Home page
Strange "spin" is NOT a real thing
Quantum mechanical Hall effect is unreal
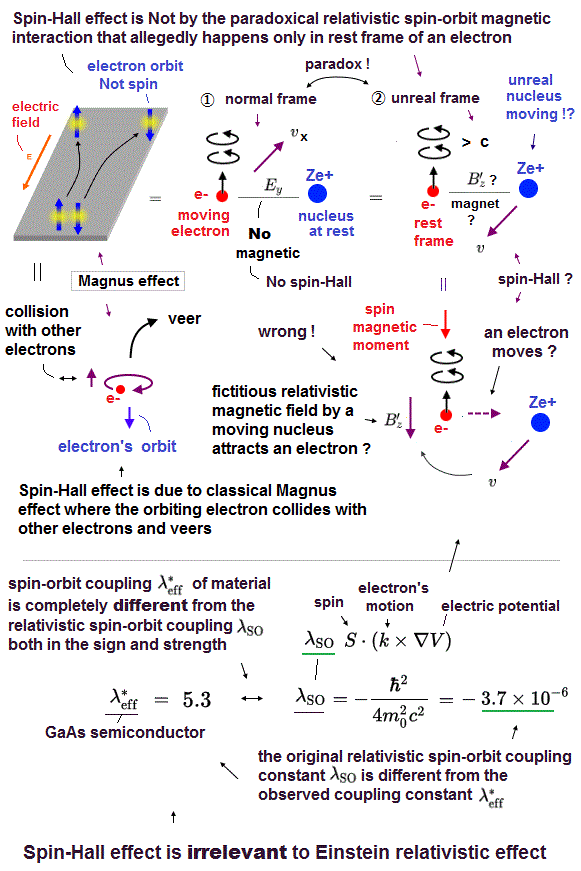
(Fig.H) Spin Hall effect is caused by classical Magnus effect on electron's orbit (= Not spin ).

In spin-Hall effect (= SHE ), a electron (= moved by electric field ) with the downward-angular momentum (= due to electron's orbit, not the unrealistic spin ) veers to the right, and an electron with the upward-angular momentum veers to the left due to classical Magnus effect (= irrelevant to quantum spin ).
This spin Hall effect usually observed only at very low temperature is too weak and useless, because the (spin-)polarized electron can move only several μm. ( this 6th-paragraph, ).
This p.11-8.conclusions say
"At present, it is difficult to predict whether
this (spin-Hall) effect will have any practical applications" ← The spin Hall effect is still useless (= forever ).
There is No evidence of electron spin in spin-Hall effect where only the direction of the magnetization (= arrows in the upper figure ) can be vaguely measured by seeing how polarization of light reflected from the magnetization change (= Not by spin but by electron's orbit ) in classical Kerr effect ( this p.2-right-last-paragraph ).
This p.1-left says -- No quantum mechanics
"the underlying mechanisms of
the SHE (= spin Hall effect ) remain somewhat mysterious and poorly understood" ← Clear mechanism of spin Hall effect is still unclear in the current quantum mechanics, so No evidence of spin ( this p.43-left-2nd-paragraph ).
"The absence of an experimental blueprint for measuring the SHE accurately (= so spin Hall effect is impractical ) is related to the inherent difficulty in calculating the spin-Hall current"
One of factors causing this spin Hall effect is said to be the relativistic spin-orbit magnetic effect ( this p.10-11 ), which is paradoxical and impossible, though.
As shown in the upper figure, an electron (= e- ) moving under the external electric field feels only the electric field from the stationary nucleus (= Ze+ ) which does Not generate magnetic field ( this 4th-paragraph ).
↑ So in this frame of the moving electron (= rest frame of the nucleus = normal frame ), there is No magnetic field, No spin-orbit magnetic interaction, hence, No spin-Hall effect happens, which is clearly paradox.
The paradoxical relativistic theory has no absolute frame, so only in the rest frame of the electron (= abnormal frame ), the heavy nucleus (= Ze+ ) appears to be moving and causing fictitious relativistic magnetic field B ( this p.10, this p.3-Fig.3 ).
The electron with the upward spin has the downward magnetic moment, which is parallel to this fictitious relativistic magnetic field (= lower magnetic energy ) caused by the moving nucleus (= from the viewpoint of an electron, the stationary nucleus appears to be moving in the opposite direction ), so the electron veers to the right to lower this fictitious magnetic energy in the spin-Hall effect.
But as I said, this relativistic spin-magnetic interaction or spin-Hall effect happens only in the (unrealistic) rest frame of the electron (= heavier nucleus appears to be moving ! ), which is paradoxical and wrong.
(Fig.2) Spin Hall effect contradicts the original relativistic spin-orbit effect.
The important point is that this spin-Hall effect contradicts the original Einstein relativistic theory, so wrong.
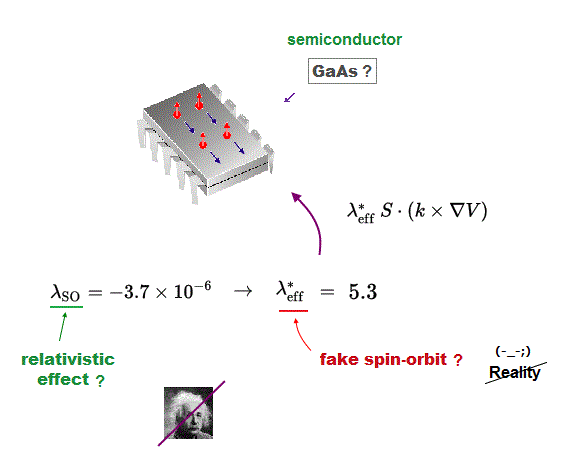
As shown in the upper figure, the spin-orbit coupling constant based on the original relativistic theory is very small = -3.7 × 10-6 ( this p.6 = vacuum ).
↑ This spin-orbit coupling is the universal constant, so if the original relativistic theory is right, the spin-orbit coupling in all materials must be this value of -3.7 × 10-6.
But in actual materials, this spin-orbit coupling constants are completely different from the original relativistic theory (= even the signs of these constants are the opposite ! ), so spin-Hall effect and relativistic spin-orbit effect are contradictory and wrong.
For example, the semiconductor GaAs is said to have the spin-orbit coupling constant of as large as 5.3 in spin-Hall effect, which is 106 times larger than the original relativistic theory, and the opposite sign ( this p.9,p.24, this p.2-right-1st,4th-paragraphs ). ← The fact that these constants' signs are the opposite means the relativistic spin-orbit interaction is illusion.
This p.2-left-1st-paragraph says
"results from relativistic corrections in the Pauli equation and is known as Thomas
term, with λ = −ℏ2/4m2c2
≈ −3.7 × 10−6 Å2 (= original relativistic spin-orbit constant )..
for GaAs one finds λ = 5.3 Å2.
Thus,
the SO (= spin-orbit ) coupling in n-GaAs is by six orders of magnitude stronger than in vacuum (= original relativistic weak spin-orbit coupling ) and has the opposite sign"
↑ And the current (unphysical) condensed matter can only give fake effective mass (= m* ) of an (fictitious) electron or quasiparticle in spin-Hall effect ( this p.5, this p.14-3.11~p.15 ). ← Clarifying real mechanism behind spin Hall effect by fictional quantum mechanical model is impossible.
This wide discrepancy in the spin-orbit coupling constants clearly shows spin-Hall effect has nothing to do with relativistic spin-orbit interaction, contrary to the current mainstream explanation.
This spin Hall effect can be naturally explained by classical Magnus effect ( this-p.3-lower, this-1st-paragraph ) where the electron orbiting downward (or upward ) feels friction or collision from the surrounding electrons, and veers into right (or left, this p.3, this p.13-a, this p.3 ).
↑ The electron's orbital motion with the downward angular momentum means the left side of the electron's orbit moving forward experiences more friction and pressure from the surrounding electrons on the left side than the right side of the orbit moving backward, hence, this orbit tends to veer rightward.
↑ This spin Hall effect by the classical Magnus effect (= more powerful collision than the weak relativistic spin-orbit magnetic interaction, this p.3-lower ) perfectly agrees with experimental observation, and can remove the wide discrepancy between the current spin-Hall theory and the original weak relativistic spin-orbit effect with the opposite sign.
Physicists often artificially choose (fake) relativistic pseudo-potentials in the current most-widely-used one-pseudo-electron density functional theory (= DFT ) to explain spin-Hall effect ( this 2~3rd-paragraph, this p.8-upper, this p.2~3, this p.15-16, this p.6-left-last-paragaph-first-principle ) in the unrealistic way.
The free choice of these fake pseudo-potentials has nothing to do with the prediction of (unphysical) quantum mechanics or relativity (← Quantum mechanical Schrödinger equations for multi-electron atoms are unsolvable, unable to predict anything ).
Actually, quantum mechanics failed to give the clear mechanism of spin-Hall effect as this p.1-left says "the underlying mechanisms of
the SHE (= spin Hall effect ) remain somewhat mysterious and poorly understood.
.. The conventional
spin current is physically meaningless."
This-p.3-left-Results-2nd-paragraph says
"scalar-relativistic PAW pseudopotentials.. The
↑ Quantum mechanics just artificially chooses fake pseudo-potentials and free parameters such as U without predicting spin-Hall effect.
The 2nd and 3rd paragraphs of this overhyped news (6/24/2025) say
"Quantum physicist.. has demonstrated the quantum spin Hall (QSH) effect in graphene for the first time without any external magnetic fields (= electric field was needed )"
"Such circuits hold promise (= still useless ) for next-generation technologies, including faster and more energy-efficient electronics, quantum computing, and advanced memory devices" ← false. spin Hall effect is useless for any technology, and irrelevant to quantum computers.
↑ This p.1-abstract says nothing about the detailed application including quantum computers, contrary to the above hyped news.

Feel free to link to this site.