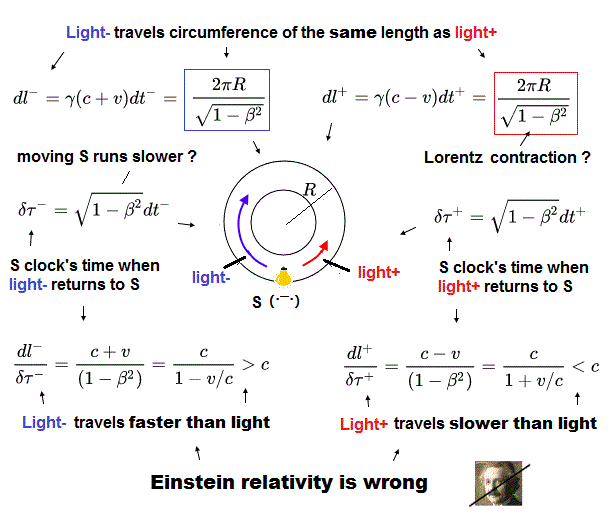
As seen by the rotating S, both light- and light+ travel the same distance of the loop circumference, which may be slightly longer than 2πR due to inverse Lorentz-length contraction (= ignoring Ehrenfest paradoxes disproving Einstein relativity here ).
And due to the moving clock S running slightly slower (= ignoring twin paradox disproving Einstein relativity here ), light- (or light+ ) returns to S when the rotating S clock time is dt- × square root of 1-v2/c2 (or dt+ × square root of 1-v2/c2 ).
As a result, as seen by the rotating S, the light- (or light+ ) travels faster > c (or slower < c ) than light, which clearly disproves Einstein relativity
See this-p.9-(29)(30),p.10-(33)(34), p.11-(36)-(38) where light- and light+ travel the same distance ( dl- = dl+ = circumference of a loop ), and return to S at different times of dt- and dt+ (= measured by the outside clocks ) or square root of 1-v2/c2 × dt- (= δτ- ) or dt+ (= δτ+ ) measured by the rotating clock S.
(Fig.3) Wrong papers claim light- clockwise and light+ counter-clockwise return to the rotating S at the same time, which disagrees with the actual observation, so Einstein is false.
As seen by the rotating S, the light- traveling clockwise faster than light and light+ traveling counter-clockwise slower than light return to S at different times, which can be easily confirmed by outside clocks and experiments in Sagnac effect.
↑ This Sagnac effect clearly contradicts Einstein relativity claiming the light speed observed must always be the constant c.
↑ If Einstein relativity is right, these light- and light+ must unrealistically return to S at the same time (= because light- and light+ must travel the same circumference of same length at the same light speed c as seen by S, if Einstein relativity is right ), which clearly contradicts the actual fact and experiments.
Some wrong papers using unreal artificial time correction claim these light- and light+ may return to S at the same time by traveling at the same constant light speed c, even as seen by the rotating S (= this-p.12-(45)~p.13 ), which clearly contradicts the fact that light- and light+ emitted by the rotating S returns to S at different times.
↑ This wrong paper ↓ -- Wrong simultaneity
p.7-last-paragraph, p.8-(19)(20) uses artificial unreal relations indicating clock times (= x0 = ct where c is light speed, t is the time ) in different places (= P1 and P2 ) in the rotating frame. ← But Sagnac effect uses only one clock of the rotating S (= in one fixed position in the rotating frame ), so this artificial relation comparing different positions (= P1 and P2 ) is meaningless.p.9-(26), p.11-last-paragraph, p.12 uses this unreal relation to claim there may be three different clocks running differently in the same position of the rotating S (= angle dφ = 0, ±2π into the artificial time equation ), as if there were 3 different parallel worlds in the same S position, which causes the illusion that light- and light+ emitted from the rotating S may return to S at the same time.
p.14-(51) wrongly claims the same initial position (= EA ) having only one clock time paradoxically experiences different clock times by losing (illusory) simultaneity or something, though this rotating loop using only one S clock (= light emitted from S can return to the S clock ) has No problem of simultaneity nor synchronization .

Feel free to link to this site.