(Fig.1) ↓ Quantum dot (= QD ) was invented by researchers' experience, trial-and-error approach, Not by (useless) quantum mechanical prediction.

Nobel prize chemistry in 2023 was awarded to quantum dot (= QD ).
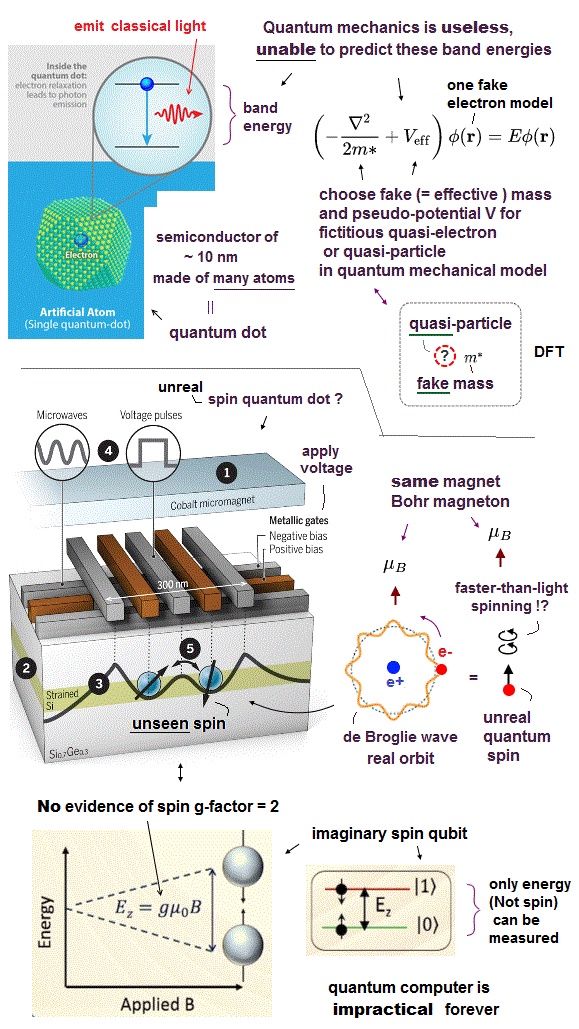
Contrary to this confusing name "quantum", the quantum dot has nothing to do with quantum mechanics or quantum mechanical "prediction".
Quantum dots are semiconductor particles or objects (= called artificial atoms ) of less than 10 nm size (= each quantum dot is made of many atoms ), which can emit some (classical) light of some wavelength depending on the semiconductor's size and shape.
The size of the quantum dot is related to the electron's Bohr radius ( this middle ) and de Broglie wavelength ( this p.7, this p.1-lower ).
↑ Concepts of de Broglie wave and Bohr radius originating from realistic classical atomic model are used also in quantum mechanics, which is why they want to call them "quantum effect". ← It means quantum mechanics (= replaceable by other more realistic atomic model in de Broglie wave and Bohr radius. ) is unnecessary in quantum dots.
The energy difference (= band gap energy ) between two energy levels called valence and conduction band determines the wavelength of the light (= colors ) emitted from the semidonductor or quantum dot.
The point is quantum mechanics is unable to predict these band gap energies of any materials such as semiconductors, metals, and quantum dots, so quantum mechanical prediction has been completely useless for any modern technologies, transistors, spintronics (= giant magnetoresistance ) and quantum dots, all of which were invented by researchers' long experience and unexpected discovery which quantum mechanics failed to 'predict' ( this-lower-trial and error, this p.1-introduction ).
Quantum mechanical Schrödinger equations are unable to solve or give analytical energy solutions of any multi-electron atoms ( this p.6(or p.3)-3rd-paragraph ).
So the quantum mechanics has to artificially choose (fake) approximate solutions for the unsolvable multi-electron atoms and molecules with No power to predict their energies ( this p.21 ), which approximate manipulation of free parameters to fit experimental values is just "art" rather than science.
↑ Even this approximate (= illegitimate ) quantum mechanical methods are unrealistically time-consuming and inapplicable to actual molecules or materials made of many atoms and electrons ( this p.2-3, this p.31-32, this p.7-lower, this p.3-upper, this p.1-intro-2nd-paragraph, this p.3-second-paragraph ).
Such an useless quantum mechanics has No choice but to rely on fake approximate quasi-electron or quasi-particle model with fake (= effective ) mass (= m*, this p.2 ) and pseudo-potential ( this p.2-4, this p.2-left-lower, this p.2, this p.2-right, this p.1-second-paragraph ).
↑ These fake (effective) mass and pseudo-potential of electrons can be freely changed and adjusted to experimental results, hence the quantum mechanics intrinsically has No ability to predict any physical values from its original theory ( this p.4,p.8 ).
Density functional theory (= DFT ) or Kohn-Sham theory unscientifically replacing the actual many-electron material by only one pseudo-electron model with fake (= effective ) mass and fictitious effective potential is the current mainstream quantum mechanical approximate methods to explain various materials such as semidonductors, transistors and quantum dots ( this p.1-lower-p.3, this 2.materials and methods, this p.2-right~p.5, this p.3-right ).
This most widely-used DFT approximate method has to artificially choose various different pseudo-potentials called exchange-correlation functionas (whose exact universal form is unknown, this p.3-5, this p.1-left ) in different materials ( this p.1-inroduction ).
Hence, this DFT just choosing different pseudo-potentials or functionals fitted to experimental results is also just an empirical (= pseudo-ab-initio ) theory unable to predict any physical phenomena from the theory itself ( this p.23, this p.10-second-paragraph, this p.2-second-paragraph, this p.21, this p.2-last, this p.11-left-1st-paragraph ) with No physical picture ( this last-paragraph ).
As a result, all the modern technologies (= transistor, spintronics, quantum dot .. ) are irrelevant to the quantum mechanical prediction that was an illusory unnecessary theory.
Despite long-time researches, the exact mechanism of quantum dots is still unknown due to the unphysical mainstream theory or quantum mechanics ( this p.1-first-paragraph ).
As I said, quantum mechanics failing to solve multi-electron Schrödinger equations is unable to predict any physical phenomena , and made No contribution to any modern technology such as transistors, spintronics, quantum dots and medicine.
This is why scientists had to aritificially create fictitious scientific targets such as over-hyped parallel-world quantum computers, which are impractical forever, and ineffective vaccines even by hijacking the mainstream science prize Nobel and free-speech (= as if we went back to the old Galileo era ), as the authentic mRNA vaccine inventor warned.
In order to explain the mechanism of quantum dots and solar-energy panels, the unscientific quantum mechanics often relies on the unreal quasiparticle model called "exciton", giving up using real particles or electron.
↑ These fictitious quasiparticle models also just artificially manipulate free parameters ( this p.6-left ) such as fake (= effective ) mass and pseudo-potential ( this p.3-right-lower ) with No power to predict any physical values, which unphysical description obstructs technological innovation.
Spin quantum bits (= qubits ) confined in quantum dot for semiconductor-type quantum computers (which are impractical forever) are also irrelevant to quantum mechanics.
Physicists try to confine one ~ several electrons in very small quantum-dot space of 50~100 nm or potential well created by applied voltage for fruitlessly using each confined electron's (fictitious) spin's magnetic direction as qubit's 0 (= down-spin ) or 1 (= up-spin ) state.
Electron spin is unrealistic, because each tiny electron must spin much faster than light to generate the observed magnetic field = Bohr magneton which spin magnetic moment accidentally agrees with Bohr's realistic orbital magnetic moment ( this p.2 ) which is also Bohr magneton.
↑ The unrealistic electron spin (= Not real spinning ) itself is unmeasurable, only its magnetic field (= Bohr magneton ) is measurable, which means it is realistic to think the "electron spin" is just an electron's orbital motion (= Not faster than light rotation ) creating the same magnetic moment = Bohr magneton.
Electron spin magnetic moment is equal to one Bohr magneton (= μB ) = spin g-factor (= 2 ) × spin-angular momentum (= 1/2 ℏ ) according to the unfounded quantum mechanical interpretation, while the classical orbital magnetic moment (= hydorgen's ground state ) is also equal to Bohr magneton = orbital g-factor (=1 ) × orbital smallest angular momentum (= 1 ℏ ).
↑ Neither this spin angular momentum (= 1/2 ℏ ) nor spin g-factor (= 2 ) can be directly measuread.
In fact, in spin qubits confined in semiconductor's quantum dots by applied electric field, physicists can Not measure the spin magnetic field or spin magnetic moment, either, which means the detection of spin qubit 0 (= spin-down ) or 1 (= spin-up ) itself is impossible in these impractical spin qubits (= still Not a quantum computer at all ).
So they try to indirectly detect spin-magnetic moment's direction or spin-qubit 0 or 1 somehow, which can Not prove the existence of the (imaginary) electron spin itself.
Under some applied external magnetic field (= B ), the energy levels of spin-up and down are supposed to split into two (= actually more due to various orbital angular momentums ), because the energy level of spin magnetic moment parallel (or anti-parallel) to the external magnetic field is lower (or higher ) than the other spin-state by gμB where g should be spin g-factor 2 and μB is Bohr magneton.
↑ It means when appling some electromagnetic wave of energy equal to this energy difference (= gμB ) between spin-up and down under the external magnetic field, the electron's spin direction may flip.
Then, they created an ad-hoc unfounded hypothesis that if two electrons confined in two adjacent quantum dots have the same-directional spins (= up-up or down-down spins ), Pauli principle or Pauli exchange repulsion blocks one electron (with up spin) from flowing into the other adjacent quantum dot containing the other electron (with the same up spin), and only when these two adjacent electrons have the opposite spins (= one is up, the other is down spin ), one electron can flow into the adjacent electron's quantum dot (allegedly avoiding Pauli repulsion by two different spins), and this tiny electric current might be detected or read out ( this p.3-Fig.1c, this p.11, this Fig.1,p.3-coherent rabi oscillation ).
First of all, each quantum dot's size is bigger than 50nm, which is far bigger than an actual atomic size (= only 0.05 nm ), which means there is enough space in each quantum dot for two electrons with the same spin to enter, and Pauli principle between such big quantum dots (= having enough space for avoiding Pauli repulsion) is meaningless.
↑ And in actual experiment, the spin-g-factor they measured was Not the authentic "2" but a completely different values such as 0.35 ( this p.2-right-ESR spectroscopy ), which means their spin theory turned out to be wrong, and No evidence of spin or spin-g-factor 2.
This spin's g-factor (and fictitious effective mass ) of each electron in spin qubit can be artificially and unrealistically changed by applied voltage from the original 2 ( this p.3 ), which means what they consider "spin" or "electron" trapped in quantum dot is Not a real one but just a fictitious quasi-electron complexly mixing multiple-electron's orbital motions ( this p.4-second-paragraph ) which orbital motion's patterns (instead of imaginary spins' directions ) affects electric current and conductance (= electron's orbital motion's directions or different motion's patterns affect the collision between the electron and electrodes, other particles ), so there is No evidence of electron spin.
They try to associate the electron's spin magnetic energy with the (irrelevant) Pauli exchange energy (= exchange interaction J which is freely-adjustabele parameter, this p.3-5, this p.1-right~p.3 ), which association is contradictory and wrong.
Because (Pauli) exchange energy (= which is usually far larger than 2 eV, this 2~4th paragraph ) has nothing to do with the tiny, tiny electron's spin magnetic energy (= which is only 0.000045 eV as shown in hydrogen's tiny spin-orbit magnetic energy, this p.7-8, this p.17-18 ).
So the idea that changing electron's spin magnetic direction based on tiny magnetic energy can influence far larger Pauli exchange energy or electric current in spin qubit detection is nonsense.
Pauli exchange energy is unrealistic, Not caused by a true exchange force ( this p.8-last-paragraph, this p.5-first-paragraph, this p.6 ).
Quantum mechanics claims that this unphysical Pauli exchange energy is caused by electron's kinetic energy increase (= triplet or Pauli repulsion, this p.13-second-paragraph ) or kinetic energy decrease (= singlet or molecular bond ), Not by the tiny, tiny spin magnetic energy (= spin magnetic moment or spin qubit's direction should be irrelevant to Pauli exchange energy ).
Physcists can also freely manipulate this (unphysical) exchange energy interaction parameters J by changing applied electric voltage ( this p.1-right-lower~p.2 = irrelevant to quantum mechanical "prediction" ), which means Pauli exchange energy is just a kind of electric energy manipulated by applied voltage contradictory to the quantum mechanical interpretation.
These spin qubits are the most impractical and unstable among all types of quantum computers.
Despite long-time researches, only 6~12 (spin) qubits (= meaing only 6~12 electrons ) can be realized, which can Not do any meaningful calculations like all other types of qubits due to extremely small numbers of qubits and very high error rates.
The practical quantum computer is said to require more than millions of qubits ( this 2nd-last-paragraph, this 2nd-last-paragraph ), so all the current quantum computers including (fictitious) spin qubits (= only less than 12 qubits ! ) are far from practical use.
Also in the recent Science paper, physicists tried to baselessly treat the hydorgen's magnetic moment (= Bohr magneton ) bound to titanium (= hydrogenated Ti, this p.3 ) as an (imaginary) electron spin qubit, which offers No evidence of (unseen) electon spin, either (= hydrogen's magnetic moment can be naturally explained by the orbital motion instead of unrealistic spin ). ← Only three (electron spin) qubits (= only three atoms ) are made, which is far from the practical millions of qubits.
The most serious problem prohibiting scaling up spin qubits is that these fragile spin qubits can Not be linked to distant qubits (= individual atoms or electrons used as spin qubits cannot be connected with other individual atoms or electrons by "magical wires" = ion and neutral atomic qubits are also unable to connect distant qubits )", and the tiny atomic or electron's magnetic moments are too weak to influence distant atoms = No physical connection between distant spin qubits, unlike the current mainstream superconducting qubits ( this 4th-paragraph ).
The error rates of three spin qubits are extremely high (= ~ 20 ~ 30 % = fidelity = 70 ~ 80 %, this p.5-Fig.5g ), which is inapplicale to useful calculations.
And this spin qubit based on unphysical exchange energy or spin singlet (= antisymmetric spins )-triplet (= symmetric spins ) can Not be correctly applied to more than two qubits, which means realization of more than two spin qubits connected by (unphysical) Pauli exchange interaction is impossible forever.
For example, in this paper p.1-right dealing with three electron spin qubits, the first and second spins paradoxcially have the same-directional spins (= up-up ↑-↑ spins ) in the singlet (= though all two or three spins must be the opposite ↑↓ from each other according to quantum mechanical singlet rule ) of three qubits (= Sr = |↑↑↓| -|↑↓↑| ), which contradicts the original Pauli antisymmetric wavefunction theory.
-------------------
Illusory quantum mechanical parallel worlds seem to be still happening..
The massive motorcade with unusually heavy guard indicates Trump is a "sitting president" due to proven election frauds ( in the real world ), then, the indictment for denouncing election fraud itself is non-sensical and paradoxical like the unphysical quantum mechanics which fake mainstream science dominates the current world where the media and academia keep silent about the (inconvenient) truth (ex. about the unrealistic spin as shown above ). ← How long will this unscientific state continue ?

2023/10/8 updated. Feel free to link to this site.